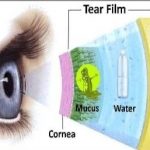
The meibomian glands are specialized sebaceous glands located within the eyelids.
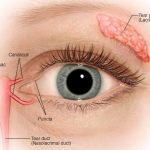
The eyelids are thin curtains of skin, muscles, fibrous tissue and mucous membrane. Eyelids are divided into two parts upper eyelid and lower eyelid. The upper eyelid is limited above by the eyebrow and lower eyelid merges with the check. Mebomian gland are situated in upper and lower eyelid. Mebomian gland are responsible for producing and secreting an oily substance called meibum, which helps lubricate the surface of the eyes and prevent tears from evaporating too quickly.
Mebomian gland are approx 31 glands in the upper lid and 26 in the lower lid. All glands are spread vertically throughout the tarsal plates in both the superior and inferior lids. Anterior to the tarsal plates lies the orbicularis oculi muscle, which assists in milking the glands during a blink. During a blink, this muscle—along with the orbicularis oculi—contracts and assists with the delivery of meibum out of the duct and onto the lid margin.
Modified sebaceous gland are open at the kid margin.
As the meibomian gland produces meibum via secretion. The contents of the oily meibum include wax and sterol esters (comprising approx 77%), including fatty acids, fatty alcohols and cholesterol, phospholipids (8%), and digylcerides, triglycerides and hydrocarbons (9%).Meibocytes located in acini are secretory cells responsible for the production of meibum. During maturation, the meibocytes’ nuclei shrink and disintegrate, forming the oily product.
It is important to differentiate between secretion and delivery of meibum. anatomy of the glands and the eyelids contains much greater complexity than described here. Make sure to assess the dry eye patient for these two structural deficits of the meibomian glands (1) gland dropout and (2) duct dilatation. Both findings indicate chronic meibomian gland dysfunction and reduced gland function, and can be staged by severity scale. Several commercially available products can assess the structure of the meibomian glands Like
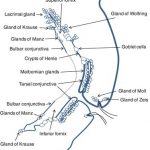
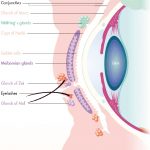
The meibomian glands consist of several parts:
1. Acinar or acini: These are the secretory units of the gland, resembling microscopic grapes. They are composed of a central lumen or cavity surrounded by specialized epithelial cells.
2. Ducts: Each acinus is connected to a small tubular duct that carries the meibum to the surface of the eyelid. These ducts merge together to form a larger main duct, known as the central duct, which opens onto the eyelid margin. The central duct is also called the orifice of the meibomian gland.
3. Glandular orifice: This refers to the opening or the orifice of the meibomian gland onto the eyelid margin. It is through this opening that meibum is delivered to the tear film.
The meibomian glands play a crucial role in maintaining the health of the ocular surface and preventing dry eye disease. Dysfunction or blockage of these glands can result in a condition called Meibomian gland dysfunction (MGD), which can lead to symptoms such as dryness, irritation, inflammation, and blurred vision.
Dysfunction of mebomian gland :- Dysfunction of mebomian gland can cause Blepharitis, Dry eye, hordelum internum and chalazion.
Blepharitis :- Blepharitis is a chronic inflammation of the margin of the kids, appearing as a simple hyperaemia or inflammation of the eyelid. Which occur two forms anterior and posteruor . The anterior may be seborrhoeic or squamous and ulcerative . Causes of blepharitis are very varied. The condition may follow chronic conjunctivitis due to Staphylococci carried to the lid margin by infected fingers.
Squamous blepharitis :- It is the condition where white dandruff like scales or yellowish greasy accumulate along the base of lashes. Treatment in this blepharitis are daily cleaning baby shampoo may ameliorate the condition
Ulcerative blepharitis :- This is the condition commonly due to Staphylococcus. Yellow crusts or dry brittle scales glue the lashes together and also seen small ulcers. The symptoms are redness of the eyelids, itching, soreness, lacrimation and photophobia.
Posterior blepharitis :- posterior blepharitis may lead to punctate keratitis and tear film instability.
Meibomian seborrhoea :- In this cases oil droplets may be seen at the meibomian gland openings which can be expressed out like foam.
Meibomianitis :- In Meibomianitis patients present with a diffuse rounded posterior lid margin and thickening around meibomian gland opring. Treatment are warm compress and lid massage together with doxycyline for 6 weeks.
Hordeolum internum :- Hordelum Internum is a suppurative inflammation of a meibomian gland. Its inflammatory symptoms are more violent than stye. It is more common common in children and young adults and who are rubbing of the eyes, treatment are hot compress antibiotic drops, anti inflammatory and analgesic are used and pus is drained out by a vertical incision from the tarsal conjunctiva.
Chalazion :- Chalazion also called tarsal or meibomian cyst, is a chronic non -infective lipogranulomatous inflammation of the meibomian gland. Chalazion are first occurs mild grade infection of the meibomian gland by organisms of very low virulence. There result occurs proliferation of the epithelium and Infiltration of the wall of the ducts. There occurs retention of secretion in the gland, causing its enlargement. The pentup and extravasated e secretions act like an irritant and excite non infective lipogranulomatous inflammation of the blocked meibomian glands and surrounding tissue. Treatment are topical antibiotic eye drops and oral anti inflammatory drugs , surgical treatment when chalazion are big in size.