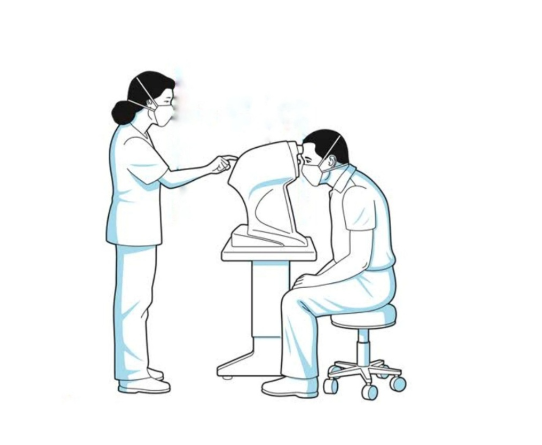
Tonometry is a non-invasive procedure that measures the pressure inside the eye. It is
used to diagnose and monitor glaucoma, a condition that damages the optic nerve and
can lead to blindness.
Applanation tonometry is the most common type of tonometry. It uses a small metal disc
to apply pressure to the cornea, the clear front part of the eye. The amount of pressure
needed to flatten the cornea is measured and used to calculate the intraocular pressure.
Tonometry is a painless procedure that takes just a few seconds. It is usually performed
by an eye doctor or optometrist.
Types of Tonometry:-
Applanation tonometry:
It does this by applying a small amount of pressure to the
cornea, the clear front part of the eye. The amount of pressure required to flatten the
cornea is then used to calculate IOP.
There are two main types of applanation tonometers: Goldmann applanation
tonometers and Perkins applanation tonometer. Goldmann applanation tonometer are
the most common type and are used in most doctor's offices. Perkins applanation
tonometer are less common and are used in some hospitals and clinics.
Applanation tonometers are very accurate and are the gold standard for measuring IOP.
They are also very safe and painless.
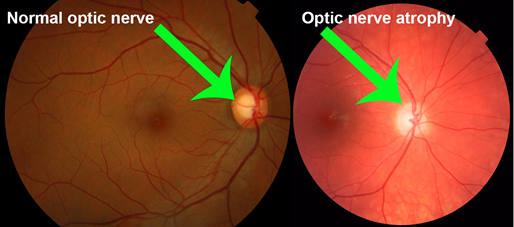
IOP is important because it can be a sign of glaucoma, a serious eye disease that can
damage the optic nerve and lead to blindness. Glaucoma is often called the "silent thief
of sight" because it can cause vision loss without any symptoms.
If you have any concerns about your vision, it is important to see an eye doctor for a
comprehensive eye exam.
Non contact tonometry:
It does this by using a puff of air to gently deflect the
cornea, the clear front part of the eye. The amount of deflection is then measured to
calculate the eye pressure.
Non-contact tonometers are more comfortable for patients than traditional tonometers,
which require a drop of anesthetic to be placed in the eye. They are also more accurate
and can be used to measure the pressure in both eyes at the same time.
How It Works:
During NCT, a puff of air is directed at your cornea, slightly flattening it.
The force needed to flatten the cornea correlates with the intraocular pressure.
Higher intraocular pressure indicates a greater risk of developing glaucoma.
Schiotz tonometry:
A Schiotz tonometer is an analog, weight-based tool to assess
intraocular pressure. It uses a weight on a flat transducer which is opposed by the
intraocular pressure. The IOP is transferred through the weighted tonometer arm and
gives a reading on a needle, which is then used on a conversion table to calculate IOP.
Measurement Process:
The examiner places the curved footplate on the patient’s cornea.
The weighted plunger sinks into the cornea, and the depth of indentation is recorded.
The scale reading is converted to an IOP value using the conversion table.
Clinical Use:
The Schiotz tonometer is primarily used to measure and monitor intraocular pressure.
It is especially valuable in cases of suspected increased intraocular pressure or as a
preventive examination for early detection of glaucoma
Digital Tonometry:
Digital tonometery measure the pressure inside the eye by
applying a small amount of pressure to the surface of the cornea. This is not a abel to
give accurate IOP.
Who needs a tonometry test?
Individuals over 40 years old
Those with a family history of glaucoma
People with other chronic eye conditions
Those who have injured their eye in the past
Individuals with diabetes, high blood pressure, or poor blood circulation