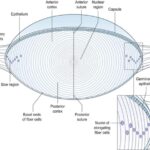
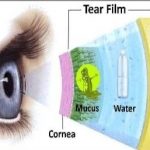
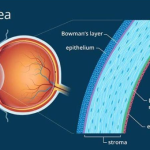
The precorneal tear film plays a major role in the maintenance of the functional integrity of the cornea. It protects, nourishes & lubricates the cornea. The cornea is made up of the refractive elements. The transparency & health of cornea are of utmost importance. The contact lens necessarily interferes with the normal harmonious relationship between the cornea & the tear film – to a greater or lesser extent. This disturbance may not only result in the impairment in the health & functioning of the cornea but may also ultimately impair the efficacy & acceptability of the contact lens itself.The interactions that take place between the tear film & contact lens are summarized below:
Positioning of Lens And Tear Film
The only logical approach to position the contact lens on the eye is to either somehow clamp the lens to cornea or by sticking the lens to the cornea. Both these are not practically feasible, and the precorneal tear film with its properties of surface tension and viscosity functions as a reversible sheeting & glue to hold the contact lens to the cornea. As soon as the lens is inserted in the eye, conjunctival mucus is rubbed on to the lens surface after several blinks, and then tear fluid will wet the lens with each blink. The tear film not only wet the lens, but the thin sheet that spread over the lens anchors itself all around the periphery of the lens to the surrounding tear film.
Optical considerations
The tear lens or the post-lens tear film plays a major role in supplementing the function of contact lens. The back of tear lens fills the irregularities of cornea, thus presenting a uniform optical surface and the front surface of contact lens. The refractive index of tears is 1.337 and that of cornea is 1.376. If these indices were equal, all degrees of corneal astigmatism and irregularity would be perfectly corrected with contact lens.
Effect Of Contact Lens On Corneal Nutrition
Contact Lens can potentially embarrass the cornea in at least four ways. It can
1.Reterd the evaporation of tears and interfere with hypertonicity of tears.
2.present a physical barrier for delivery of oxygen.
3.Trap wastes and interfere with waste disposal.
4.Traumatize The delicate epithelial cells of cornea.
Average hard lens covers 50%-80% of corneal surface and with normal lens mobility 70%-85% of this covered area is permanently covered. Hence, this area of cornea is dependent for nutrition on the tear film under the contact lens. This post-lens tear film has to be constantly renewed in order that the corneal oxygen needs are met. It has been found that under static conditions, the oxygen in the post-lens tear film is exhausted in about 90s with hard lenses or with soft lenses with 40% hydration. Since the nonoxygen-dependent pathway for obtaining energy is only about 1/18th as efficient as oxygen-dependent pathway and further there is accumulation of lactic acid, The corneal nutrition suffers and there is corneal oedema & haziness.
The Blinking provides a pump mechanism kn the cornea-contact lens system & the lid pressing on the lens expels The post-lens tear film which is formed against subsequently. Efficiency of tear pump depends on the following :
1.volume of tears behind contact lens
2.percentage of exchange with eash blink and
3.Frequency of Blinking.
In soft lens, the large diameter of lens almost wholly covers the corneal epithelium. However, since soft lens is hydrophilic, an aqualung effect seen. The post-lens tear film obtains oxygen from tear film on contact lens surface. However, even here, in absence of Blinking the cornea suffers from lack of oxygen. The pump effect is not so evident in these cases. Oxygen delivery is only 1/10th that with hard lens. But the flexibility of lens permits a capillary layer of lacrimal fluid under the lens. Deturgescence of cornea may be impaired due to hypotonicity of tear film caused by the following :
1.Excessive tear secretion
2. Impairment of evaporation and
3. Altered Blinking rate.
Lens Edge Flare

The contact lens is surrounded by patients tears which produces a prism-shaped meniscus at the lens edge. If the edge crosses the pupillary area as with small hard lenses- there is formation of second out of focus image on retina. This phenomenon is known as Edge Flare or ghost image.
Contact Lens Integrity
The tear fluid plays a role in maintaining the normal Integrity of soft lenses. The hydrophilic soft lenses have a water content between 25% and 85%. These lenses when deprived of their water content become hard and brittle, and the refractive index and dimensions vary with the amount of hydration. It has been noted in HEMA lens that after 2 min of loss from the eye about 10% of its water content is lost and after 15 min about 50% of water content is lost.
Lens Spoilage And Tear Film
It is indeed ironic that the tear fluid which plays such a vital role in the acceptability of adaptability to and functioning of soft contact lens is also responsible for the Spoilage of soft contact lenses.
A soft contact lens is subject to deposits on its surface, which effect its optical properties. In most cases, these deposits diminish the efficiency of the soft lens within 6months. These deposits are due to various causes as follows:
1.Irregularities of lens surface due to manufacturing defects.
2.porosity of the lens.
3.pH of the lens.
4.Composition of tear fluid.
5.Volume of tear fluid.
6.Rapid break-up time and
7.Blinking deficiencies
Some Important Things
1.Do tears affect contact lenses?
Will crying make your contacts blurry? Crying can affect your vision, at least temporarily. The enzymes, lipids and mucus found in tears can leave deposits that stick to your contact lenses and make your vision blurry.
2. Can you use tear drop while wearing contacts?
While some of them may be OK for use with contact lenses, they are designed to not only lubricate the eye but to promote healing of the eye’s surface. It is best to stick with eye drops that specifically state, “for contact lenses.” However, many other artificial tears for dry eyes are OK to use with contact lenses.
3.What is the effect of contact lens wear on tear protein concentration?
There were no changes in other tear film or ocular surface parameters. The protein concentration and lipid layer appearance did not change during lens wear for either population. Prior to lens wear, tolerant subjects had a statistically longer NI-TBUT, higher phenol red thread test and higher tear flow rate.
4.What is the importance of tear film in the patient being considered for contact lens wear?
The tear film is crucial for maintaining a healthy and comfortable ocular surface. When contact lens wearers experience dryness and discomfort, it is often from lens use.
5.Can you put contact solution in my eye?
Contact Solution is mainly used to clean your contact lenses from the daily grime and germs that buildup. It is not meant for use in your eyes as drops. Although contact solution does contain the saline solution, which is safe for the eyes, it also has cleaning compounds.