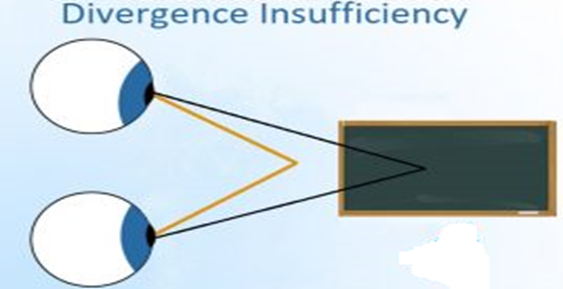
What is Divergence ?
Divergence is the opposite of convergence and is the ability to turn the two eyes outwards to look at a distant object. [Convergence is the ability to turn the two eyes inward toward each other to look at a close object ]
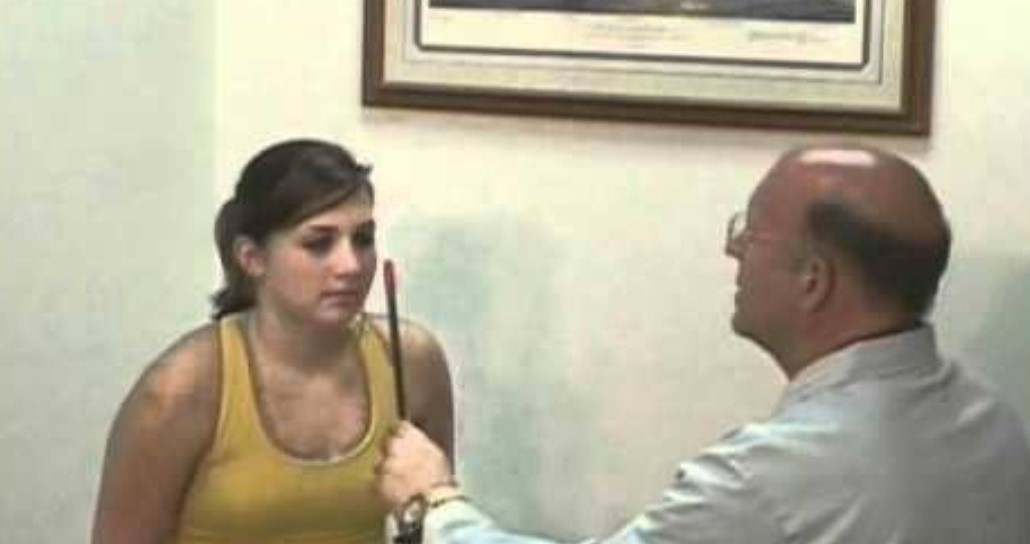
This test can be performed using a prism bar or a rotatory prism (Risley Prism ) or single prism. A prism bar consists of a series of prism of increasing strength . it is held by the examiner infront of one of the patient’s eyes and merely needs to be moved higher or lower to bring a stronger or weaker prism into the line of sight .
Amplitudes of divergence are measured first and those of convergence second .

SYNAPTOPHORE METHOD :– To measure the divergence , the arms of the synoptophore are slowly diverged and the patient is instructed to report occurrence of diplopia or the disappearance of one or the other control mark of the picture (suppression).this point- the break point- is recorded and the arms of the synoptophore are slowly converged and the recovery point , where fusion occurs is noted .
DIVERGENCE INSUFFICIENCY :- Divergence insufficiency refers to a clinically defined acquired disorder of ocular horizontal version . It is an unusual form of strabismus with esotropia and diplopia only at distance and single binocular vision at near. Actually it’s not synonymous with divergence paralysis, but it is a separate clinical entity .
Recently, the term “divergence insufficiency” has been challenged, since alternate etiologies have been introduced that do not necessarily imply insufficient divergence amplitudes as the cause of this disease-state. Additionally, the pattern of divergence insufficiency esotropia can be seen in a wide range of ages, and likely has a differing underlying etiology in young patients compared with older adults, given that the pattern of divergence insufficiency esotropia is more often related to a neurological problem when it occurs in young children, the focus of this discussion will be on divergence insufficiency pattern esotropia in older adults, also known as “age-related distance esotropia.”
CHARACTERISTIC FEATURES ARE AS FOLLOWS :-
- Esodeviation – Intermittent or constant esodeviation is much larger at distance than near. Usually patients maintain the fusion at near . esodeviation is comitant in all fields of gaze .
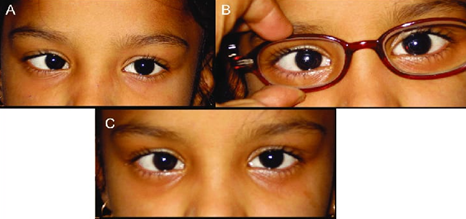
- Ductions and versions are normal in all the directions
- Fusional divergence is markedly reduced both at distance and near fixation.
- Absence of any neurologic disease (Divergence paralysis)
[Divergence paralysis is a rare entity characterized by a sudden onset esotropia at distance fixation and a homonyumous diplopia]
TREATMENT :-
PRISMOTHERAPY – Divergence insufficiency is a self – limiting condition . However, to alleviate the patient of symptoms , prism base –out is prescribed to provide comfortable single vision at distance. Prism power is decreased stepwise in months and ultimately discarded .
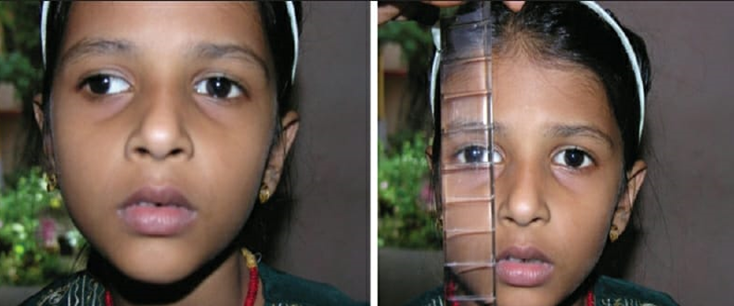
SURGICAL TREATMENT – Patients with divergence insufficiency pattern of esotropia can be treated surgically if they do not respond to or do not desire prism therapy. The surgical treatment of divergence insufficiency esotropia can be approached by several differing techniques, all of which have satisfactory results. As the etiology of divergence insufficiency is further elucidated, surgical treatments may evolve as well, in order to target the underlying pathological features.
- LATERAL RECTUS RESECTION – Lateral rectus muscle resection has been advocated by many authors. Proponents of lateral rectus muscle resection claim that this surgical approach is more likely to improve the distance esotropia without causing convergence insufficiency at near.
- MEDIAL RECTUS RESECTION – As the understanding of divergence insufficiency advanced, some surgeons began to advocate the use of medial rectus recession as an alternative treatment. In 2000, Thomas reported seven patients with divergence insufficiency pattern esotropia, albeit a younger population (aged 7–41 years).
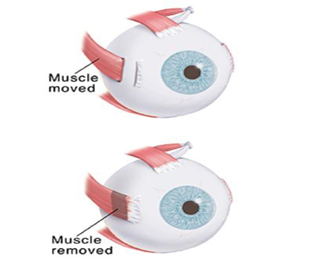
RESECTION
CONCLUSIONS : – Divergence insufficiency esotropia may be better described as “age-related distance esotropia.” The underlying pathogenesis of this disease entity is still under active investigation, but may be related to mechanical factors such as degeneration of the lateral rectus-superior rectus band leading to lateral rectus muscle pulley displacement. Surgical treatment is often successful and may include unilateral or bilateral medial rectus recession or lateral rectus resection. Complications such as recurrence of distance esotropia or new-onset convergence insufficiency are rare, and patients are generally satisfied. Lateral rectus equatorial myopexy may be used in the future for this category of patients, but this technique is still under investigation.