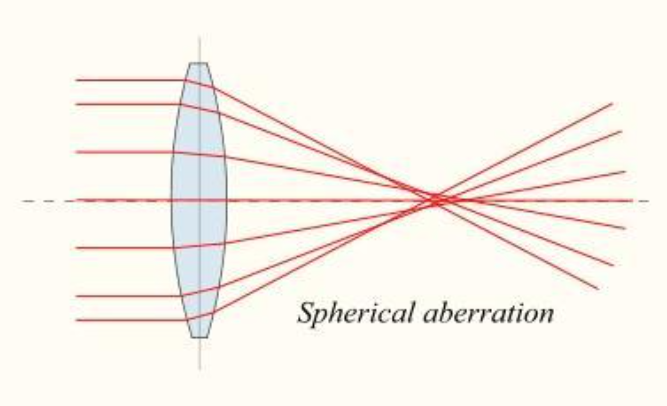
Spherical aberration is an optical aberration that occurs when all incoming light rays after passing through spherical surface end up focusing at different points . Lights rays that strike a spherical surface off centre are refracted more or less than those strike close to the centre . The human eye , having a Power of about +16D , was long thought to suffer from various amounts of spherical aberrations .
The presence of spherical aberration is indicated by a cubic or S shaped curve , under correction , giving a graph in which the line joining the ends of the curve is more uphill than the tangent line at the principle ray point . If the line joining the ends of the curve is more downhill , then the spherical aberration is over corrected .
- Causes of spherical aberration
- An aberration of the eye occurs when there is an any abnormalities in the cornea such as – corneal ulcer , corneal dystrophies , corneal scarring .
- Surgery such as LASIK or Keratoplasty can also increase the risk of developing spherical aberration.
III. Spherical aberration occurs because curvature in a lens or mirror causes rays falling on the outer edges to be brought to a focus at a different point than those falling on the middle .
- How does spherical aberration affect our human vision ?
It is normal to have some degree of aberration – as no eye is perfect- but if it is unusually high , vision can be noticeably affected .
- Spherical aberration can alter the focusing ability of the eye , specially in dark room or dimly lit environments .
- Some may also see halos or starburst around lights .
- Patients face vision problem and their vision decrease dramatically .
- Patients may have large pupil .
- Patients face problems in their daily life work and their working life have hamper .
- Diagnosis
- At first doctors get past history from patient . First the doctor will ask the patient to know if there was any incident / accident happened with patient in which his / her eyes were damaged .
II. Then doctors take vision to the patient because vision is most important in any disease in ophthalmology. If the vision decrease a lot and patients see halos or starburst around lights then we move to further tests.
III. Doctors must see the patients on slit lamp to detect if there have ant abnormalities in the cornea or not .
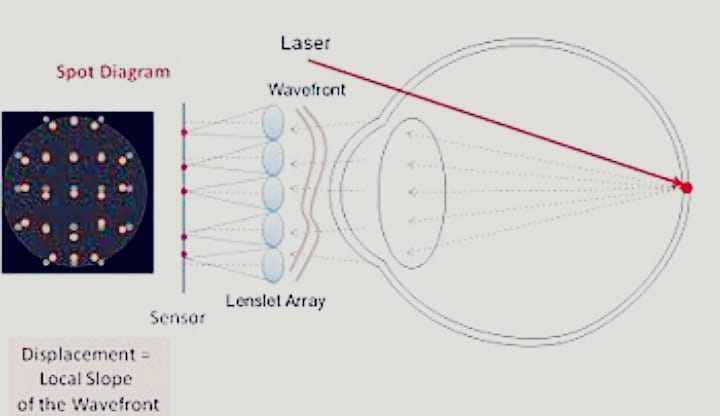
- Aberration can be examined and diagnosed through wavefront technology , using an instrument called an aberrometer .
V Aberrometer measures how light passes through the crystalline lens and cornea , which parts of the eye .
This information is vital in determining and prescribing any vision correction that may br needed .
- Treatment –
An optical aberration is a loss of clarity of images formed by the eye and aberration can occur in eyeglass lenses or optical degree of aberration , but correction is rarely required. However , in severe cases causing lower quality vision , you may need special treatment.
Higher-order aberrations such as spherical aberration are so complex that they cannot be improved with ordinary eyeglasses or soft contact lenses. However, they can be treated with rigid contact lenses.
Some other advanced options can be used to correct spherical aberration, which may include one of the following:
- Special eyeglass lenses
- Intraocular lenses
- Refractive surgery
If spherical aberration (or another type of HOA) begins distorting your vision, your ophthalmologist will recommend the best treatment for your specific case.
Factors that contribute in diminishing the spherical aberration of human eye :
Peculiar curvature of the cornea , I.e. flatter periphery than the centre .
Peculiar structure of the crystalline lens , wherein the central portions have a greater density and are arranged in layers of greater curvature than the peripheral portion .
Iris blocks the peripheral rays to enter the eye and thus in ordinary circumstances, refraction of only paraxial rays of light takes place .
Lens systems with aberration correction are usually designed by numerical ray tracing. For simple designs one can sometimes analytically calculate parameters that minimize spherical aberration. For example, in a design consisting of a single lens with spherical surfaces and a given object distance o, image distance I, and refractive index n, one can minimize spherical aberration by adjusting the radii of curvature R1 and R2 of the front and back surfaces of the lens such that –
R1+R2 2(n^2–1) I+0
——– = ——— (—–)
R1-R2 n+2 I–0
Spherical aberration is not a threat to eye health, but cases that impair vision should be assessed and treated as recommended by your eye doctor.