Suppression
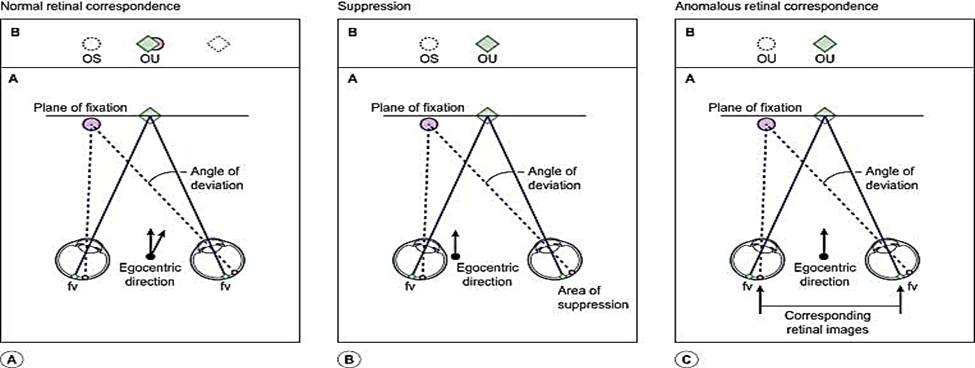
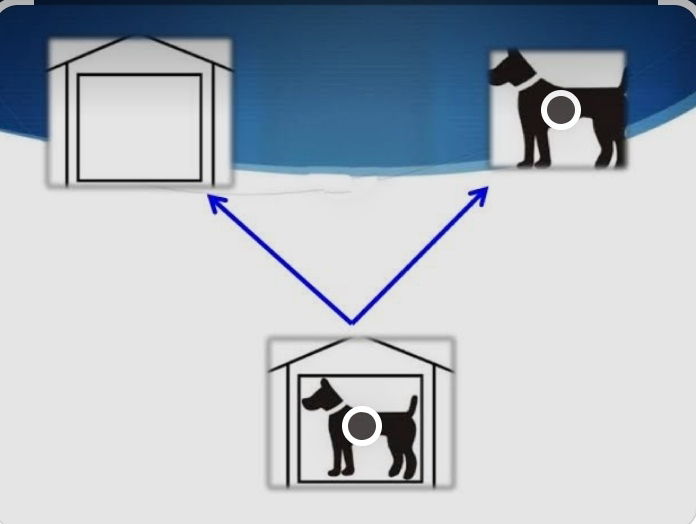
It’s a neuro physiological active inhibitor mechanism in which when corresponding retinal area are stimulates by dissimilar stimuli or when non corresponding retinal area are stimulates by similar stimuli ,one or other is are temporarily inhibited or suppressed
to prevent confusion or diplopia respectively. Suppression is foveal in order to tackle confusion and extrafoveal in order to avoid diplopia.
Types of suppression :
It is classified into 2
1. Facultative
2. Obligatory
Facultative suppression : Facultative suppression is only under binocular condition with no persisting “hang over” under monocular condition. Thus the visual acuity under monocular condition and there are no uniocular scotoma in the visual field. Obligatory suppression : obligatory suppression is the effect which carrier On even on under monocular condition resulting in diminution Of visual acuity .Amblyopia is the fallout of this obligatory suppression.
Clinical association of suppression.
o strabismus
o Anisometropia
o Aniseikonia
Relation between suppression and strabismus
When squints develop before the age of six, suppression of the misaligned eye develops to avoid diplopia. Suppression is an active, cortical process that leads to decrease in sensitivity in parts of visual field, the suppression scotoma. In case of microstrabismus, which is defined as a convergent squint less than 6 degree, the central part of visual field of the misaligned eye is suppressed. The sensitivity in other parts of retina may remains
normal.
Investigation
Following are the investigation used for the suppression :
Worth 4 dot test
Bagolini striated glasses
4prism base out test
After image test
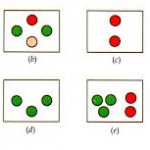
WORTH FOUR DOT TES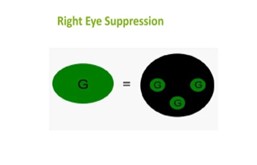
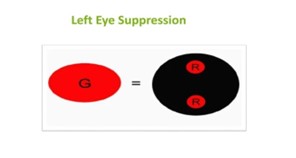
To diagnose the suppression involving the peripheral retina.
For this test red green goggle are used ,red in right eye and green in left eye.
Pt have left suppression will see (2 red light)
Pt have Right eye suppression (3 green light)
In presence of alternate suppression Pt will see alternately 2 red light and 3
green light.
4 D BASE OUT PRISM TEST
This test is performed for detection of small angle heterotopia’s & presence of
central suppression scotoma.
To perform this test pt fixates penlight than 4 D prism
is placed with Base out in front
Of right eye.
Examiner observes the presence of biphasic corrective movement of left eye.
This is absent in presence of central suppression scotoma.
BAGOLINI STRIATED GLASSES
A pair of striated glasses are used in front of each eye.
A source of light is seen as a line at right angle to striation.
BSG are glasses of no dioptric power that have many narrow striation running
parallel in one meridian, these glass causes fixation light to appear as an
elongated streak perpendicular to striation
The lenses are usually placed at 135 degree in front of one eye and 45 degree in
front of other .
This test is used to determine the direction of a
pseudofoveal, arc, suppression and diplopia.
If the 2 streak intersect at their centre in the form of an oblique cross ,the Pt
has BSV if the eyes are straight or harmonic ARC in the presence of manifest
strabismus.
If 2 lines are seen but do not form a cross diplopia is present.
If only one streak is seen ,there is no simultaneously perception and
suppression is present.
If a small gap is seen in one of the streak , a central suppression scotoma is
present.
AFTER IMAGE TEST
o The objective angle of deviation is measured with synaptophore.
o The tube are set at zero and the slide are inserted.
o The current is switched on when the Pt is ready for the test to start .
o Each is stimulated for about 20 second.
o After each eye has been stimulated, after image slides are removed and the
automatic binocular flashlight devices is switched on.
o Then the Pt is asked to draw the after image position.
o In this test right fovea is stimulated with vertical and left with a horizontal bright
light and Pt is asked to draw position of after image.
Interpretation : for Suppression draw Only vertical or horizontal image in presence
of suppression.
Management
1. proper refractive corrective
2. Occlusion therapy
3. Alignment of visual axes.
4. Anti suppression orthoptic exercise
Indication
Pt with intermittent tropia.
Pt with convergence insufficiency
Person with constant tropia
Person with fully corrected accommodative esotropia.
Post surgical Pt with slight under correction.
Pt with shallow suppression may begin treatment using a more natural viewing
environment such as Bagolini lenses or polarizing filter.
Treating suppression involves 4 steps :
1. Identify an appropriate treatment environment ,based on know characteristics of Pt suppression that is treatment chosen should enable the Pt to achieve normal fusion without suppression.
2. Next step is to encourage normal sensory fusion by stimulating the suppressed image.
3. Requires the Pt maintain perception of the suppressed image for a specific length of time (this conscious mental effort is thought to significantly improve Pts ability to eliminate suppression
4. Involves changing the treatment changing treatment environment by introducing smaller suppression control and generally waking it harder for the Pt.
Treatment goal
Eliminate suppression
Accurately asses correspondence and sensory skills.
Provide some condition under which sensory fusion can possibly be established .
Stabilize sensory fusion whenever suppression is absent.
Obtain diplopia when strabismic , obtain visual confusion when strabismic.
Improve motor fusion skills in any procedure where suppression has been eliminated
and sensory fusion has been stabilized.