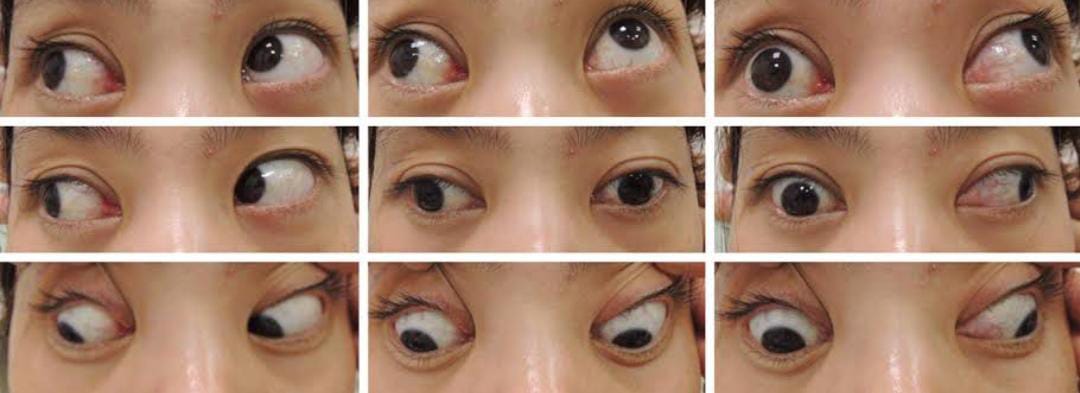
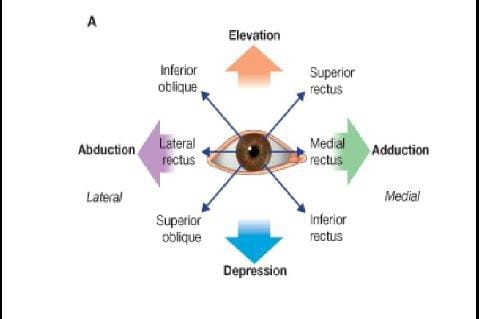
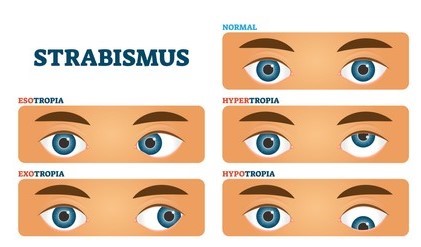
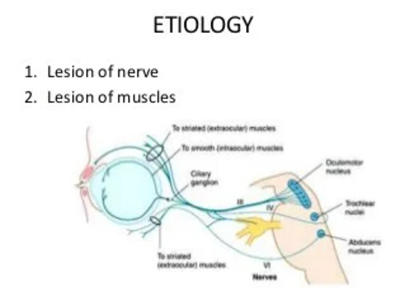
Def– Paralytic strabismus refers to an ocular deviation with misalignment of the visual axes of both eyes due to paralysis of one or more of the extraocular muscles(EOM) in which the angle of deviation varies in different directions of gaze and with fixation of eyes.
• Paralytic strabismus also known as Incomitant Strabismus
Etiology – Different types of lesions which affect the cranial nerve supplying the muscles. The lesions may be neurogenic, myogenic, or at the level of the neuromuscular junction.
- Neurogenic lesions: These may occur at the level of the nerve nucleus, nerve root, or any part of the nerve in its course. It is often bilateral and occurs due to lesions of the 3rd cranial nerve.
Common causes of Neurogenic lesions are –
- Congenital – Hypoplasia Or absence of the 3rd and 6th cranial nerve palsies.
- Inflammatory – These may be in the form of encephalitis, meningitis, neurosyphilis, peripheral neuritis(viral), infectious lesions of cavernous sinus and orbit.
- Neoplastic lesions – These include brain tumors, involving nuclei, nerve roots, or intracranial part of the nerves and intraorbital tumors involving peripheral parts of the nerves
- Vascular lesions – These are known in patients with Diabetes mellitus(DM), Hypertension (HTN) and atherosclerosis, Hemorrhage, thrombosis, embolism, aneurysms, or vascular occlusions. It is often unilateral, persists for days Or weeks, and even tends to become permanent in some cases due to paralysis of the 3rd cranial nerve( more common) 4th and 6th cranial nerves.
- Traumatic lesions – These include head injury and direct or indirect trauma to the nerve trunks.
- Toxic lesions – These include carbon monoxide poisoning, effects of diphtheria toxins, alcohol, and lead neuropathy.
- Demyelinating lesions – Ocular palsy may occur in multiple sclerosis and diffuse sclerosis.
- Myogenic lesions :
- Congenital lesions – These include absence, hypoplasia, weakness, mail insertion, and musculofacial anomalies.
- Traumatic lesions – These may be in the form of laceration, disinsertion, or hemorrhage.
- Inflammatory lesions(myositis) – It is usually viral in origin and may occur in influenza, measles, and other viral fevers.
- Dystrophy
- Orbito-myopathies – These include thyroid myopathy and carcinomatous myopathy which are associated with certain drugs. Chronic progressive Ophthalmoplegia (CPO) is a bilateral myopathy of extraocular muscles (EOM) which is the most common type of mitochondrial myopathy. It is characterized by-
- Bilateral Ptosis
- Diplopia
- Other associated symptoms of Chronic progressive Ophthalmoplegia(CPO) include hearing loss, ataxia, sensory axonal neuropathy, and clinical depression.
- Neuromuscular junction: It includes myasthenia gravis- a rare chronic autoimmune disease marked by muscular weakness without atrophy and caused by a defect in the action of acetylcholine at the neuromuscular junction.