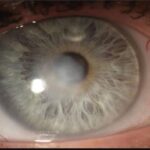
As many as a 45million people in the country wear contact lenses to improve their vision. contacts are usually safe, but several serious complications can occur especially if proper care is not taken. Contact lenses do cause a variety of insults to the cornea and conjunctiva including hypoxic changes, chemical toxicity, hypersensitivity reactions, mechanical trauma, desiccation, and infections. These in turn can lead to a number of clinical complications.
•Corneal complications:-
1) Epithelial oedema:-Minor degree of epithelial edema is the commonest and earliest corneal change. It occurs due to hypoxia of corneal epithelium and is generally reversible.
2) Epithelial Microcysts:-These is associated with a depressed corneal epithelial metabolism sustained over a period of weeks to months. These occur frequently with soft contact lenses and most commonly with EWLs.
3)Corneal Abrasions:-These may be caused by mechanical injury from the lens itself or by traumatic insertion or removal. Occasionally a foreign body embedded in the lens substance may also be responsible for corneal abrasions. The patients generally complain of pain, redness, and watering from the eyes.
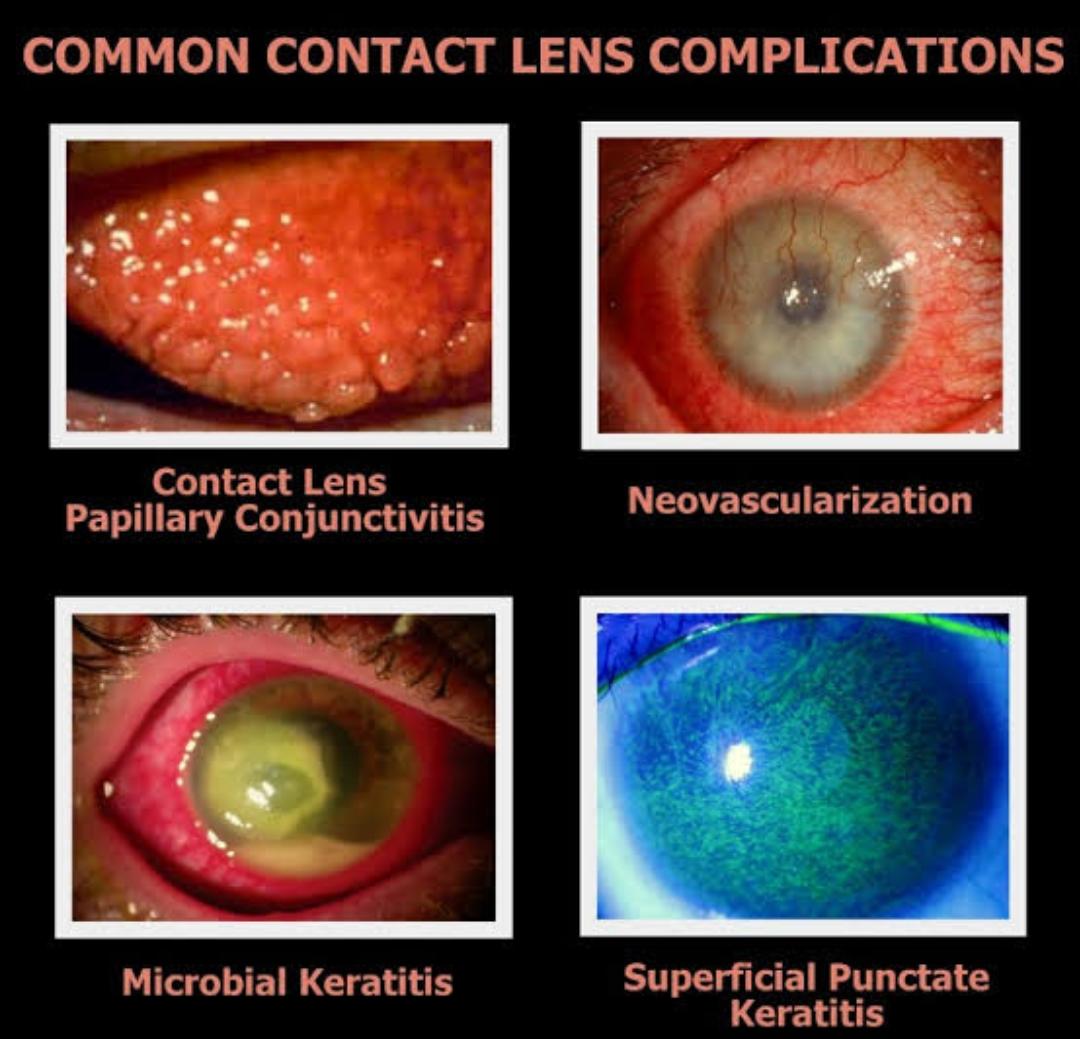
4) Superficial punctate keratitis:-Superficial punctate keratitis in a contact lens wearer may occur because of the following factors:-
A) Mechanical injury from the lens or traumatic insertion and removal.
B)Chemical toxicity from contact lens solutions generally causes diffuse punctate keratitis. This may be due to preservatives in the saline solution, improper rinsing of the lenses after the use of surfactant or enzyme cleaner, or failure to neutralize hydrogen peroxide disinfectant.
C) Associated external diseases such as dry eye and blepharitis.
5)3 and 9 O’clock staining:-
It is caused by desiccation of the cornea due to interruption of tear flow or disruption of the tear layer at the nasal and temporal cornea. It may be associated with poor lens edge fitting, limited lens movements, low riding lens, poor blinking, pinguecula, and lens adherence.It occurs most commonly in RGP lenses.
6)Corneal Neovascularization:-Corneal Neovascularization is often the result of chronic hypoxia, from excessive deposit formation on the lenses or from tight or thick lenses.
7)Microbial Keratitis:-It is the most serious, but the fortunately not very common complication of contact lens wear. It may occur with soft or rigid contact lenses but occurs with greater frequency with soft lenses in general and more so with extended wear contact lenses.
8)Corneal warping:-Corneal warping resulting in severe and permanent astigmatism may occur in some eyes as a response to chronic hypoxia, for example following prolonged wear of impermeable hard lenses.
9)Corneal endothelial changes:-Endothelial changes are not clear exactly. They are thought to be secondary to hypoxia which leads to lactate accumulation, elevated carbon dioxide levels, and reduced pH.
•Conjunctival complications:-
1)Allergic conjuctivitis:-It is a common problem with thiomersal-containing contact lens solutions. Fewer soft lens care solutions now contain thiomersal. The patient present with redness, burning, and itching soon after lens insertion. These symptoms may develop within days to months following the initial exposure to thiomersal. Examination reveals Conjunctival hyperemia and a fine papillary Conjunctival reaction.
2)Giant papillary conjuctivitis:-GPC has an immunological origin in which contact lens deposits, especially proteins,act as allergies.The incidence of GPC is influenced by patient susceptibility, wear schedule, care regimen and lens factors such as material and design. Soft lenses are most frequently implicated in the causation of GPC. Patients with asthma, hay fever, or animal allergies may be at increased risk.
3) Superior limbic keratoconjunctivitis:-Superior limbal keratoconjunctivitis is reported to occur as hypersensitivity to thiomersal or other preservatives in contact lens solution.The condition is generally bilateral but asymmetrical.The patients may complain of a foreign body sensation,redness and contact lens intolerance.Clinical signs include inflammation and hypertrophy of superior bulbar Conjuctiva bthat stains with rose Bengal, punctate staining and micropannus of the superior cornea and a fine papillary reaction of the superior tarsal Conjuctiva.
Contact lens related complications:-Contact lens can be damaged with time and create problems of various types.Lens spoilage may be physical due to alteration in the lens geometry and chemistry.The contact lens spoiled following changes:-
1)Physical changes to lens in the form of chipping or fracture may occur while handling i.e. during insertion,removal or storage.Physical damage to lens may occur due to biochemical degradation of lens plastic which tends to get easily fractured.
2) Discolouration of lens may occur following topical use of fluorescein and phenylephrine and systemic use of rifampicin.
3)Len loss occurs more often in children than adults. It is reported to occur more frequently in hard than soft and in EWLs than DWLs.
4)Lens deposits, the occurrence of lens deposits especially is not an uncommon problem. Deposits can be prevented by proper care and maintenance procedures including mechanical cleaning and regular enzyme cleaning. Proper follow-up and monitoring are always important.