Introduction:
The eyes are not only windows to the soul but also delicate organs that are vulnerable to injury. Ocular injuries can range from minor irritations to severe
trauma, potentially causing vision loss or even blindness. Understanding the types of ocular injuries and how to prevent them is crucial for maintaining eye health and preventing long-term damage.
Types of Ocular Injuries:
1. Corneal Abrasions:
Corneal abrasions occur when the surface layer of the cornea, the clear outermost part of the eye, is scratched or scraped. This can happen due to foreign objects, such as dust or sand, entering the eye or from trauma like rubbing the eyes forcefully. Symptoms include pain, redness, tearing, and sensitivity to light. Treatment typically involves antibiotic eye drops and avoiding rubbing the eyes to prevent further damage.
2. Chemical Burns:
Chemical burns to the eye can result from exposure to acids, alkalis, or other caustic substances. These burns can cause immediate damage to the cornea and conjunctiva, leading to severe pain, redness, blurred vision, and in severe cases, permanent vision loss. Immediate irrigation with water is crucial to dilute the
chemical and minimize tissue damage. Prompt medical attention is necessary to assess the extent of the injury and prevent complications.
3. Foreign Body Injuries:
Foreign bodies, such as dust, metal shards, or wood splinters, can enter the eye and cause irritation or injury. Symptoms include pain, tearing, redness, and the
sensation of having something in the eye. Depending on the size and location of the foreign body, it may require removal by an eye care professional. Attempting to remove it at home can worsen the injury and increase the risk of infection.
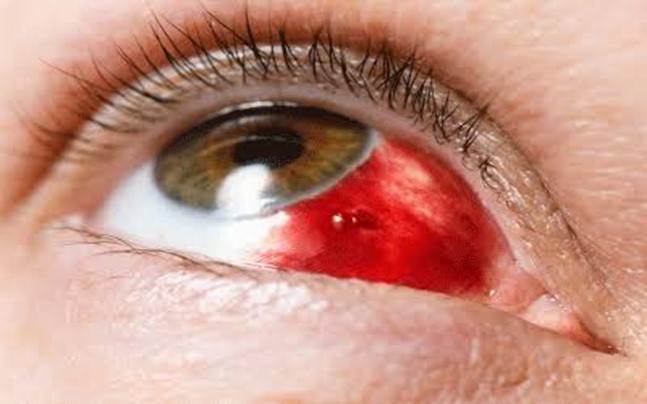
4. Blunt Trauma:
Blunt trauma to the eye can result from accidents, falls, or sports-related injuries. It can cause various injuries, including orbital fractures, hyphemas (bleeding in the front chamber of the eye), retinal detachment, and traumatic cataracts. Symptoms may include pain, swelling, bruising around the eye, double vision, and decreased vision. Immediate medical attention is necessary to assess the extent of the injury and prevent complications.
5. Penetrating Injuries:
Penetrating injuries occur when a foreign object, such as a sharp tool or projectile, pierces the eye. These injuries are severe and can cause significant damage to intraocular structures, leading to vision loss or blindness. Immediate medical attention is critical to assess the extent of the injury, repair any damage, and minimize the risk of complications such as infection or retinal detachment.
Prevention of Ocular Injuries:
1. Use Protective Eyewear:
Wearing appropriate eye protection, such as safety glasses or goggles, can prevent many ocular injuries, especially during activities such as sports, yard work, or
working with hazardous materials.
2. Handle Chemicals Safely:
When working with chemicals or household cleaners, always wear protective eyewear and follow safety guidelines to minimize the risk of chemical burns to the
eyes.
3. Avoid Rubbing Your Eyes:
Rubbing your eyes forcefully can cause corneal abrasions or exacerbate existing injuries. Instead, rinse your eyes with clean water if they feel irritated or itchy.
4. Be Mindful of Foreign Objects:
Be cautious when working in environments where foreign objects are present, such as construction sites or woodworking shops. Always wear eye protection and be mindful of potential hazards.
5. Seek Prompt Medical Attention:
If you experience an eye injury or notice any symptoms such as pain, redness, or decreased vision, seek prompt medical attention from an eye care professional. Early intervention can prevent complications and preserve vision.
Conclusion:
Ocular injuries can have serious consequences, ranging from temporary discomfort to permanent vision loss. Understanding the types of ocular injuries and taking preventive measures is crucial for maintaining eye health and preventing long-term damage. By wearing protective eyewear, handling chemicals safely, and seeking prompt medical attention when needed, we can reduce the risk of ocular injuries and safeguard our vision for years to come.