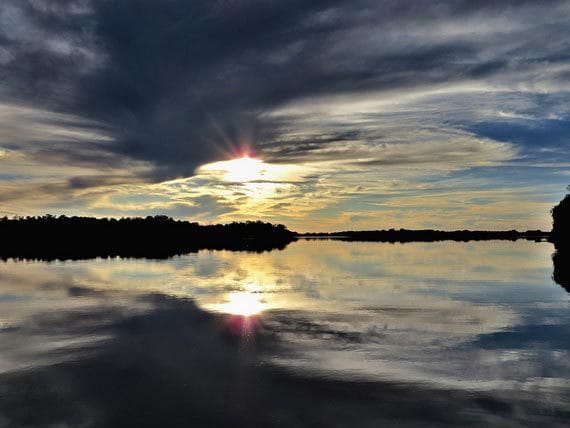
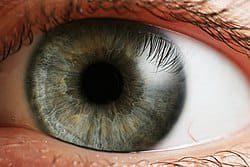
The pupil is the mirror of various diseases. The various reflection of pupil shape, size and reaction represent the various disease. Many ocular diseases are diagnosed by the pupillary reaction and structure.
By the torch light examined we easily find lots of ocular problem.
This is how I discussed some various shape,size and reaction of the pupil .
The discussion topics are ——
~ 𝘞𝘩𝘢𝘵 𝘪𝘴 𝘗𝘶𝘱𝘪𝘭
~ 𝘕𝘰𝘳𝘮𝘢𝘭 𝘗𝘶𝘱𝘪𝘭 𝘴𝘩𝘢𝘱𝘦 & 𝘴𝘪𝘻𝘦
~ 𝘊𝘩𝘢𝘯𝘨𝘦 𝘰𝘧 𝘗𝘶𝘱𝘪𝘭 𝘴𝘪𝘻𝘦 𝘥𝘶𝘦 𝘵𝘰 𝘷𝘢𝘳𝘪𝘰𝘶𝘴 𝘥𝘪𝘴𝘦𝘢𝘴𝘦𝘴 𝘢𝘯𝘥 𝘴𝘵𝘢𝘵𝘦
~ 𝘊𝘩𝘢𝘯𝘨𝘦 𝘰𝘧 𝘗𝘶𝘱𝘪𝘭 𝘴𝘩𝘢𝘱𝘦 𝘥𝘶𝘦 𝘵𝘰 𝘷𝘢𝘳𝘪𝘰𝘶𝘴 𝘤𝘰𝘯𝘥𝘪𝘵𝘪𝘰𝘯 & 𝘥𝘪𝘴𝘦𝘢𝘴𝘦𝘴
~ 𝘗𝘶𝘱𝘪𝘭𝘭𝘢𝘳𝘺 𝘭𝘪𝘨𝘩𝘵 𝘳𝘦𝘢𝘤𝘵𝘪𝘰𝘯
~ 𝘝𝘢𝘳𝘪𝘰𝘶𝘴 𝘤𝘰𝘭𝘰𝘶𝘳 𝘰𝘧 𝘱𝘶𝘱𝘪𝘭𝘭𝘢𝘳𝘺 𝘳𝘦𝘧𝘭𝘦𝘤𝘵𝘪𝘰𝘯
~ 𝘗𝘶𝘱𝘪𝘭𝘭𝘢𝘳𝘺 𝘭𝘪𝘨𝘩𝘵 𝘳𝘦𝘧𝘭𝘦𝘹 𝘱𝘢𝘵𝘩𝘸𝘢𝘺.
1) ᴡʜᴀᴛ ɪs ᴘᴜᴘɪʟ?
Ans:- In the centre of the iris there is a round shape opening structure called pupil.
𝘚𝘪𝘻𝘦- Normally, it varies between 2-4 mm. It may be smaller ( 𝘮𝘪𝘰𝘴𝘪𝘴) or may be larger ( mydriasis).
For the refractive status size of the pupil is normally changed.
In 𝘔𝘺𝘰𝘱𝘪𝘤 𝘱𝘢𝘵𝘪𝘦𝘯𝘵, the size of the pupil > equal to 4 𝘮𝘮 ( Mydriasis).
In 𝘏𝘺𝘱𝘦𝘳𝘮𝘦𝘵𝘳𝘰𝘱𝘪𝘤 𝘱𝘢𝘵𝘪𝘦𝘯𝘵, the size of thr pupil < equal to 2 𝘮𝘮 ( 𝘔𝘪𝘰𝘴𝘪𝘴).
In 𝘌𝘮𝘮𝘦𝘵𝘳𝘰𝘱𝘪𝘤 𝘱𝘢𝘵𝘪𝘦𝘯𝘵, the size of the pupil lying between (2 to 4 )mm.
The reaction of pupil in 𝘔𝘺𝘰𝘱𝘪𝘤 𝘱𝘢𝘵𝘪𝘦𝘯𝘵 is good and fast and in 𝘏𝘺𝘱𝘦𝘳𝘮𝘦𝘵𝘳𝘰𝘱𝘪𝘤 𝘱𝘢𝘵𝘪𝘦𝘯𝘵 is normal and slow.
𝘞𝘩𝘢𝘵 𝘢𝘳𝘦 𝘵𝘩𝘦 𝘤𝘢𝘶𝘴𝘦𝘴 𝘰𝘧 𝘮𝘪𝘰𝘴𝘪𝘴 𝘗𝘶𝘱𝘪𝘭?– small pupil
=Including thypermetropia there are lot of factor which are responsible for the miosis Pupil.these are —
(1) ᴇxᴛʀᴇᴍᴇ ᴏғ ᴀɢᴇs = In the older of size of pupil becomes gradually decreasing. For this recover in extreme of age the size of Pupil miosis.
(2) ɪɴ ʙʀɪɢʜᴛ ʟɪɢʜᴛ= sunlight or bright light the Pupil is constricteal for this recover Size of pupil become small.
(3) ᴍᴏʀᴘʜɪɴᴇ ɪɴsᴛʀᴜᴄᴛɪᴏɴs= morphine is a very story painkiller when is talles. By the reaction of it’s the size of the Pupil become miosis.
(4) ᴘᴏɴᴛɪɴᴜᴇ ʜᴇᴍᴀʀᴀɢᴇ=pontinue hemarage is a form of a intra cranial hemarage the most common cause of this problem is long standing poorly uncontrol chronic hypertension.
(5) ᴀᴄᴜᴛᴇ ɪʀɪᴛɪs= iritis is intranation of the iris ,when the iritis develops suddenly,over .for the acute iritis pupil become miosis.
Acute Iritis – Iritis is the inflammation of the iris, when the Iritis develops suddenly , over hours and days is known as acute Iritis. For the acute Iritis pupil become miosis.
Use of Miotic drug- Use of Miotic drug the size of the pupil become smaller ( eg – Pilocarpine ).
2) ᴡʜᴀᴛ ᴀʀᴇ ᴛʜᴇ ᴄᴀᴜsᴇ ᴏғ ᴍʏᴅʀɪᴀsɪs? (big pupil size>4mm)
Ans:- Including moderate high myopia there are lot of factors which are responsible for 𝘱𝘶𝘱𝘪𝘭 𝘮𝘺𝘥𝘳𝘪𝘢𝘴𝘪𝘴, they are :
i) 𝘖𝘱𝘵𝘪𝘤 𝘈𝘵𝘳𝘰𝘱𝘩𝘺 – When the optic nerve gets damage anywhere along the path from retina to LGB(Lateral Geniculate Body), then 𝘮𝘺𝘥𝘳𝘪𝘢𝘴𝘪𝘴 takes place.
ii) 𝘈𝘤𝘶𝘵𝘦 𝘢𝘵𝘵𝘢𝘤𝘬 𝘪𝘯 𝘢𝘯𝘨𝘭𝘦 𝘤𝘭𝘰𝘴𝘶𝘳𝘦 𝘨𝘭𝘢𝘶𝘤𝘰𝘮𝘢 – It occurs when the iris bulges forward due to narrow or blockage in the drainage angle ,fluid can’t circulate through the eye and pressure increases resulting in 𝘮𝘺𝘥𝘳𝘪𝘢𝘴𝘪𝘴.
iii) 𝘈𝘣𝘴𝘰𝘭𝘶𝘵𝘦 𝘎𝘭𝘢𝘶𝘤𝘰𝘮𝘢 – It is the end stage in all types of glaucoma. The eye has no vision, there is totally absence of pupillary light reflex and pupillary response, due to this size of pupil increases.
iv) 𝘊𝘰𝘮𝘢𝘵𝘰𝘴𝘦 𝘱𝘢𝘵𝘪𝘦𝘯𝘵 –
Coma is a state of prolonged unconsciousness with dilated pupil.
v) 𝘏𝘦𝘢𝘥 𝘪𝘯𝘫𝘶𝘳𝘺 – It sometimes results in 𝘮𝘺𝘥𝘳𝘪𝘢𝘴𝘪𝘴.
vi) 3𝘳𝘥 𝘯𝘦𝘳𝘷𝘦 𝘱𝘢𝘭𝘴𝘺- The pupil becomes fixed and dilated due to paralysis of 𝘴𝘱𝘩𝘪𝘯𝘤𝘵𝘦𝘳 𝘱𝘶𝘱𝘪𝘭𝘭𝘢𝘦, pupil become larger.
vii) 𝘜𝘴𝘦 𝘰𝘧 𝘮𝘺𝘥𝘳𝘪𝘢𝘵𝘪𝘤𝘴 – Pupil gets dilated due to the use of drugs like atropine, homatropine, phenylphrine.
viii) 𝘐𝘯 𝘥𝘢𝘳𝘬 𝘱𝘭𝘢𝘤𝘦𝘴 – The pupil gets larger in dark areas to allow more amount of light.
𝘛𝘩𝘦 𝘴𝘩𝘢𝘱𝘦 𝘰𝘧 𝘵𝘩𝘦 𝘱𝘶𝘱𝘪𝘭 𝘤𝘩𝘢𝘯𝘨𝘦𝘴 𝘣𝘺 𝘵𝘩𝘦 𝘷𝘢𝘳𝘪𝘰𝘶𝘴 𝘰𝘤𝘶𝘭𝘢𝘳 𝘥𝘪𝘴𝘦𝘢𝘴𝘦𝘴. 𝘏𝘦𝘳𝘦 𝘐 𝘥𝘪𝘴𝘤𝘶𝘴𝘴𝘦𝘥 𝘪𝘯 𝘷𝘦𝘳𝘺 𝘴𝘩𝘰𝘳𝘵𝘭𝘺 ——
(𝘈) ɪʀʀᴇɢᴜʟᴀʀ 𝘴ʜᴀᴘᴇ :- 𝘛𝘩𝘦 𝘴𝘪𝘻𝘦 𝘰𝘧 𝘵𝘩𝘦 𝘱𝘶𝘱𝘪𝘭 𝘣𝘦𝘤𝘰𝘮𝘦 𝘪𝘳𝘳𝘦𝘨𝘶𝘭𝘢𝘳 𝘢𝘧𝘵𝘦𝘳 𝘵𝘩𝘦 𝘵𝘳𝘢𝘶𝘮𝘢 𝘰𝘳 𝘪𝘳𝘪𝘵𝘪s.
(𝘉) ᴅ-𝘴ʜᴀᴘᴇᴅ ᴘᴜᴘɪʟ :- 𝘛𝘩𝘦 𝘴𝘪𝘻𝘦 𝘰𝘧 𝘵𝘩𝘦 𝘱𝘶𝘱𝘪𝘭 𝘢𝘱𝘱𝘦𝘢𝘳𝘴 𝘢𝘴 𝘋- 𝘴𝘩𝘢𝘱𝘦𝘥, 𝘸𝘩𝘦𝘯 𝘪𝘳𝘪𝘥𝘰𝘤𝘺𝘤𝘭𝘪𝘵𝘪𝘴 𝘱𝘳𝘰𝘣𝘭𝘦𝘮 𝘢𝘳𝘦 𝘱𝘳𝘦𝘴𝘦𝘯𝘵.
(𝘊) ʙᴏᴀᴛ ᴏʀ ʜᴀᴍᴍᴏᴄᴋ 𝘴ʜᴀᴘᴇᴅ :- 𝘞𝘩𝘦𝘯 𝘷𝘪𝘵𝘳𝘪𝘰𝘶𝘴 𝘭𝘰𝘴𝘴 𝘥𝘶𝘳𝘪𝘯𝘨 𝘤𝘢𝘵𝘢𝘳𝘢𝘤𝘵 𝘴𝘶𝘳𝘨𝘦𝘳𝘺, 𝘵𝘩𝘦𝘯 𝘵𝘩𝘦 𝘱𝘶𝘱𝘪𝘭 𝘣𝘦𝘤𝘰𝘮𝘦 𝘉𝘰𝘢𝘵 𝘰𝘳 𝘩𝘢𝘮𝘮𝘰𝘤𝘬 𝘴𝘩𝘢𝘱𝘦𝘥.
(𝘋) ᴘᴇᴀʀ 𝘴ʜᴀᴘᴇᴅ ᴀɴᴅ ᴜɴᴅʀᴀᴡɴ ᴘᴜᴘɪʟ :- 𝘐𝘯𝘤𝘢𝘳𝘤𝘦𝘳𝘢𝘵𝘪𝘰𝘯 𝘰𝘧 𝘪𝘳𝘪𝘴 𝘸𝘪𝘵𝘩 𝘤𝘰𝘳𝘯𝘦𝘢𝘭 𝘸𝘰𝘶𝘯𝘥.
(𝘌) ғᴇ𝘴ᴛᴏᴏɴᴇᴅ ᴘᴜᴘɪʟ :- 𝘐𝘳𝘪𝘥𝘰𝘤𝘺𝘤𝘭𝘪𝘵𝘪𝘴 (𝘢𝘤𝘶𝘵𝘦 𝘪𝘯𝘧𝘭𝘢𝘮𝘢𝘵𝘪𝘰𝘯 𝘰𝘧 𝘵𝘩𝘦 𝘐𝘳𝘪𝘴 𝘢𝘯𝘥 𝘤𝘪𝘭𝘪𝘢𝘳𝘺 𝘣𝘰𝘥𝘺) 𝘪𝘴 𝘵𝘩𝘦 𝘮𝘰𝘴𝘵 𝘤𝘰𝘮𝘮𝘰𝘯 𝘧𝘦𝘢𝘵𝘶𝘳𝘦𝘴 𝘰𝘧 𝘶𝘷𝘦𝘪𝘵𝘪𝘴.
(𝘍) ᴍɪᴅ – ᴅɪʟᴀᴛᴇᴅ & ᴏᴠᴀʟ ᴘᴜᴘɪʟ :- 𝘍𝘰𝘳 𝘵𝘩𝘦 𝘢𝘯𝘨𝘭𝘦 𝘤𝘭𝘰𝘴𝘶𝘳𝘦 𝘱𝘢𝘵𝘪𝘦𝘯𝘵 𝘨𝘭𝘢𝘶𝘤𝘰𝘮𝘢 𝘱𝘢𝘵𝘪𝘦𝘯𝘵𝘴 𝘱𝘶𝘱𝘪𝘭 .
(𝘎) ᴍɪᴅ ᴅɪʟᴀᴛᴇ ᴏᴠᴀʟ ᴀɴᴅ ɪɴғᴇʀ𝘴ᴏɴᴀʟ :- 𝘞𝘩𝘦𝘯 𝘵𝘩𝘦 𝘪𝘳𝘪𝘴 𝘪𝘴 𝘢𝘣𝘴𝘦𝘯𝘵 (𝘪𝘳𝘪𝘴 𝘤𝘰𝘭𝘰𝘣𝘰𝘮𝘢), 𝘵𝘩𝘦 𝘴𝘩𝘢𝘱𝘦 𝘰𝘧 𝘵𝘩𝘦 𝘱𝘶𝘱𝘪𝘭 𝘤𝘩𝘢𝘯𝘨𝘦 𝘢𝘯𝘥 𝘪𝘵 𝘤𝘰𝘯𝘷𝘦𝘳𝘵 𝘪𝘯𝘵𝘰 𝘢 𝘰𝘷𝘦𝘳 𝘴𝘩𝘢𝘱𝘦.
Key hole appeance- After optical iridectomy key hole apperance are seen in the pupil.
𝘝𝘢𝘳𝘪𝘰𝘶𝘴 𝘤𝘰𝘭𝘰𝘶𝘳 𝘳𝘦𝘧𝘭𝘦𝘹 𝘰𝘧 𝘵𝘩𝘦 𝘗𝘶𝘱𝘪𝘭𝘭𝘢𝘳𝘺 𝘢𝘳𝘦𝘢
(1) ᴊᴇᴛ ʙʟᴀᴄᴋ ᴘᴜᴘɪʟʟᴀʀʏ ʀᴇғʟᴇx :- For the aphakic eye the reflection of the pupil is jet black colour.
(2) ᴡʜɪᴛᴇ ᴘᴜᴘɪʟʟᴀʀʏ ʀᴇғʟᴇx :- White pupillary reflex are seen in the cataract eye.
(3) ɢʟᴀsʏ ᴘᴜᴘɪʟʟᴀʀʏ ʀᴇғʟᴇx :- For pseudophekic eye glasy pupillary reflex are visible.
(4) ᴀᴍᴀᴜʀᴀᴛɪᴄ ᴄᴀᴛ’s ᴇʏᴇ ʀᴇғʟᴇx :- If the Retiono blastoma, eongenital cataract, PHPV, Endopthalmitis, coloboma of Choroid like these type of problem present then the Amauratic cat’s eye reflex are visible.
𝙋𝙐𝙋𝙄𝙇𝙇𝘼𝙍𝙔 𝙇𝙄𝙂𝙃𝙏 𝙍𝙀𝙁𝙇𝙀𝙓
In this topic, I will dicsuss —
~~Pupillary Light Reflex Pathway.
~~How To Localize The Site Of Lesion In Cases Of Abnormal Pupillary Reflex.
So I will start with the very basics.
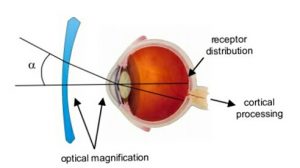
This is the diagram of the eye. This circular brown structure is the Iris and this round gap in the center of the Iris is known as the Pupil.
The normal size of the Pupil ranges from 2-4 mm in diameter. Light enters our eye through the Pupil.
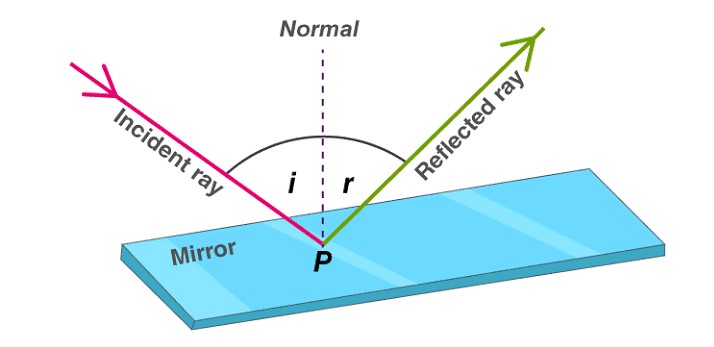
Now, when bright light is shone on the Pupil, the Pupil responds by decreasing in size. This is known as “Constriction of the Pupil” and this constriction of the Pupil in response to light stimulus is known as “Pupillary light reflex”.
Pupillary light reflex can be a Direct light reflex or it can be an Indirect light reflex which is also known as Consensual light reflex.
𝘋𝘌𝘙𝘌𝘊𝘛 𝘓𝘐𝘎𝘏𝘛 𝘙𝘌𝘍𝘓𝘌𝘟
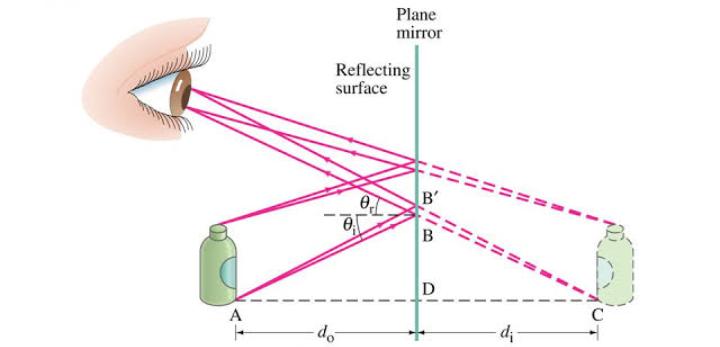
Direct light reflex is when constriction of the Pupil is seen in response to light shone in the 𝘚𝘢𝘮𝘦 𝘦𝘺𝘦, that is the Ipsilateral eye.
For example, if this the right eye of the patient and we shine light in this right eye & in response we see the Pupil of the right eye constricting, it is known as Direct light reflex because the response is occurring in the same eye that is receiving the stimulus.
𝘊𝘖𝘕𝘚𝘌𝘕𝘚𝘜𝘈𝘓 / 𝘐𝘕𝘋𝘐𝘙𝘌𝘊𝘛 𝘓𝘐𝘎𝘏𝘛 𝘙𝘌𝘍𝘓𝘌𝘟
The other reflex is the consensual light 𝘳𝘦𝘧𝘭𝘦𝘹. Consensual light reflex when the light stimulus is given to one eye but the response to that stimulus is seen in the opposite eye that is the Contralateral eye.
So, again in this patient, when we show light in the right eye, we will see constriction of the Pupil in the opposite eye that is the left eye. So this constriction of Pupil that occurs in response to light stimulus given in the contralateral eye is known as Consensual light reflex.
Both of these responses that is the direct light reflex as well as the consensual light reflex they occur simultaneously that is they occur together at the same time. So, if we shine light in the right eye, we will see both pupils constricting together, which means that the right eye will show direct light reflex and the left eye will show consensual light reflex and both of these reflexes are seen in response to the same light stimulus that was given in the right eye.
ᴘʀᴏᴄᴇᴅᴜʀᴇ
So how do you perform pupillary light reflex test?
First of all, it should be done in a semi dark room. ‘Semi dark’ so that you are able to observe the response in the contralateral eye. So we ask the patient to fixate on a distant object . If the patient fixate on a near object, the near reflex pathway will get activated which will cause pupillary constriction.
So we want to eliminate any cause of pupillary constriction when we are checking the pupillary light reflex pathway.
So we first observe the position, size and shape of the pupil in each eye. Then we shine the torch in one eye and we observe the response of the pupil in the same eye. This is the Direct light reflex. Then again we shine light in the same eye but this time we observe the response in the opposite eye. That is the contralateral eye & this is the consensual light reflex. And then we repeat the procedure on the other eye to check the direct & the consensual light reflex to light stimulus given on the opposite side.
ɴᴏᴍᴇɴᴄʟᴀᴛᴜʀᴇ
Before proceeding further, we need to be absolutely clear about certain terminologies. Suppose in a patient, light is shone in the left eye and both pupils constrict, we document it as left direct light reflex present and light consensual light reflex present. So the nomenclature is with respect to the eye which is responding to the stimulus and not with respect to the eye which is receiving the stimulus.
Suppose in a patient’s case sheet it written that right direct light reflex and right consensual light reflex is present, it means that the right eye constricts to light stimulus given to the right eye which is the direct reflex and it also constricts to light stimulus given in the left eye which is the consensual reflex. So, right consensual reflex doesn’t mean that light stimulus is given in the right eye. It means that the pupillary response to light stimulus is seen in the right eye.
I hope this is clear for you now.
ɪʀɪs ᴍᴜsᴄᴜʟᴀᴛᴜʀᴇ
Now the storma of the iris has 2 muscles. The “Sphincter pupillae” and the “Dilator pupillae”.
sᴘʜɪɴᴄᴛᴇʀ ᴘᴜᴘɪʟʟᴀᴇ
Sphincter pupillae muscle is circulary arranged at the border of the pupil. So when the sphincter pupillae contracts it leads to constriction of the pupil & this occurs via the parasympathetic pathway. This constriction of the pupil is known as Miosis.
ᴅɪʟᴀᴛᴏʀ ᴘᴜᴘɪʟʟᴀᴇ
The dilator pupillae muscle is inserted at the root of the iris and from there it extends radially to 2 mm from the pupillary margin. So, the dilator pupillae muscle gets activated by the dark reflex pathway which is a Sympathetic pathway and this results in dilatation of the pupil & dilatation of the pupil is known as Mydriasis.
Now the diameter of the pupil the result of the balance between these two antagonistic muscles of the iris that is the sphincter pupillae and the dilator pupillae of the iris.
Since in this topic I am talking about the light reflex pathway I will be restricting ourselves to only parasympathetic pathway that results in constriction of the pupil via the sphincter pupillae muscle.
ᴘᴜᴘɪʟʟᴀʀʏ ʟɪɢʜᴛ ʀᴇғʟᴇx
So, Pupillary light reflex pathway is a parasympathetic pathway with an afferent limb and an efferent limb.
“Afferent limb” means that Sensory stimulus is carried to the brain via this route.
“Efferent limb” means that this route carries signals from the brain to the effector organ, that is the sphincter pupillae muscle in this case.
ᴘᴜᴘɪʟʟᴀʀʏ ʟɪɢʜᴛ ʀᴇғʟᴇx ᴘᴀᴛʜᴡᴀʏ
As we all know, Light enters the eye through pupil. Then it falls on the Retina of the eye. From the retinal gangionic cells, the information is carried by the the optic nerve. Optic nerve is the second cranial nerve. Optic nerve carries impulses from the nasal half of the retina and the temporal half of the retina. So the fibers here that are arranged laterally represent the temporal fibers and the fibers that are present medially represent the nasal fibers. Then the optic nerve reaches the optic chiasma. Optic chiasma is located just above the Pituitary gland. At the optic chiasma, decussation of these nerve fibers takes place. Now what is the meaning of decussation?
~ Decussation means that the nerve fibers from one side cross over to the opposite side. So the fibers that were carrying signals from the nasal half of Retina on the right side cross over to the left side but the fibers that were carrying from the temporal half of the Retina do not cross. They continue to travel along the same side that is along the right side. It is seen that the ratio of crossed to uncrossed fibers is approx 53:47 which means that more fibers cross over than those that stay on the same side. This decussation occurs on both the sides. So nasal fibers of the right eye cross over to the left side and then they continue with the temporal fibers of the left eye. While the nasal fibers of the left eye cross over to the right side and then they continue with the temporal fibers of the right eye. They continue as optic tracts. Thus each optic tract contains ipsilateral temporal fibers and contralateral nasal fibers. Now the pathway that we are discussing here is the pupillary light reflex pathway. But we also know that it is the same optic nerve that carries signals to the optical cortex of the brain via the visual pathway and this is how image processing takes place and I am able to see things. This means that the optic nerve carries afferents for vision as well as for pupillary constriction. Now how are these two pathways separate from each other?
So most of the nerve fibers that are carried by the optic tracts synapse in the lateral geniculate body. Lateral geniculate body is located in the thalamus and from the lateral geniculate body, the signals are carried to the visual centre which is located in the occipital lobe of the brain. So this is the visual pathway in brief. However a small number of these fibers- they don’t go to the lateral geniculate body. They exit from the optic tract and instead of going to the lateral geniculate body, they go to the pretectal nucleus. Pretectal nucleus is located in the midbrain at the level of the superior colliculus.