Convergence insufficiency has an excellent prognosis in the majority of cases.children are treated when fusional vergence are poor and the patient is showing signs of becoming exotropic . Adults with this condition receive treatment only in the presence of symptoms. Treatment of convergence insufficiency includes : Optical treatment, orthoptic treatment,prismotherapy and surgery.
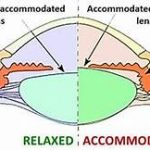
- Optical Treatment: Proper refraction should be carried out and the correct glasses should be prescribed for any associated refractive error. Myopes are given full correction and hypermetropes undercorrection to stimulate their accommodation which will simultaneously stimulate convergence. In adults above the age of 40 years, proper presbyopic correction should also be done.
- Orthoptic treatment:
Aim of orthoptics exercise is to improve the binocular convergence and to increase the amplitude of fusional convergence. ‘vision therapy ‘ . The term used for orthoptic treatment includes:
- Conventional or non computerised exercise for :
- In-office vision therapy, and
- Home vision therapy
- Computerised orthoptic exercise for:
- In-office vision therapy
- Home vision therapy
Conventional or non computerised exercises
Orthoptic treatment for convergence insufficiency is by and large same as for Exophoria and includes the following exercises:
- Exercises to improve near point of convergence:
i.Advancement exercise: It is a good convergence exercise which can be done at near. In it , patient is asked to hold a target (preferably a small detailed picture or fine print) away from his or her nose where fusion is possible. He or she is asked to slowly advance the target towards his or her nose until diplopia is appreciated. At this point, he or she is asked to stop and try to stop and try to converge more and thus to unite the two images again. If he or she cannot do this, he or she should move the target back to a small distance to get single vision and then try to bring it closer again. This should be repeated until the patient can converge to his or her nose or at least reasonably close to it.
- Jump convergence exercise: Jump convergence is more elaborate and more effective from of the ‘ picture – to – nose’ convergence exercise. It trains the patient to achieve bifoveal single vision following a sudden change in the convergence requirement. This is usually possible only after convergence has been improved to some extent by other exercises and therefore,is not used before the fourth week of convergence training, depending upon the progress. This exercise may carried out by any of the following methods:
- The simplest way of doing this exercise is to have two fixation targets, one fixed Target at a distance of about 6 metres and other movable target held about 33 cm infront of the eyes.
- Another way of performing jump convergence exercise is the use of prism
- Jump convergence exercise can also be performed with synoptophore.
- Exercises to increase amplitude of fusional convergence:
- Convergence exercises with prism: It is similar to that described for Exophoria, except that in it, prism are placed base-out in front of the eyes. While the patient is performing this exercise, the opthoptist should watch the patients eyes to make certain that he or she is converging and has not diverged and suppressed.
- Convergence exercises using synoptophore: It is performed as described for Exophoria, except that in it, the instrument arms are slowly converged , beginning at an angle at which patient can fuse the picture.
- Exercise using convergence card : convergence card consists of dots on either side, so also known as physiologic dot card . On one side of the card, dots are coloured red and on the other side blue. Dots identical in size of the card and these are of three sizes – large, medium and small.
- Physiologic diplopia exercise using stereogram in the uncrossed position.
- Convergence exercise using diploscope.
- Training of voluntary convergence:
It is very helpful, if the patient is intelligent an co-operative. It aims at developing the control of the position of the eyes. Patient is made to understand physiological diplopia which he or she practices.
- Relaxation exercises:
Relaxation using relative negative convergence may be carried out after the treatment by any of the following methods:
- Stereogram in crossed position.
- Divergence with prisms.
- Synoptophore exercises.
Criteria for good orthoptic management
- Patient should be symptom free
- There should be good binocular convergence.
- Voluntary convergence should be possible easily.
- Patient should have good fusional reserves.
- Prismotherapy
When all the exhaustive orthoptic exercises fail, then prismotherapy may be tried to relieve symptoms.
- Base in prism reading glasses or bifocals with prism In the lower segment are useful as relieving prisms.
- Relieving prisms and bifocals in young age should be avoided.
- Surgical treatment
As a last resort, when all other measures fail especially when convergence insufficiency is associated with a large Exophoria at near vision, medial rectus muscle resection can be performed in one or both eyes. In some cases, Exophoria at near fixation tends to recur.
Convergence insufficiency treatment trial
Convergence insufficiency treatment trial (CITT) was conducted to compare three forms of vision therapy with office -based placebo therapy:
- Office -based vision therapy with a trained therapist along with home reinforcement.
- Home-based pencil push-up therapy.
- Home- based computer vision therapy and pencil push-ups.
- Office -based placebo therapy.
CITT concluded that office -based vision therapy with a trained therapist plus at- home reinforcement was most effective in treating CI in children 9 to 17 years old.