Myopia is the most prevalent refractive error in the World and it’s incidence is increasing, along with conservative methods of treatment, various surgical procedure have been proposed. The standard goal of treating nearsightedness is to improve vision by helping focus light on the retina through the use of corrective lenses or refractive surgery. Managing nearsightedness also includes regular monitoring for complications of the condition, including glaucoma, cataracts, retinal tears and detachments and damage to central retinal areas.
Treatment of Myopia:-
- Optical treatment of Myopia:- It constitutes prescription of applicable concave lenses, so that clear image is formed on the retina.
- Basic rule of correcting myopia:- Conversely to Hypermetropia, the minimum acceptance providing maximum vision should be prescribed in Myopia.
- Guidelines for correcting low degrees of Myopia up to -6D:-
- In children up to 3 years of age, guidelines for correcting myopia, as described in preferred practice pattern:-Paediatric eye evaluation, AAO etc.
- Myopia=
- Age<1year=-5.00 or more,
- Age1-2 years=-4.00 or more,
- Age2-3 years=-3.00 or more
- *In children above 3 years of age, Myopia should be fully corrected band instructed to use their glasses continually, both to avoid developing the habit of squinting and to improve developing a normal accommodation-convergence reflex. It must be impressed upon the patient that in the matter of near work, the glasses are not meant to improve the vision but to make one read at proper distance and to keep one’s eyes in proper relationship.
- *Never overcorrected Myopia:-
- Young Myopic patients will often set up more minus power in the manifest refraction than they need for best acuity because the additional minus enhances the contrast of the dark test letters on the light chart background. During the subjective refraction, to help prevent overcorrection, ask to patient if the letters are actually clearer and or if the letters are just darker and smaller.
- Adults:- Adults, younger than 30 years generally accept their full myopic correction. Those older than 30 years are not able to tolerate a full correction over 3D if they have never worn glasses before, as their ciliary muscles are not used to accommodate. So, some patients may be prescribed less than full correction with which the patient has by comfortable near vision, with resulting undercorrected distance vision. A patients should be asked that a full correction may be given in the future ,if desired.
- Guidelines for correcting high Myopia:- Irrespective of the age of the patient, full correction can rarely be tolerated in case of high Myopia (more than -10D). Generally an undercorrection to the tune of 1-3 D or even more may be required, depending upon the age of the patient and degree of Myopia. Undercorrection is always better to avoid the problem of near vision and that of minification of images.
- Modes of prescribing concave lenses:-These are Spectacles and contact lenses. Their advantages and disadvantages over each other are the same as described for hypermetropia. Contact lenses are particularly justified in cases of high Myopia as they avoid peripheral distortion and minification produced by strong concave spectacle lens. It is important that a myopic patient wearing a full contact lens correction needs more accommodation for near work as compared with a spectacle wearer. So, they develop presbyopia comparatively earlier.
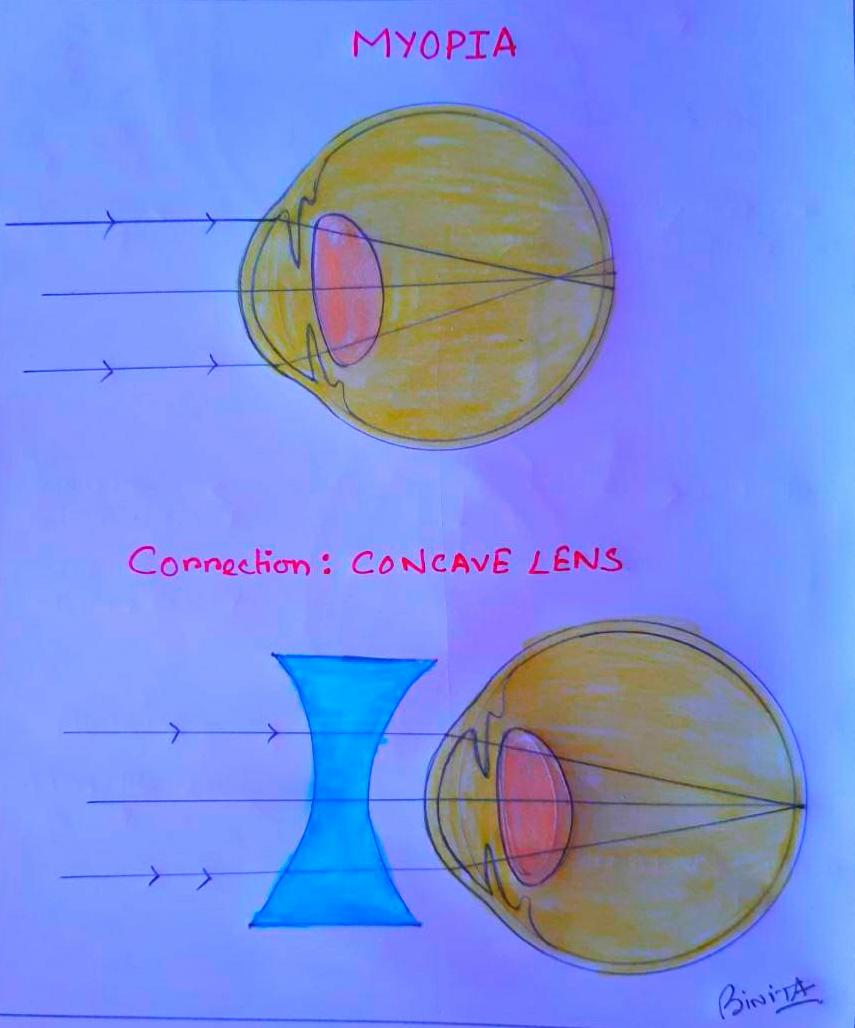
Refraction in a Myopic eye corrected with concave lens
- Surgical treatment of Myopia:-
- Refractive surgery for myopia:
- Keratorefractive Surgeries:-
- Incisional procedures
- Radial Keratotomy
- Lamellar Corneal refractive procedures
- Freeze Keratomileusis of Barraquer for Myopia (KMM)
- Nonfreeze Keratomileusis
- Keratomileusis in situ
- ALK
- Small incision lenticule extraction (SMILE)
- Corneoplastique
- laser ablation corneal refractive procedures
- Surface ablation corneal refractive procedures include:
- Photorefractive Keratectomy (PRK
- LASEK
- E-LASIK
- Intrastromal ablation corneal refractive procedures
- LASIK
- C-LASIK
- Intralase laser in situ Keratomileusis (iLASIK)
- LASIK Extra-LASIK + C3R
- Orthokeratology
- Intracorneal implants
- Intracorneal contact lenses
- Intrastromal corneal ring segments
- Gel injectable adjustable keratoplasty
- Lens-based procedures
- PRLs
- II) RLE
- Combined lens and cornea-based refractive procedures
- Bioptics
- Trioptics
- Combined lens and cornea-based refractive procedures
- Radial Keratotomy (RK):- It is a type of refractive surgery meant to correct myopia. RK, as today, refers to making deep( 90% corneal thickness)radial incisions in the peripheral part of cornea, leaving about 4mm central optical zone. These incisions on healing flatten the central cornea, thereby reducing its refractive power. It was the very first refractive surgical procedure, this procedure will help to reduce issues like nearsightedness. This is an obsolete procedure.
- Keratomileusis:- Keratomileusis or corneal reshaping is the surgical improvement of the refractive state of the cornea by surgically reshaping it. A lenticule is prepared from removal anterior part of the cornea and re-shaped. This is the most common form of refractive surgery. This is also an obsolete procedure.
- Clear lens Extraction:- Refractive lens exchange also known as CLE is a surgical procedure for vision correction that replaces the natural lens of the eye with an IOL. Extracapsular cataract extraction with posterior chamber intraocular lens (PCIOL) implantation may be a good choice in high Myopia. The lens may be clear without any cataractous change. The clear lens of the eye is removed and replaced with an IOL to change the focusing power of the eye. This procedure uses the same IOLs used in cataract surgery and it’s able to treat all types of visual disorders, including nearsightedness.
- LASIK:- It’s stand for laser in situ Keratomileusis, is a good Surgery that can correct vision in people who are nearsighted or farsighted, or who have Astigmatism. It’s one of many vision correction popular surgeries that work by reshaping the cornea, the clear front part of the eye, so that light focuses on the retina in the back of the eye. Here, the superficial corneal flap is lifted first, and then central corneal stromal bed is ablated by excimer laser to correct myopia. It is a very costly procedure.
- Preventive measures which may be useful include:-
- Therapeutic interventions reported to prevent progression of myopia are as follows:-
- Atropine even in low strength of 0.01% eye drops, instilled nightly are reported to slow down the progression of Myopia, by blocking the muscarinic receptors of sclera with minimum side effects. Mydriasis and cycloplegia, however, may be of some concern.
- 2% gel, applied twice a day, is also reported to prevent the Myopia progression.
- Preventive measures which may be useful include:-
- Therapeutic interventions reported to prevent progression of myopia are as follows :- Atropine even in low strength of 0.01% eye drops, instilled nightly are reported to slow down the progression of Myopia, by blocking the muscarinic receptors of sclera with minimum side effects. Mydriasis and cycloplegia, however, may be of some concern.
- Pirenzepine 2% gel, applied twice a day, is also reported to prevent the Myopia progression.
- General measures:- Empirically believed to affect the develop of myopia include balanced diet rich in vitamins and proteins, and early management of associated debilitating disease.
- Genetic Counselling :- As the pathological Myopia bhas a strong genetic basis, the hereditary transfer of disease may be decreased by advising against marriage between two individuals with progressive myopia. A parent with degenerative Myopia should be warned that any offspring may have same inability. To highly Myopic adults with degenerative changes should never, from the medical point of view ,have children.

4) Visual Hygiene:- It is very important in case of children like good nutritional diet, exercise, environment, proper position for reading in good illumination. Care needs to be taken for proper posture and adequate illumination during close work. It is most essential to avoid asthenopic symptoms.
5) Low-Vision aids:- These are indicated in patients of progressive myopia with advanced degenerative changes. where good vision can’t be acquired with Spectacles and contact lenses.
Prognosis:-
- In simple myopia, the prognosis is good. The error generally does not progress beyond 6-8 D and stabilizes by the age of 21years.
- In pathological Myopia ,visual prognosis is always guarded. In many cases, the possibility of progressive visual loss due to degenerative changes and danger of complications such as retinal detachment.