EYE AND IT’S REFRACTIVE MEDIAS:-
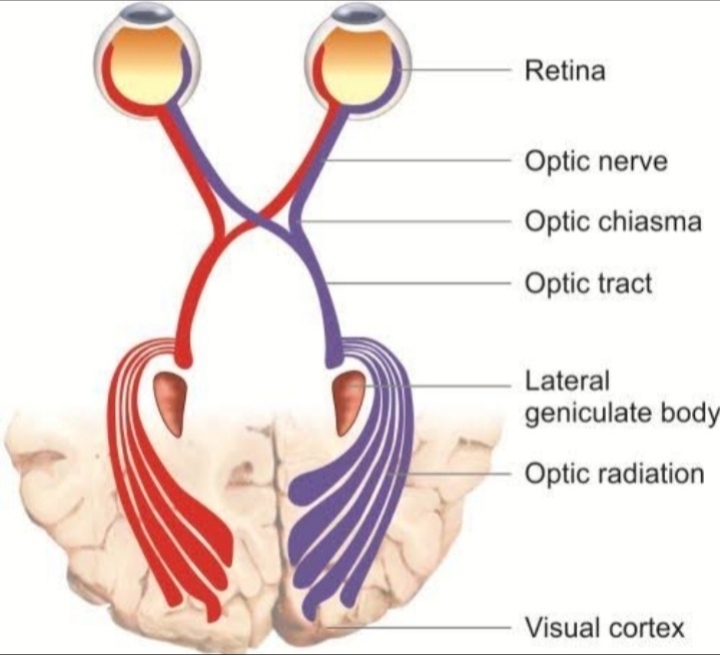
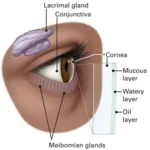
The Eye of a human body acts as an imaginary window from where one can visualise the beauty of this materialistic world. Eye is one of the most important part of our visual pathway as well as it is among one of the sense organ. Our visual pathway consist of contralateral and ipsilateral optic nerve fibres of each eye, optic nerve, optic chiasma, optic tract, lateral geniculate bodies, Optic radiations and visual cortex. From anterior to posterior there are different anatomical structures of eye. Starting from eyelids, pre corneal tear film, cornea, aqueous humour, conjunctiva, tenon’s capsule, sclera, uvea(iris, ciliary body, choroid), zonules, crystalline lens, ora serata, vitreous humour, retina, macula, fovea centralis optic
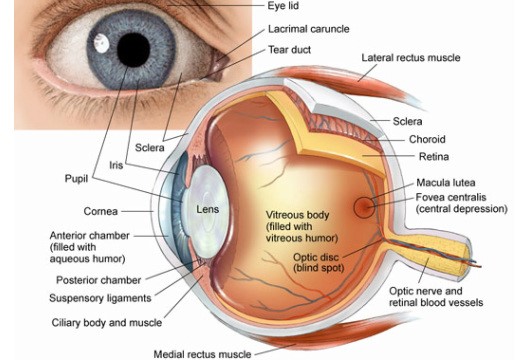
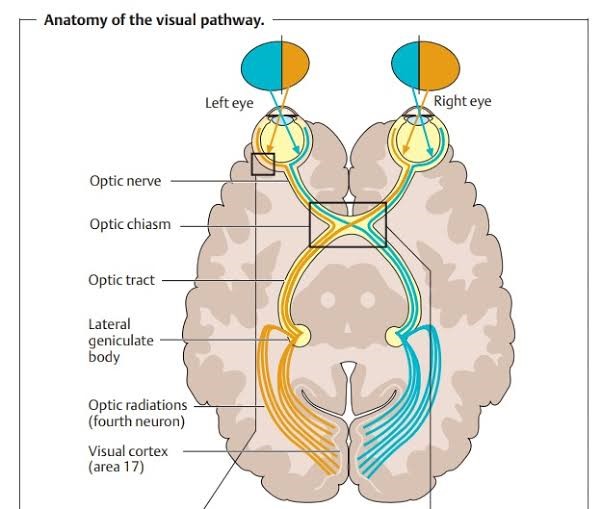
At first the light enters to our eye via different refractive medias and fall on retina, then retina sends electrical impulses via optic nerve and visual pathway to our brain, then our brain processes that and after that we see.
The refractive medias of our eye plays very important role in our vision or the ability to see.
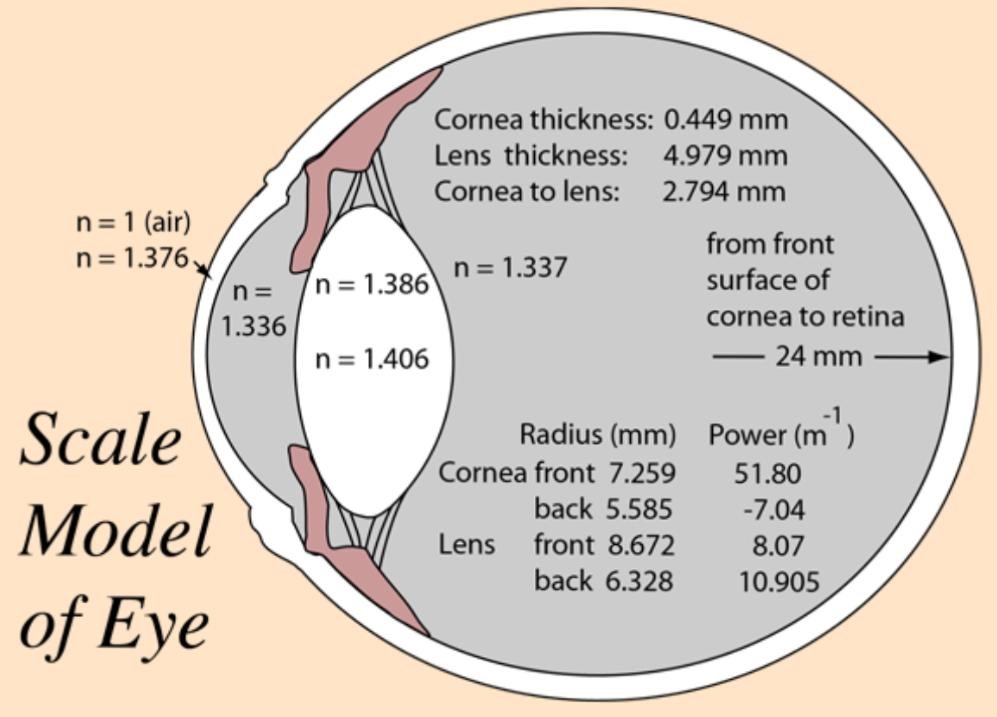
The refractive media of eyes are:-
- Pre corneal tear film
- Cornea
- Aqueous humour
- Crystalline lens
- Vitreous humour
The refractive medias refract the light and allows it to reach the retina. Any opacities or disturbance to this refractive medias cause diminution of vision.
WHAT ARE CATOPTRIC IMAGES? :-
CATOPTRIC comes from the Greek word “katoptrikos” or “katoptron” which means specular or mirror. Basically it deals with the properties of mirror i.e; reflection. It is also known as Purkinje images or Purkinjesanson images after the name of Jan Evangelista Purkyne, a Czech anatomist, (year1787 to 1869) and also the name of Louis Joseph Sanson, a French physician,(year of 1790 to 1841).
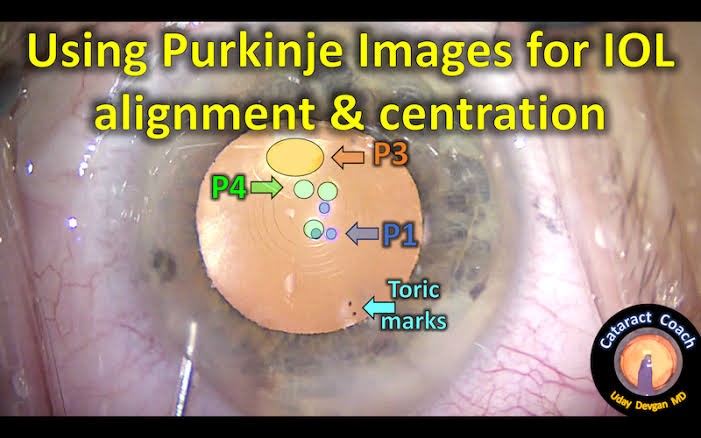
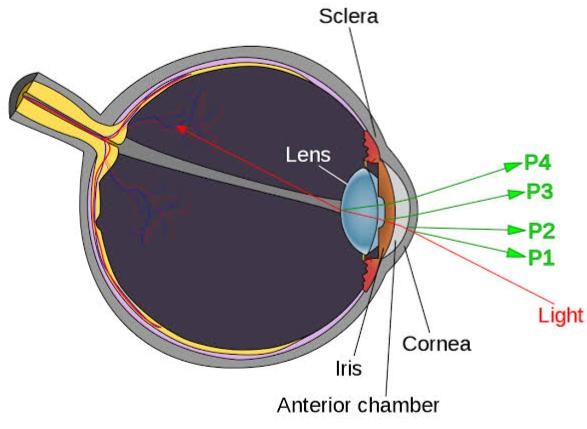
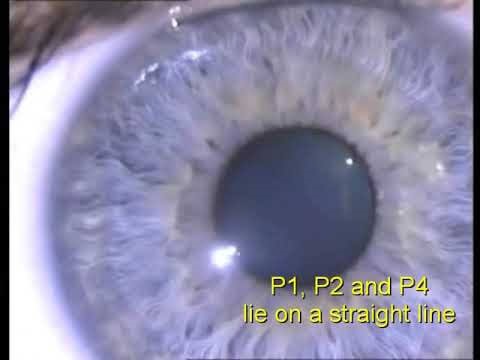
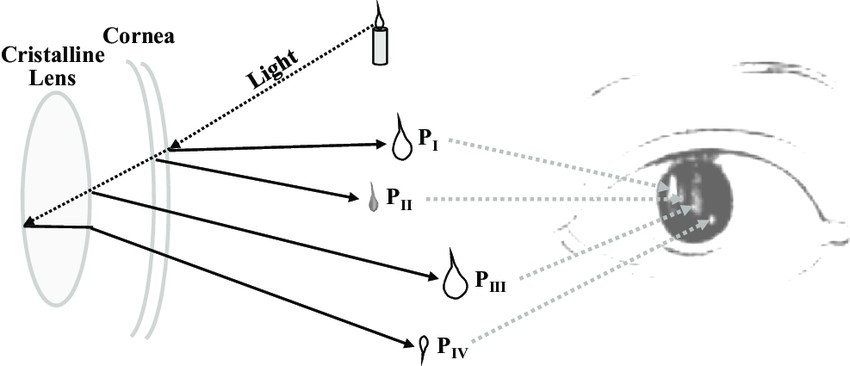
These are the images that form inside our eye. There are all total 4 Purkinjesanson images coming from different refracting interface, P1, P2, P3, P4.
P1(First Purkinje image): It is coming from the anterior surface of cornea. It is virtual and erect because anterior surface of cornea act as a convex lens.
P2(Second Purkinje image): It is coming from the posterior surface of cornea. It is virtual and erect because posterior surface of cornea act as convex lens.
P3(Third Purkinje image): It is coming from anterior surface of crystalline lens and it is virtual and erect because anterior surface of crystalline lens act as convex lens.
P4(Fourth Purkinje image): It is coming from posterior surface of crystalline lens and it is real and inverted because posterior surface of lens acts as concave mirror.
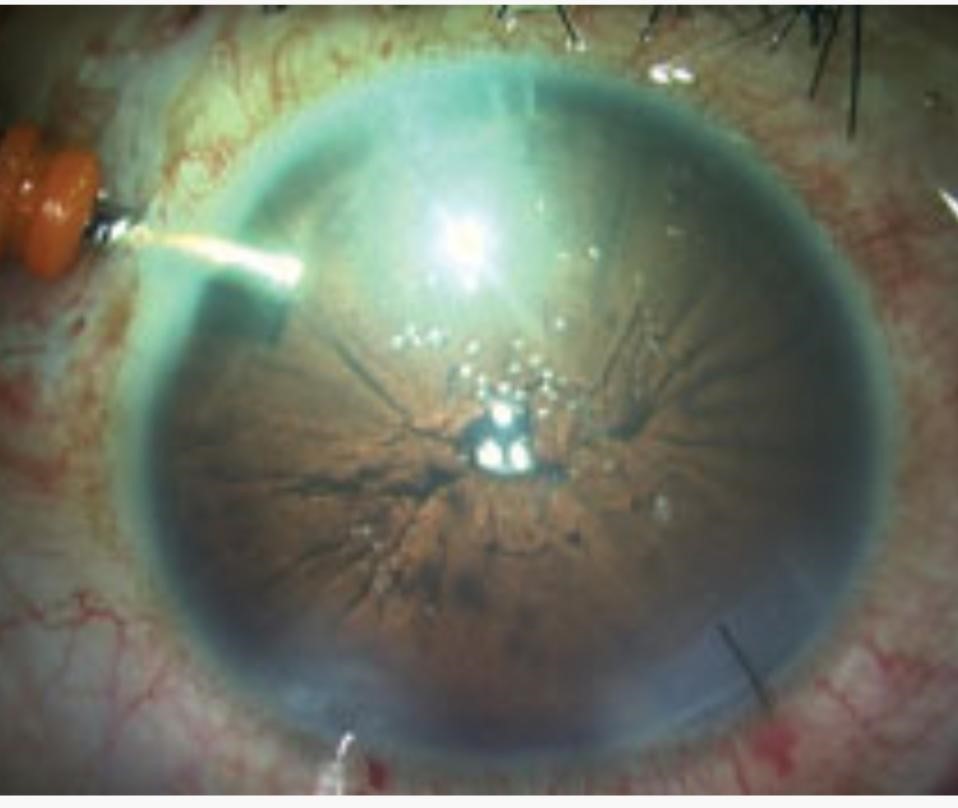
Purkinje images in Pseudophakia, aphakia, Immature Senile Cataract (IMSC) and Mature Senile Cataract (MSC):-
- Pseudophakia is a condition which means surgical removal of crystalline lens and replacing it with IOL due to any pathology (cataract) or trauma. Here all the 4 catoptric images are present. The 3rd and 4th image is formed by anterior and posterior surface of IOL. The shiny reflex of IOL that we used to see to confirm the Pseudophakia by torch light is nothing but the 3rd image which is very bright and large occurs due to the material of IOL.
- Aphakia which literally means no lens in the patellar fossa in the posterior chamber. Here only 1st and 2nd images are formed from anterior and posterior surface of cornea.
- IMSC is a type of cataract in which due to cortical hydration of lens, it becomes partially opaque. Here all the 4 Purkinjesanson images will be present but comparatively 4th image will be dull or blurred.
- MSC is the progressive stage of IMSC, here the lens become fully opaque and only the 4th image is either extremely blurred or absent due to the fully opacification of lens.
CLINICAL SIGNIFICANCE OF CATOPTRIC IMAGES
- Keratometry is done to measure the radius of curvature and dioptric power of cornea in vertical and horizontal meridian as K1 and K2 and it is based on 1st Purkinje image. The anterior surface of cornea acts as a specular reflector and a ring of known size is placed in front of cornea, the virtual reflection of the ring below it’s surface is the 1st Purkinje image.
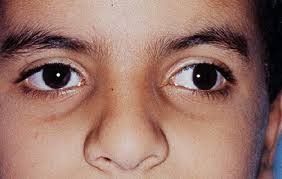
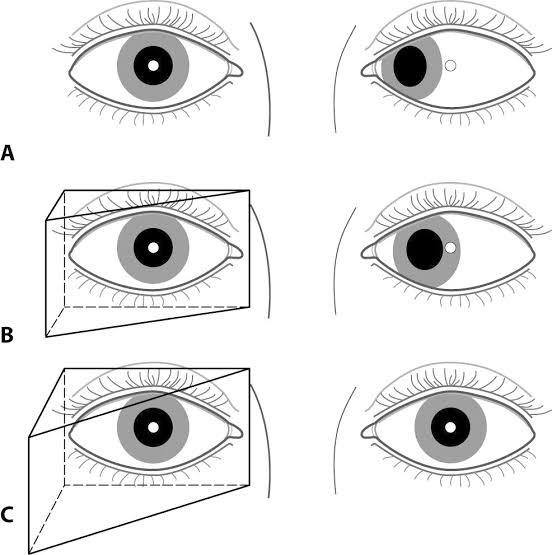
- Hirschberg corneal reflex test is based of 1st Purkinje image. It the rough estimation for measurement of angle of deviation and angle Kappa in tropias. Here from 33cm a light is shone and patients are asked to fixate at the light with both the eyes, the it’s been checked whether the 1st Purkinje image is at the centre of pupil or not. If the 1st image form on temporal side of pupil then the patient may have esotropia and if it form on nasal side, then the patient may have exptropia.
- Krimsky’s corneal reflex test is also based on 1st Purkinje image. It is same like Hirschberg corneal reflex test but here prisms are used until the 1st Purkinje image confident with pupillary margin.
- 3rd and 4th Purkinje image is used to check the lens subluxation, dislocation, Pseudophakia, aphakia, IMSC and MSC.
- The 3rd and 4th image is also used for IOL centration and correct alignment in cataract extraction.
- Pinhole Pupilloplasty is a surgical technique which is done to patients with higher spherical aberration. Here surgically the normal pupil is converted to miotic or pinhole pupil. The Purkinje image is used here to check whether the crafted miotic pupil is aligned with visual axis or not.
- Purkinje images are also used in 3D direction and tracking the movement of eyeball in different gazes.
Brightness of Purkinje images:-
P1 is the brightest image among all then P3 and P4 having almost same brightness and then P2 having dimmest light.
As per Fresnel equation –
“Intensity or the Brightness = (n1 – n) 2/ (n1 + n) 2”
Wherein the n1 and then in the Fresnel’s equation refers to the “refractive indices” after and before a thing reflects the surface.