VISION ASSESSMENT FOR PAEDIATRIC
Visual acuity :- It is the ability or power of the eye by which objects are distinguished one from the other. It also measures the smallest retinal image, formed at the foveal region which can be appreciated regarding shape and size. Visual acuity is tested for distant and near objects called distant vision and near vision. Each eye is to be tested separately without spectacle with spectacle and with pinhole for distant vision only. Assessment of visual acuity – Assessment of visual acuity by following methods such as dot visual acuity test, catford drum test, Boek candy bead test, STYCAR
graded ball’s test, Schwarting metronome test , snellen’s E chart, Landolt’s C
chart , Sjogren’s hand test , Arrows test, etc.
Assessment of visual acuity from birth up to 3 months :- At birth , visual is 1 feet but while time changing it improves day to day . When vision 1/60 the child is only able to see close objects . Upto 3 months visual acuity is assessed by following methods –
Eye popping test – Eye popping test is done by light , in this case the eye popping reflex indicates at least the baby’s ability to detect changes in the room illumination. When the room lights are suddenly dimmed the baby upper eyelids should pop open wide for a moment when the lights are brought up back.
Blink Reflex test – In this test bright reflex is shown then see normal infant should respond by blinking.
Vestibulo Ocular reflex – The vestibulo ocular reflex is generally tested by turning the new born ‘s head on his /her long axis and observing for the doll’s eyes response.
Assessment of visual acuity from 3 to 6 months –
Bruckner’s red reflex test – Bruckner’s red reflex test used to detect strabismus , anisometropia , cataracts and other media opacities in young children and infants . Direct ophthalmoscope is focused from about one meter away and observe the red reflex.
Fixation behaviour test – It is the ability to fix and follow the face of the examiner , toys or interesting object. The test is done first with both eyes open followed by monocular testing by occluding the other eye by hand.
Menace Reflex test – in this test reflex closure of the eyes on the approach of an object is usually present after the age of 5 months,
if vision is normal.
Assessment of visual acuity from 6 to 12 months –
Preferential looking test – The preferential looking test is a visual assessment method primarily used for infants . In this test ,the examiner presents a series of patterned and plain stimuli ,
such as black and white stripes or checkerboards, to the patient.
Cat ford drum test – In this test visual acuity test is useful in infants and children less than 2 years of age. In this test , the child is made to observe an oscillating drum with black dots of
varying sizes. Assessment of Visual acuity from 1 to 3 years –
Marble game test – This test can be used to estimate visual function , in this test child is asked to place to marbles in the holes of a card or in a box . This test is not measure the
visual acuity but compare the visual function of each eye .
Sheridan ball test – in this test a series of styrofoam balls of progressively smaller sizes. Once records the smallest ball that the infant can fixate and follow at a distance of 10 ft.
Worth Ivory ball test :- ivory ball are rolled on the floor infront of the child and asked to retrieve each ball . Visual acuity is noted in this process
Coin test – in this test two faces different sizes are held at different distance and child is asked to identify each faces . Assessment of visual acuity in preschool children and school going children –
Pre school children –
Landlot’s C test – In this test landlot’s C are presented with the optotype 3,6,9,12o’ clock.
Broken wheel test – in this test a pair of cars in progressively smaller sizes, one of which has a wheel cut across, like landlot’s c test .
Illiterate E test – in this test the child is given a cutout of an E and asked to match this E with isolated Es of varying sizes.
School going children and adults –
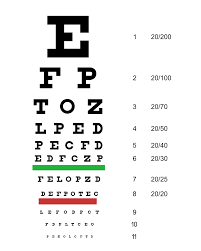
Snellen’s test types – in this test distant vision has recorded . It consists of a series of black capital letters on a white board, arranged in lines , each are progressively diminishing in the size.
LogMAR visual acuity test – A logMAR chart comprises rows of letters and has equal number of letters in each line. It is used at a distance of 4 m.