An exam that uses a magnifying lens and a light to check the posterior segment of the eye, including the retina and optic nerve is called Fundus Examination.
It is a diagnostic procedure that employs the use of mydriatic drugs to Dilate the pupil in order to obtain a better view of the fundus.
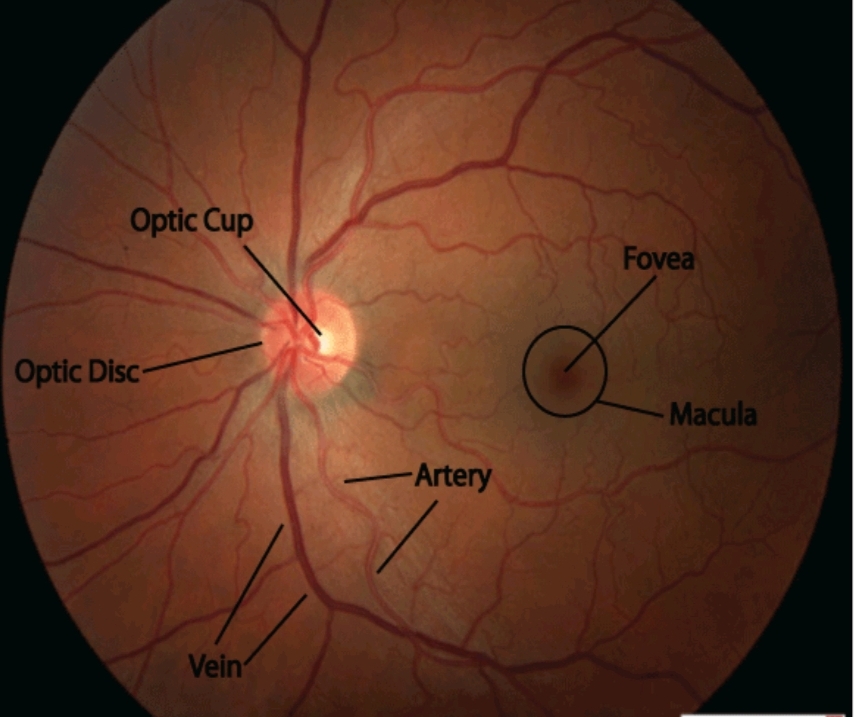
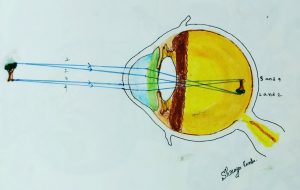
Once the pupil is dilated, the examiner uses an Ophthalmoscope to view the posterior segment, Allowing assessment of the retina, Optic nerve head, blood vessels and other features.
Methods:
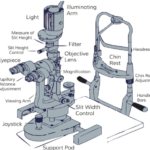
i. Indirect Slit lamp Biomicroscopy:- Fundus Biomicroscopy with the slit lamp is done by using the 90D Lens. Effects of using different lens powers on examination condition like position of the slit lamp, visible field size and magnification were evaluated.
ii. Direct Ophthalmoscopy- It is a hand-held device that shows an unreversed or upright image with 15x magnification. The direct ophthalmoscope is used to inspect the fundus. Opacities and macular degeneration of the lens can be detected through direct ophthalmoscopy.
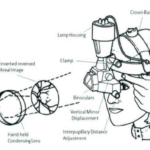
iii. Indirect Ophthalmoscopy- It is a device that produces a reversed or inverted image with 2 to 5x magnification. An indirect ophthalmoscope has a specifically designed objective lens(+20D) and has proven to be an exceptionally valuable device for the treatment and diagnosis of detachments, holes, and many diseases in the posterior segment of the eye . For an Indirect ophthalmoscopy, the patient’s pupils must be completely dilated by using Mydriatic Eye Drops.
Instruments:
Some instruments are needed for Fundus Examination.
They are: i. Direct Ophthalmoscope- It is a handheld device which is used for Fundus Examination by monocularly. It produces an unreversed fundus image with 15x magnification.
ii. Indirect Ophthalmoscope- It is a device worn on the examiner’s head and fundus is viewed through a condensing lens which produces an inverted fundus image with 2 to 5x magnification.
iii. Slit Lamp- Slit lamp examination is a standard diagnostic procedure. It is also known as Biomicroscopy.
iv. 20D Lens- It is a hand-held lens which is used during indirect Ophthalmoscopy
v.90D Lens- It is also a hand-held lens which is used during direct Ophthalmoscopy,
vi. Hruby Lens- It is a Plano-concave form of lens with refractive power of -55D and designed to be used within 9–11mm in front of the patient’s eye.
It has also the advantages of producing an unreversed, real image of the internal retina that is correctly orientated. vi. Scleral indenter- It is an instrument which is used to inspect the peripheral part of the retina, Ora serrata, pars plana at alternative angles in dynamic nature.
Procedures:
First we need to check the patient in Slit lamp Bio Microscope.
Then we need to dilate the patient by using Mydriatic (Parasympatholytic) eye drops like Tropicamide.
Before instilling the drop we need to explain to the patient about the pro’s and con’s of dilation.
After Fully dilation tell the patient to focus on a distant object.
Then Look at the right fundus with your right eye and the left fundus with your Left eye.
Ophthalmoscope should be close to your eyes. Your head and the Ophthalmoscope scope should move together
Then Set the lens opening at +8 to +10 diopters. With the ophthalmoscope 12-15 inches from the patient’s eye, check for the red reflex and for opacities in the lens or aqueous.
While adjusting the diopter setting, approach the patient more closely and systematically inspect the disc, noting the colour, shape, margins and cup-to-disc ratio.
Then monitor the vessels, noting obstruction, calibre and arterial/venous ratio.
Note the presence of arterial/venous nicking and arterial light reflex.
Check the background by monitoring for pigmentation, haemorrhages and hard or soft exudates.
Next, try to identify the macula.
Diagnosis: Fundus Examination is a must needed examination to detect:
i. Measuring CDR.
ii. Ocular Manifestations of Hypertension & Diabetes mellitus.
iii. Vitreo-Retinal Problems like PVD, Lattice Degeneration, HST, RD, CD, ARMD, etc.
iv. Glaucoma, Optic nerve head Atrophy etc.
v. It can also show drusen, abnormal bleeding, scar tissue, and areas of atrophy.
vi. Findings of papilledema.Procedure of Fundus Examination
Read more Articel: