What is Optometry?
According to the World Council of Optometry (WCO), Optometry is a healthcare profession that is concerned with the examination, diagnosis, treatment, and management of disorders and conditions of the visual system, the eye, and associated structures. Optometrists are primary healthcare practitioners of the eye and visual system who provide comprehensive eye and vision care, which includes:
– Refractive correction and vision therapy.
– Detection and management of eye diseases.
– Prescription of medications and other treatments.
– Counseling on visual health and wellness.
The Role of Optometry in Managing Diabetic Retinopathy: A Comprehensive Guide.
Diabetic retinopathy (DR) is a leading cause of vision loss worldwide, affecting millions of
people with diabetes. As the prevalence of diabetes continues to rise, the importance of
optometry in managing DR cannot be overstated. Optometrists play a vital role in detecting,
monitoring, and treating DR, working closely with other healthcare professionals to prevent
vision loss and improve patient outcomes. In this article, we will delve into the role of
optometry in managing DR, exploring the latest research, diagnostic techniques, and treatment
options.
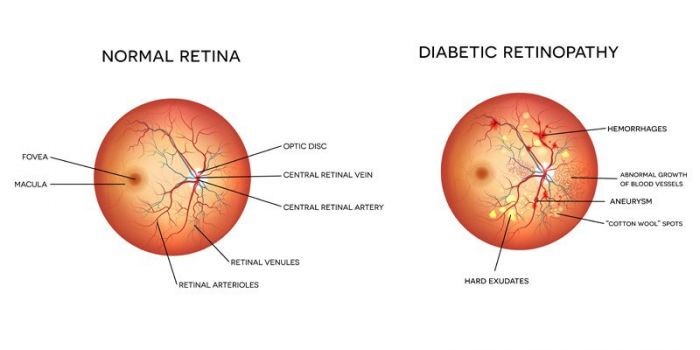
Understanding Diabetic Retinopathy:
DR is a complication of diabetes that occurs when high blood sugar levels damage the blood
vessels in the retina. This damage can lead to fluid leakage, scarring, and even retinal
detachment. There are two main stages of DR: non-proliferative (NPDR) and proliferative (PDR).
NPDR is characterized by mild to moderate damage, while PDR is marked by severe damage
and the growth of new, fragile blood vessels.
The Optometrists Role in Detection:
Optometrists are often the first point of contact for patients with diabetes, making them critical
in detecting DR. Comprehensive eye exams, including dilated fundus exams and optical
coherence tomography (OCT), enable optometrists to:
1. Identify early signs of DR, such as microaneurysms and retinal hemorrhages.
2. Monitor disease progression and response to treatment.
3. Detect related conditions, like cataracts and glaucoma.
Diagnostic Techniques:
Optometrists employ various diagnostic techniques to detect and monitor DR, including:
1. Visual Acuity Assessment: Monitoring visual acuity to detect changes in vision.
2. Retinal Imaging: Utilizing OCT and fundus photography to track retinal changes.
3. Fluorescein Angiography: Injecting dye to visualize blood vessel damage.
4. Ultrasound: Using high-frequency sound waves to detect retinal detachment.
Optometric Management of Diabetic Retinopathy:
Optometrists employ various strategies to manage DR, including:
1. Medical Management: Educating patients on diabetes control, blood pressure management, and lifestyle modifications.
2. Laser Treatment Referral: Collaborating with ophthalmologists to provide laser treatment for advanced DR.
3. Intravitreal Injections: Administering anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) injections.
4. Low Vision Rehabilitation: Providing visual aids and rehabilitation services for patients with
advanced vision loss. Collaboration with Other Healthcare Professionals Effective management of DR requires a multidisciplinary approach. Optometrists work closely with:
1. Endocrinologists: To optimize diabetes management and blood sugar control.
2. Ophthalmologists: For advanced treatments, such as laser surgery and intravitreal injections.
3. Primary Care Physicians: To ensure comprehensive patient care and coordination.
Prevention and Education:
Preventing DR is crucial, and optometrists play a key role in educating patients on:
1. Regular Eye Exams: Annual comprehensive eye exams for early detection.
2. Diabetes Control: Maintaining optimal blood sugar levels.
3. Healthy Lifestyle Choices: Encouraging a balanced diet, regular exercise, and smoking
cessation.
Emerging Trends and Technologies:
Recent advancements in technology have improved DR diagnosis and management:
1. Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI-powered retinal analysis software enhances detection accuracy.
2. Telemedicine: Remote eye exams expand access to care.
3. Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography (OCTA): Non-invasive imaging of retinal vasculature.
Challenges and Future Directions:
Despite advancements, challenges persist:
1. Access to Care: Disparities in healthcare access and affordability.
2. Patient Compliance: Adherence to treatment plans and lifestyle modifications.
3. Research and Development: Continued investigation into DR pathophysiology and treatment options.
Conclusion:
Optometry plays a vital role in managing diabetic retinopathy, from detection and monitoring to treatment and education. By working collaboratively with other healthcare professionals, optometrists can help prevent vision loss and improve patient outcomes. As the prevalence of diabetes continues to rise, the importance of optometric care in DR management will only continue to grow.
Key Takeaways:
– Optometrists are critical in detecting and managing diabetic retinopathy.
– Comprehensive eye exams and retinal imaging are essential for early detection.
– Collaboration with other healthcare professionals is vital for effective management.
– Patient education on prevention and lifestyle modifications is crucial.
– Optometric care can significantly improve patient outcomes and prevent vision loss.
Recommendations:
– Schedule annual comprehensive eye exams if you have diabetes.
– Work with your healthcare team to maintain optimal blood sugar control.
– Adopt healthy lifestyle choices to reduce your risk of DR.
– Consult with an optometrist for personalized care.