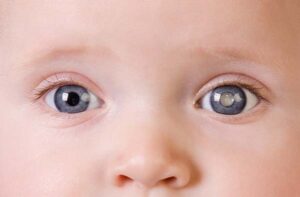
Glaucoma is a symptomatic condition where the functional integrity of the eye is disturbed , resulting in characteristics irreversible loss of visual field due to persistent raised IOP . Glaucoma is a multifactorial optic neuropathy in which there is a characteristics loss of retinal ganglion cells and atrophy of the optic nerve . Though controversial , this definition of American Academy of Ophthalmology excludes IOP as a criterion and says this is a risk factor .
Symptoms –
- Marked photophobia
- Blepharospasm
- Watering
- Headaches
- Low vision
- Vision loss
- Nausea and vomiting.
Signs –
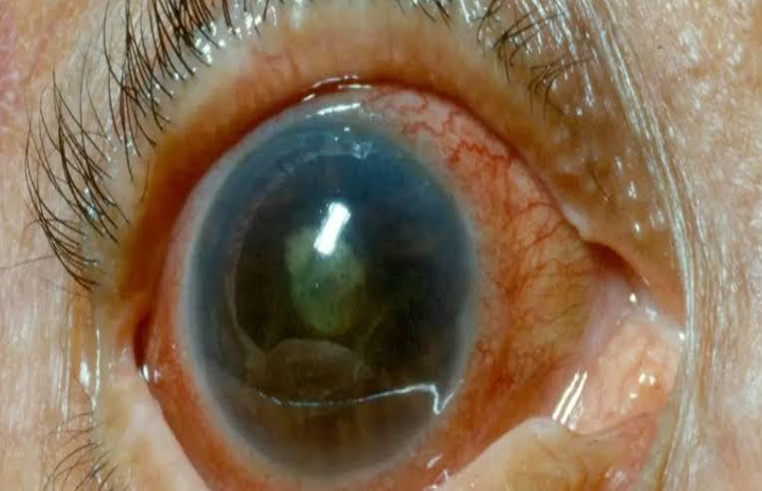
- Eyeball – it becomes enlarged , if the IOP becomes elevated prior to age of 3 years . This enlarged eyeball due to glaucoma , is known as bupthalmos .
- Sclera – bluish discoloration
- Cornea – it is enlarged , globular and steamy . Horizontal curvilinear lines are seen on the back of the cornea , known as Haab’s striae and they represent healed breaks of Descemets membrane . Corneal sensation is diminished.
- AAnterior chamber – deep
- Lens – flattened and displaced backward . There may be subluxation .
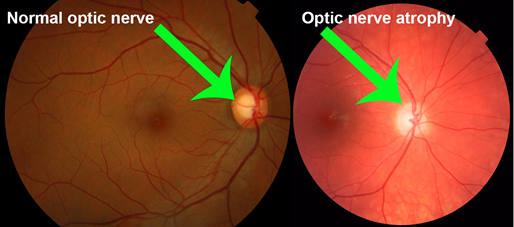
- Fundus – shows cupping of the disc , but it may regress when the IOP is normalized quickly.
- Refractive error – the patient becomes myopic. But the amount of myopia is less than anticipated from the increased axial length , owing to flattening and backward displacement of the crystalline lens .
Types –
- Open angle glaucoma
- Angle- closure glaucoma
- Congenital glaucoma
- Secondary glaucoma
Diagnosis-
- Measurements of corneal diameter-
In infant , the mean horizontal corneal diameter is 10.0 mm . If a corneal diameter is more than 12mm within first year , it is always pathological .
- Dilated eye exam to widen pupils and view your optic nerve at the back of your eyes.
- Gonioscopy to examine the angle where your iris and corneglaucoma
- Optical coherence tomography (OCT) to look for changes in your optic nerve that may indicate glaucoma.
- Ocular pressure test (tonometry) to measure eye pressure.
- Pachymetry to measure corneal thickness.
- Slit-lamp exam to examine the inside of your eye with a special microscope called a slit lamp.
Visual acuity test (eye charts) to check for vision loss.
- Intraocular tension – it is preferably measured with Parkins applanation tonometer , as the scleral rigidity is very low in children .
Management –
- Medical –
- Miotic therapy – instillation of pilocarpine 2% every 5 minutes, is usually effective in pulling the iris from the angle and aborting the attack . The fellow eye should be treated with 2% pilocarpine , 3 times daily .
- Tablet acetazolamide (250gm ) 2 tabs Stat and then followed by 1 tablet 4 times daily , with potassium supplement .
- Hyperosmotic agents –
- Intravascular injection of mannitol (20%)- the dose is 1-2 g/kg body weight . 300-500 ml is given intravenously over a period of 30-45 minutes .
- Oral glycerol (50% solution)- 30ml of pure glycerol with equal amount of fruit juice stat, and then 3 times daily . Cannot be used in diabetics.
- Isosorbide – it is used orally , and it doesn’t cause nausea. It can be used safely in diabetic patients.
- Beta blocker –
- Timolol maleate eye drops , at 12 hourly interval ( twice daily ) . It is a nonselective beta blocker . It lowers the IOP by reducing the aqueous secretion , as a result of direct action on the secretory, as a result of direct action on the secretory epithelium of the cilliary body.
- Betaxolol eye drops twice daily . It is cardioselective beta 1 blocker and is almost as effective as timolol.
- Levabunolol eye drops twice daily . It is as effective as timolol with less ocular side effects .
- Prostaglandin analogs (PGAs) – act by increasing the uveoscleral outflow by over 100 % of physiological levels . It lowers IOP by 25-35% from baseline The once daily dosing and minimal ocular side effects are advantageous . But there are expensive drugs . Exmp- Latanoprost (0.005%) eye drop , Travoprost (0.004%).
- Surgical –
- Goniotomy – an accurate incision is made with a special knife , halfway between the iris and the Schwalbe’s line.
- Goniopuncture – a puncture is made through the whole thickness of the trabecular region into the Subconjunctival space .
- Trabeculectomy – a fine metal probe is passed into the schlemm’s canal , and is then swept into the anterior chamber , thus exposing the Schlemm’s canal directly to the aqueous humor .
- Rehabilitation – It is extremely important to detect and treat any refractive error and amblyopia . Corneal opacity may be treated by penetrating keratoplasty .