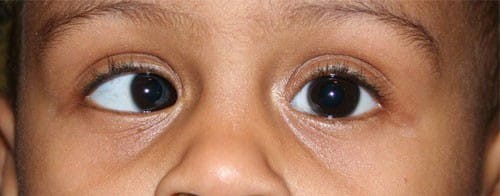
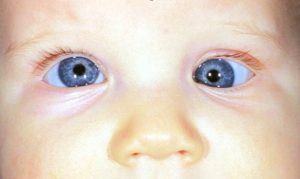
CONCOMITANT STRABISMUS :-
Which amount of deviation in the squinting eye remains constant in all dirrections of gaze , one type heterotropia or manifest squint.
Type of concomitant squint or strabismus :-
- Convergent squint(esotropia) :- inward deviation of one eye
- Divergent squint (exotropia):- outward deviation of one eye
- Vertical squint (hypertropia) :- upward deviation of one eye.
Investigation of squint or strabismus :-
At first we take patient history ,include:- chief complaint, age of onset, duration, family history , any illness about squint, which type of squint ( intermittent or constant, unilateral or alternating squint) , history of diplopia , history of head posture etc.
After taking the patient history, vision test is important for squinting patient because visual acuity is responsible for this symptoms. Then refraction should be performed under full cyclopegia.
Then retina , optic nerve and ocular media examination should be performed.
- Estimating the deviation:-
To determine an apparent and manifest squint .
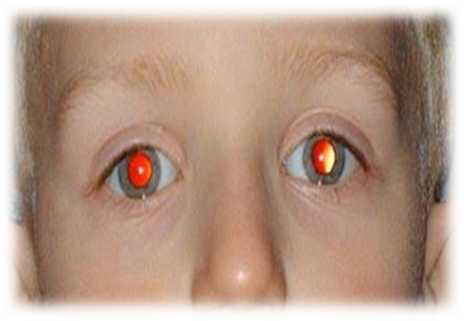
Bruckner test :-It determines if the patient has orthotropic or heterophoric or heterotropic. In this test patient is seated on the chair in dim illumination. The examiner sits at arm’s length in front of the patient and follow the light beam of a direct ophthalmoscope onto the patient’s eye. If the patient is orthotropic , the brightness and colour of the fundus reflex equal in two eyes. But squinting eye , red reflex is a brighter, red-yellow or white in colour while the other eye red reflex is brighter than the squinting eye.
Cover test :- It determines tropia or manifest squint. In this test patient is seated on the chair and patient is asked to fixate on a point. Then the normal looking eye is covered and observing the movement of other eye. In presence of apparent squint the uncovered eye will no movement but other hence in presence of manifest squint or tropia the uncovered eye will move in opposite direction than other eye.
Cover- uncover test:- It confirms the presence of latent squint. So it can be difference between latent squint and manifest squint. In this test patient one eye is covered and other eye is fixed on an object . In normal eye there will be no movement of covered eye but in presence of latent squint the eye under cover will deviate because when one eye is covered the fusion is interrupted, movement of the eye on removing the cover tell what type of latent squint.

- Estimating the eye movement :- In this test it can be determined paralytic and nonparalytic squint.
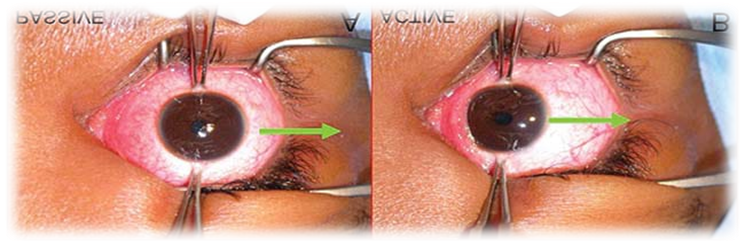
Forced duction test:- It is an attempt to rotate full movement of eyeball. It is detect to paralytic squint or non paralytic squint . It can be perfomed under local anaesthesia . The patient lie in the bed and asked to look in the direction in which movement is being tested and the maximum range is noted. The eyeball is then held at the at the opposite limbus with a toothed forceps and rotate maximally further in the same direction. The test is said to be positive if there is a resistance to full passive movement and negative result to forced duction test. A negative duction test indicates paralytic squint and positive forced duction test indicates non paralytic squint.
- Estimating the angle of deviation :- Estimating the angle of deviation is important in all type of squint.
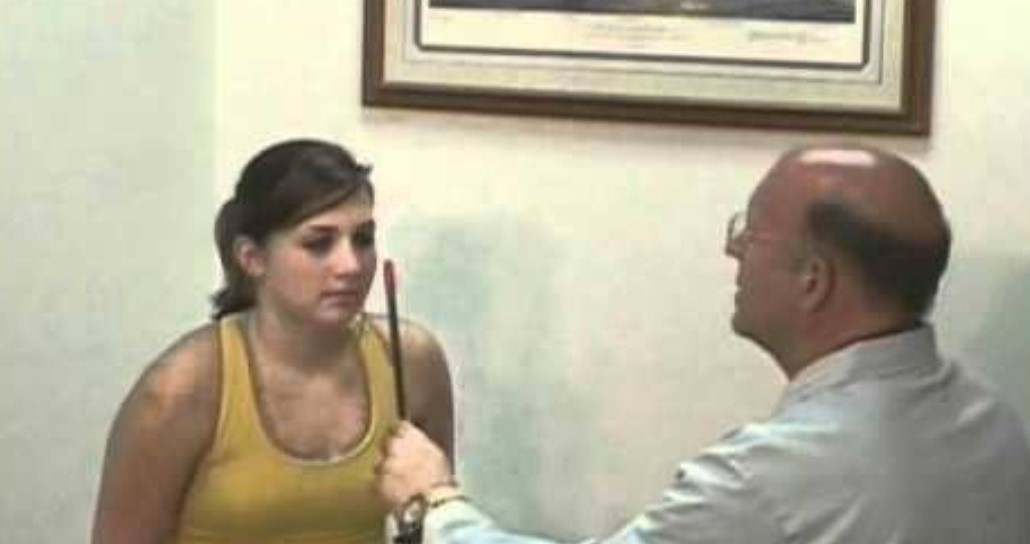
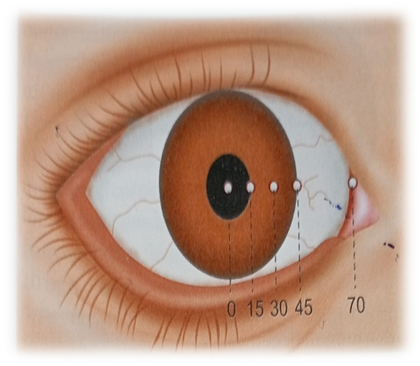
Hirschberg test :- A rough indication of the angle of squint can be obtained from the position of the corneal reflex ,light beam is thrown into patient eye by a torch light and patient asked to fixate at a point of 33 cm. In fixing eye the corneal reflex will be center in the pupil but light reflex slightly decentered in squinting eye. Roughly the angle of squint is 15 degree it means light reflex falls border of the pupil ,30 degree when light reflex falls between pupil and cornea , 45 degree when light reflex falls on the border of limbus and 70 degree means when light reflex falls on the conjunctiva. Roughly 1mm deviation of the corneal light reflex is equivalent to 7 degree of deviation. It is not accurate result this test gives only an approximate result.
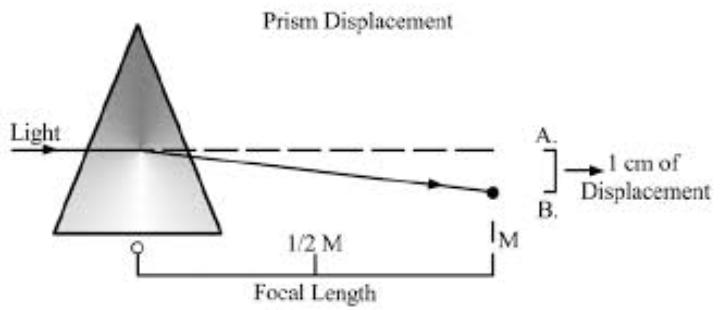
Prism bar test:– This is the most commonly used method in routine clinical practice. Prism of increasing strength with apex towards the deviation are placed in front of one eye and the patient asked to fixate an object with the other. The prism power required to negate the ocular movements, equals to the angle of deviation and it is measured in prism diopter. Roughly 1 degree of ocular movements equals to 2 prism diopter.
Krimsky corneal reflex test :- The patient is asked to fixate a point light and other eye are placed prism with increasing power until the corneal light reflex is centered in the squinting eye.
Synoptophore ;- It is the instrument to measure the angle of deviation. It consists two tubes, having a right angled bend ,mounted on a base.Each tubes contains light sources and outer end a reflecting mirror at the right angled bend and an eyepiece of +6.5D in inner end.
Detection of normal or abnormal retinal correspondences :- used to subjective or objective angles of the squint. In normal retinal correspondences subjective and objective angles are equal. In abnormal retinal correspondences objective angle is greater than the subjective angle and the difference between two angle is called , angle of anomally.
- Estimating the grade of binocular single vision and sensory functions :- Binocular single vision tests is important for all type of squints . Here we described about this,
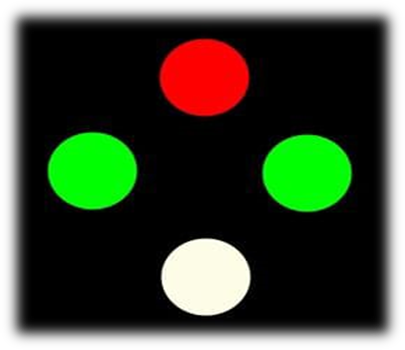
Worth four – dot test :- It is used detect diplopia , suppression, abnormal retinal correspondence. In this test patient wear a goggles with red lens infront of right eye and green lens infront of left eye and patient asked to views a four light box( one red, two green ,one white). In normal binocular single vision patients sees all the four light , in left eye suppression the patient sees only two red lights, right eye suppression the patients sees only three green lights and two red lights , in alternating suppression the patient sees three green an two red lights alternately and diplopia patient sees two red and three green lights.
Visuoscope or ophthalmoscope test:– It is used for assessing fixation status. Patient is asked to cover one eye and fix the star with other eye . And observe fixation may be centric or eccentric .
After image test :– In this test right fovea is stimulated with a vertical bright light and left fovea with a horizontal bright light and patient asked to draw the positions of after image . In normal retinal correspondence patient will draw a cross images, esotropic patient will draw vertical images to the left horizontal and exotropic patient will draw vertical image to the right of horizontal.