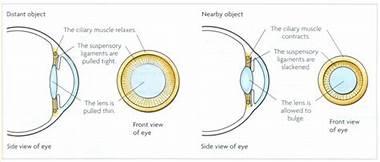
Accommodation is the ability of an eye to focus at a different distance by changing shape and size of an object. It is controlled by parasympathetic nervous system
The stimulus of accommodation depends upon the apparent size and distance of an objects and stereopsis, aberration that is chromatic, spherical and astigmatism and including convergence.
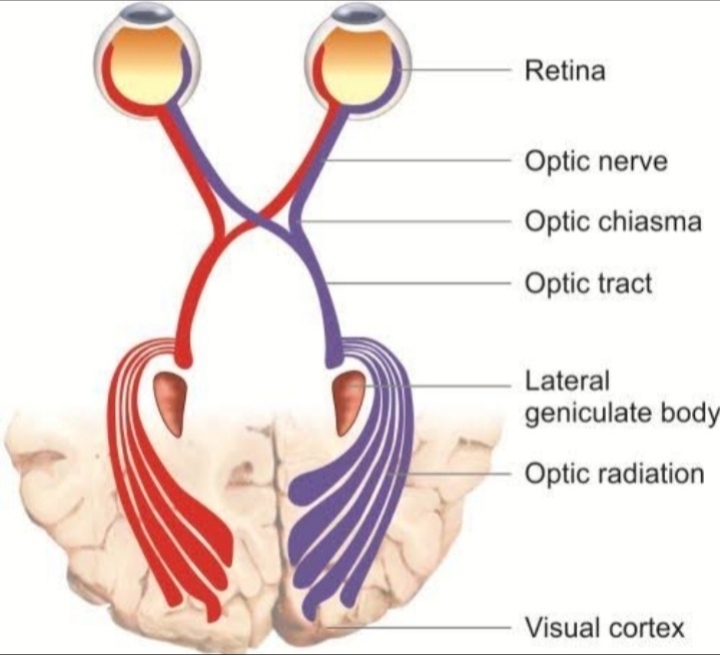
Pathway of accommodation
Afferent impulse from retina pass along the normal visual pathway to reach to optic tract to lateral geniculate body along with optic radiation to striate and parastriate area of the occipital lobe along the occipito mesencephalic tract to neulus of perlia or prectoral nucleus through Edinger westpal nucleus where efferent impulse along the 3rd cranial nerve to accessory of ciliary ganglion to sphincter pupillae and ciliary muscles.
Accommodation insufficiency defined as a condition that causes the inability to maintain near vision focus for long duration. The condition mostly seen in the age related causes that is amplitude of accommodation
Accommodative insufficiency can also be attributed with other binocular vision problems 7). Accommodative insufficiency and convergence insufficiency can be coincident in several cases. Children diagnosed with both are much more symptomatic than children with just convergence insufficiency or with normal binocular vision 8). Both conditions that can exist separately as well. Patients with accommodative insufficiency alone can have normal fusional capacities and depth of focus.
Accommodative insufficiency incorporates ill-sustained accommodation, paralysis of accommodation, and unequal accommodation. Ill-sustained accommodation is described as an early stage of accommodative insufficiency, where the amplitude can start out as normal, but deteriorates over time and causes astheopia.
Causes
Premature sclerosis of lens or ciliary muscles weakness due to systemic or local cases that associate with accommodation insufficiency. Systemic cause can be ciliary muscles weakness including glaucoma and its most common type open angle glaucoma, iridocyclitis diabetes, malnutrition, in case of pregnancy, stress
Accommodative insufficiency signs
Directmeasures of accommodative stimulation:
- Reduced amplitude of accommodation
- Difficulty clearing -2.00 with monocular accommodative facility
- High monocular estimation method finding
- High fused crossed-cylinder finding
Indirect measures of accommodative stimulation:
- Reduced positive relative accommodation
- Difficulty clearing -2.00 with binocular accommodative facility
- Low base-out to blur finding at near
Accommodative insufficiency symptoms
These symptoms are generally related to reading or other near tasks:
- Blurred vision
- Headaches
- Eyestrain
- Reading problems
- Fatigue and sleepiness
- Loss of comprehension over time
- A pulling sensation around the eyes
- Movement of the print
- Avoidance of reading and other close work
Accommodative insufficiency diagnosis
Accommodative insufficiency is frequently encountered in young school children and is related to subjective symptoms noted by the child. If any decrease in accommodative function among school children can contribute to near-work related problems and therefore have a negative effect on a child’s learning and visual experiences. Even though there are various accommodative problems associated with it, whereas accommodative insufficiency is the most common.
Accommodative insufficiency treatment
The sequential management recommended begins with correction of ametropia, added near lenses and then optometric vision therapy. Uncorrected refractive error can lead to accommodative fatigue, which can be easily remedied in many patients. Once the ametropia has been fully corrected through the optometrist evaluations as prescribing glasses, contact lens and vision therapies, retesting of the binocular and accommodative status should be considered.
Determinations of an appropriate add power is made by analyzing data collected from facility testing, amplitude of accommodation, MEM retinoscopy, and balancing the PRA/NRA. When prescribing some prefer single-vision lenses for near work while some use flat top bifocals. There was a study done by Daum in 1983 and more recent study by Abdi in 2005 which reported success rates of 90% and 98% respectively in the reduction of symptoms in patients with accommodative insufficiency and seen in early age with associating in later days of living with asthenopic symptoms.