What is Phoria?
Phoria is a misalignment of the eyes that only appears when binocular viewing is broken and the two eyes are no longer looking at the same object.
A sensorimotor anomaly of the binocular visual system is characterized by an abnormal tendency for the eyes to rotate around the anterior-posterior axis.
WHAT IS CYCLOPHORIA?
- A tendency of the eighter eye to wheel rotates around the anterioposterior axis on dislocation.
- Also known as “tensional squint”
- Cyclophoria is rare & Asso. with vertical deviation.
- Cyclotropia is a form of strabismus in which, compared to the correct positioning of the eyes, there is torsion of one eye (or both) about the eye’s visual axis. Consequently, the visual fields of the two eyes appear tilted relative to each other. The corresponding latent condition – a condition in which torsion occurs only in the absence of appropriate visual stimuli – is called cyclophoria.
Classification of cyclophoria:-
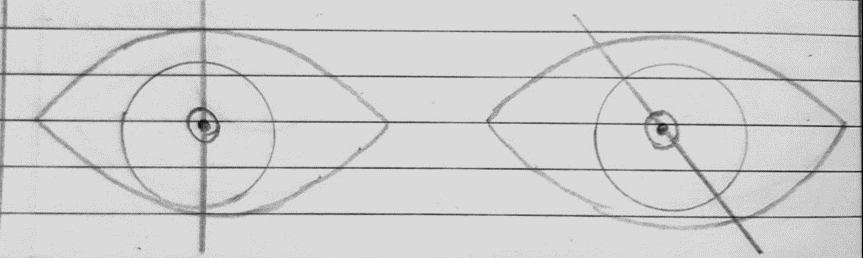
- INCYCLOPHORIA:- When the 12 o’clock meridian of the cornea of the affected eye tends to lean toward the nasal side or medial side.
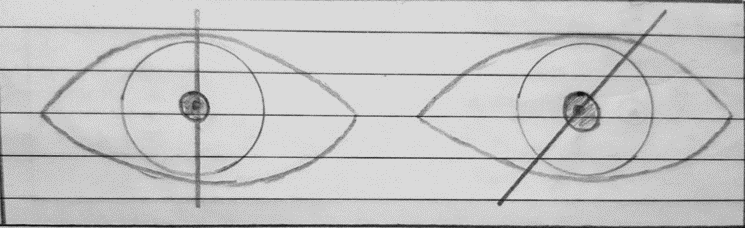
- EXCYCLOPHORIA:- When the 12 o’clock meridian of the cornea of the affected eye tends to lean towards the temporal side or lateral side.
Causes of Cyclophoria:-
Most commonly caused by an imbalance between the muscle that intorts the eye (superior oblique & superior rectus) and the muscle that extorts the eye (inferior oblique & inferior rectus)
Signs & Symptoms of cyclophoria:-
- Asthenopia
- Headache
- Tendency to close or cover one eye
- Compensatory head tilt
- General fatigue
- Dizziness/ vertigo
- Motion sickness
- Diplopia
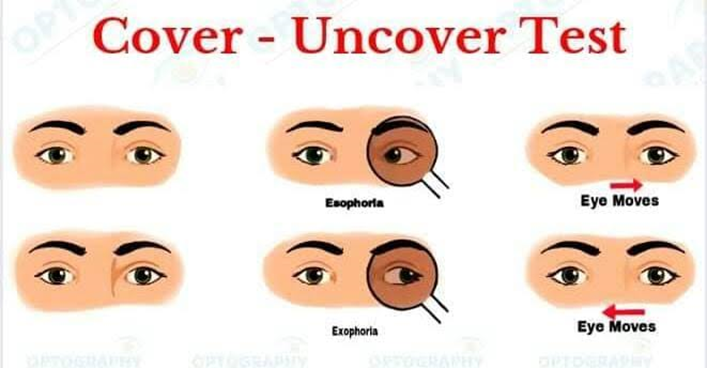
How to diagnose cyclophoria?
Cyclodeviation reported under tests of dissociation like prism cover test, cover test, etc…
Treatment
- Cyclovergence training to correct the eye alignment
- Surgery for oblique muscle disorders
- Multiple eyewear.