Introduction –
Vision is one of the most valuable senses we possess. Unfortunately, various conditions can impair our sight—one of the most common being cataracts. Cataracts are a leading cause of vision impairment worldwide, particularly among the elderly. Despite being widespread, cataracts are often misunderstood.
Definition of Cataract –
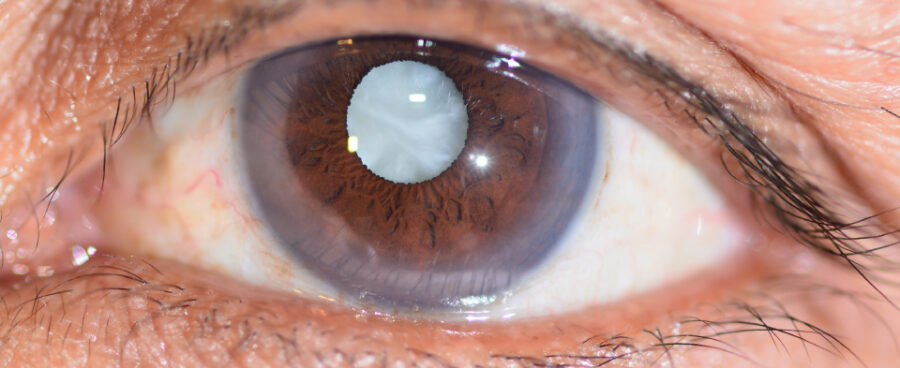
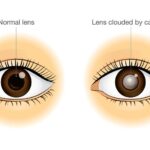
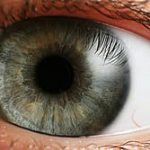
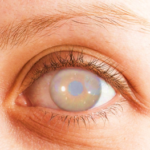
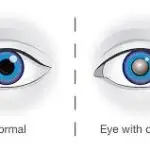
A cataract is a clouding of the normally clear lens in your eye. Imagine looking through a frosted or fogged-up window—that’s how cataracts affect your vision. The lens, located behind the colored part of your eye (iris), helps to focus light or an image on the retina. When a cataract forms, the lens becomes cloudy, making it difficult for light to pass through clearly, leading to blurred or dim vision.
Cataracts often develop slowly and can affect one or both eyes. They are not contagious and cannot spread from one eye to the other, although both eyes can be affected independently.
➤ Symptoms of Cataracts :
Cataracts usually begin with subtle changes in vision, and the symptoms become more noticeable over time. Common signs and symptoms include:
-Blurry or cloudy vision.
-Difficulty seeing at night or in low light.
-Sensitivity to light and glare lights.
-Seeing halos around lights.
-Frequent changes in eyeglass or contact lens prescription.
-Fading or yellowing of colors.
-Double vision in a single eye.
These symptoms may vary depending on the type and severity of the cataract. At first, the cloudiness may affect only a small part of the lens and might go unnoticed. As the cataract grows, it distorts more light and affects a larger portion of your vision.
➤Causes of Cataracts-
Several factors can lead to the development of cataracts. The most common cause is aging, but other causes include:
1. Age-related changes – The natural aging process causes the lens to harden and
become cloudy over time.
2. Genetics – A family history of cataracts can increase your risk.
3. Trauma or injury to the eye – Physical injuries can damage the lens and lead to cataracts.
4. Radiation exposure – UV rays or radiation therapy can increase the risk.
5. Diabetes – High blood sugar levels can cause lens swelling and contribute to cataract formation.
6. Smoking and alcohol use – These habits have been linked to a higher risk of cataracts.
7. Prolonged use of corticosteroids – Long-term use of steroids can lead to cataract development.
8. Previous eye surgeries – Surgery for other eye problems may sometimes lead to cataracts as a side effect.
Although aging is the most significant risk factor, younger individuals and even children can develop cataracts due to inherited disorders or injuries.
➤ Treatment Of Cataracts-
There is currently no medication or eye drop that can cure or reverse cataracts.
However, effective treatment is available—surgery.
1. Early Stage Management
In the early stages, vision may be improved temporarily with:
-Stronger eyeglasses or contact lenses
-Using magnifying lenses
-Improving lighting at home
-Reducing glare with special sunglasses
However, these are only temporary measures and do not treat the cataract itself.
2. Cataract Surgery
When the cataract interferes with daily activities—such as reading, driving, or recognizing faces—surgical removal becomes necessary. Cataract surgery is one of the safest and most commonly performed procedures worldwide.
-During surgery:
The cloudy lens is removed.
A clear artificial lens, called an intraocular lens (IOL), is implanted.
The surgery typically takes less than 30 minutes and is performed under local
anesthesia. Recovery is generally quick, with most people returning to normal activities within a few days.
Success rates for cataract surgery are very high. Over 95% of patients experience improved vision after surgery, especially if there are no other eye conditions.
➤ Prevention of cataract –
While cataracts cannot always be prevented, you can reduce your risk by:
-Wearing sunglasses that block UV rays.
-Eating a diet rich in antioxidants (vitamins C and E).
-Quitting smoking and limiting alcohol intake.
-Managing health conditions like diabetes.
-Having regular eye check-ups, especially after age 40.
Early detection is key to preserving your vision.
Conclusion-
Cataracts are a common yet treatable eye condition that affects millions of people
globally. While they may start small, cataracts can significantly reduce the quality of life
if left untreated. Thankfully, with advancements in eye care, cataracts can be safely and
effectively managed through surgery. If you or someone you know is experiencing
symptoms of cataracts, don’t ignore them—consult an eye specialist or Optometrist for
proper evaluation and guidance. Remember, early detection and timely treatment can
restore vision and help you see the world more clearly again.