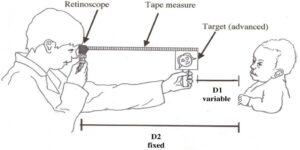
What is strabismus ?
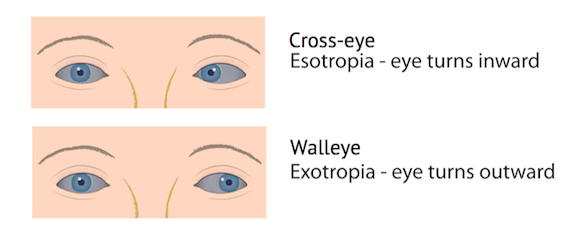
Strabismus is a condition in which the eyes do not properly align with each other when looking at an object .
This condition may be present occasionally or constantly, if present during a large part of childhood , it may result in amblyopia or lazy eye and if present during a adulthood, it may result in double vision .
The most common form of strabismus is known as “crossed eyes”
Vertical strabismus refers to a vertical misalignment of the visual axis or vertical deviation. This could be comitant (deviation that is the same magnitude regardless of gaze position ) incomitant (it is magnitude varies as the patient shifts his or her gaze )most vertical deviations are incomitant .

CLASSIFICATION :-
- Depending upon constancy of deviation
- Hyperphoria – it is an eye condition in which the eye points upwards but not permanently .
- Intermittent hypermetropia – it is common vision condition in which you can see distant objects clearly but sudden blurring of vision for near objects.
- Hypertropia – it is a form of vertical strabismus or misalignment of the eyes that occurs when one eye turns upward .
- Depending upon the direction of deviation in the non – fixating eye
- Hypertropia
- Hypotropia – it is a from of vertical strabismus or misalignment of the eyes that occurs when one eye turns downward .
- Depending upon comitance of deviation
- Comitant vertical deviation
- Induced (refractive)
- End result of long standing paralytic deviation
- Incomitant vertical deviations
- Apparent oblique muscle dysfunction
- Paretic vertical deviations
- Restrictive vertical deviations
- Dissociated vertical deviation (DVD)
- Monocular DVD
- Bionocular or alternating DVD
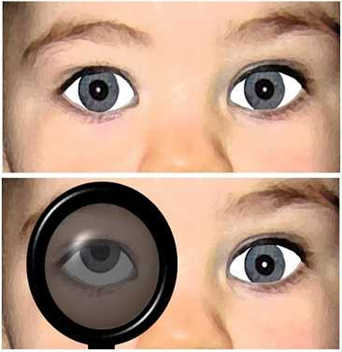
DISSOCIATED VERTICAL DEVIATIONS (DVD)
Dissociated vertical deviation is an upward movement of one eye when the other eye is fixing on a target , the deviation often involves both eyes but is most frequently asymmetric , such that the primary concern is vertical movement of one eye .
A few of the other names by which this condition has been described are : Alternating sursumduction, Alternating hyperphoria , Alternating hypertropia , Alternating sursumvergence , Occlusion hyperphoria , Occlusion hypertropia , Double hypertropia, Dissociated vertical divergence , Dissociated hyperdeviation.
Dissociated vertical deviations are basically characterized by hyper deviation in one eye that is present while the other eye is fixing .the non fixing eye is also extorted and slightly abducted.
PATHOGENESIS
A few such theories are mentioned below
- Bielschowsky’s theory of positive and negative subcortical vertical divergence centres . he theorized that DVD occurs due to alternating and intermittent excitation of both subcortical vertical divergence centres .
- Theory of imbalance of binocular stimulation . Spielmann theorized that the frequent occurrence of DVD is essential infantile esotropia and the occasional occurrence with sensory heterotropia.
- Brodsky theory . he theorized that DVD is a vestigial remnant of the dorsal light reflex of lower animals .
- Other theories are
- Theory of bilateral paralysis of the depressor muscles .
- Theory of defective mid brain stimuli .
- Theory of two monocular conjugate mechanisms plus a binocular mechanism
- Theory of defective monocular nasal retinal quadrant stimuli.
- Guyton’s theory
CLINICAL FEATURES
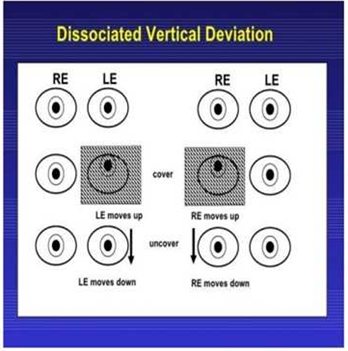
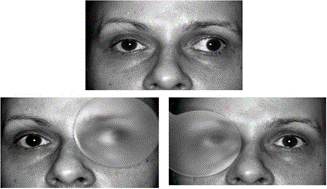
- Deviation – DVD is characterized by spontaneous occurrence of vertical deviation in either eye , when the patient is fatigued ,or day dreaming (manifest DVD) or when fusion is interrupted by artificial means (latent DVD).
- Association of DVD – DVD may also occur as an isolated phenomenon in patients with apparently normal binocular function . its common associations include – a. Infantile esotropia , b. Infantile exotropia
Excycloduction and latent nystagmus are frequently associated with DVD
- Head posture – Approximatlely one third of patients with DVD have a spontaneous abnormal head posture .
- Laterality – DVD is frequently bilateral (alternating sursumduction ) usually asymmetric rarely it may be monocular.
- Monocular dissociated hyperdeviation- its may be seen in the presence of an intermittent exotropia .
- Bilateral DVD or alternating sursumduction- it is a situation in which either eye elevates under cover(double hyperdeviation).
- Symmetric versus asymmetric DVD ,(Bilateral DVD may be symmetric or asymmetric) .
- Comitance – DVD may be comitant or incomitant
- Comitant DVD – DVD that measures roughly the same (within 7 PD) in primary position adduction and abdution is called comitant DVD.
- Incomitant DVD – It refers to measurable disparity in the magnitude of DVD (>7PD) between the primary position ,abduction, adduction .
- Binocular vision and sensory adaptions
- Suppression usually develops in patients with spontaneous DVD and thus eliminates diplopia.
- Peripheral fussion is often present in patients wit DVDhaving a manifest deviations of 4D or less.
- An absolute facultative central in one eye, while both eyes are being used together for peripheral vision , is present even in patients having a latent DVD .
DIAGONOSIS
- Cover-uncover test
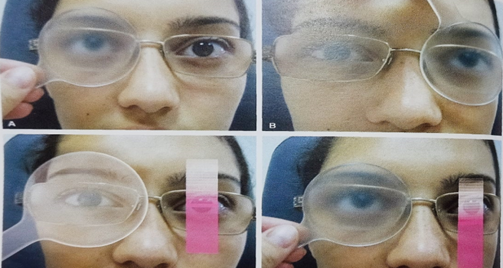
- Spielman’s translucent occlude test
- Head tilt test
- Red glass (filter)test
- Demonstration of Bielschowsky phenomenon test
- Measurement of DVD
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGONOSIS
DVD is often mistaken for over- action of the inferior oblique extra ocular muscles . DVD can revealated on ocular movement testing when one eye is occluded by the nose on lateral gaze . this eye will then elevate , simulating an inferior oblique over action however , in a unilateral case overaction of the superior rectus muscle in the unaffected dominant eye, can also be a causing factor as well as causing a V pattern exophoria .
TREATMENT
- Non – surgical treatment
- Conservative therapy to strengthen the fusional mechanisms. (optimal spectacle correction, correcting an associated horizontal deviation ,treating amblyopia, treating heterophoria)
- Conservative therapy in the form of changing the fixation pattern .
- Surgical treatment
- Surgical procedures for comitant DVD.
- Faden operation with superior rectus recession.
- Large recession of superior rectus muscle .
- Resection of the inferior rectus muscle .
- Recess – resect procedure .
- Surgical procedures for incomitant DVD
- When DVD is larger in the field of inferior oblique of the non- fixating eye in adducted position
- When DVD is larger in adducted position but significant in abduction
- When DVD is more in abduction due to associated superior oblique over reaction (SOOA) and “A” pattern .
DISSOCIATED HORIZONTAL DEVIATION (DHD)
Dissociated horizontal deviation is defined as a change in horizontal ocular alignment, unrelated to accommodation , that is brought about solely by a change in the balance of visual input from the two eyes.
CHARACTERISTIC FEATURES
- DHD usually manifests as spontaneous unilateral exodeviation or an exodeviation of greater magnitude in one eye during prism and alternate cover testing.
- Unlike in other froms of intermittent exotropia, the observed exodeviation is slow, variable and asymmetrical in the two eyes.
ASSESSMENT
- To assess the horizontal dissociated deviation , the same procedure as described for DVD is performed with base –in prism over the eye with DHD until no further inward movement of that eye is seen . Movement of the contralateral eye with this can be ignored.
- DHD may be distinguished from other horizontal strabismus by lack of a corresponding exodeviation of the contralateral eye on alternate cover testing.
TREATMENT
DHD depending upon the amount , is treated with lateral rectus recession of 3-8 mm on the affected side.