Optical Coherence Tomography is a non invasive imaging test. OCT uses light waves to take cross section pictures of the retina. With OCT, an optometrists can see each of the retina’s distinctive layers. This allows your optometrists to map and measure their thickness. These measurements help with diagnosis. They also provide treatment guidance for glaucoma and diseases of the retina. These retinal diseases include Age related Macular Degeneration, Diabetic eye diseases, etcetera.
Procedure of OCT Test
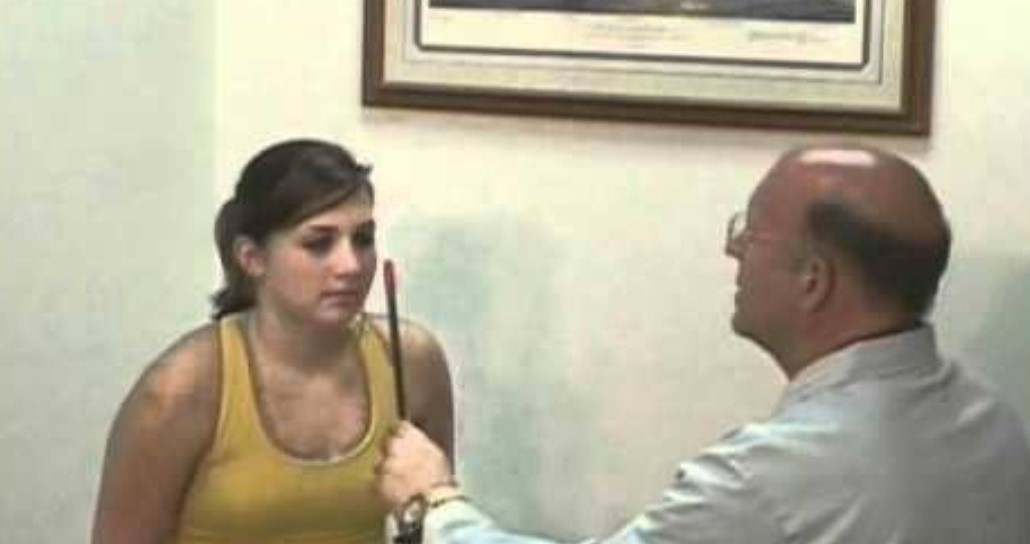
To prepare for an OCT exam, optometrists may or may not put dilating eye drops in the eyes. These drops widen the pupil and make it easier to examine the retina.
In this test, the patient will be seated infront of the OCT machine and rest his/her head on a support to keep it motionless. The equipment will then scan the eye without touching it. Scanning takes about 5 to 10 minutes. If the eye’s are dilated, they may be sensitive to light for several hours after the exam.
Conditions OCT helps to diagnose
Oct is useful in diagnosing many eye conditions such as:
- Macular hole
- Macular pucker
- Macular edema
- Age related macular degeneration
- Glaucoma
- Central Serious Retinopathy
- Diabetic Retinopathy
- Vitreous traction
OCT is often used to evaluate disorders of the optic nerve as well. The OCT exam helps optometrists to see changes to the fibers of the optic nerve. It can detect the changes caused by glaucoma.
OCT relies on light waves. It cannot be used with conditions that interfere with light passing through the eye. These conditions include dense cataracts or significant bleeding in the vitreous.
Uses of Optical Coherence Tomography:
OCT can be used in the following conditions:
- Monitoring eye diseases like uveitis.
- Discounting or verifying suspected retinal swelling.
- To check the effectiveness of the given medication regime.
- To check or compare OCT results against visual acuity.
- In recent times, Optical Coherence Tomography is used in graft assessment after corneal surgery.
Basic principle of Optical Coherence Tomography:
An OCT consists of a light source which is a low coherence broadband light source. The light which is emitted by the source is coupled into an interferometer. Then divides itself into the reference arm and the sample arm. The light from the reference arm is reflected in the reference mirror and the sample arm light is transmitted to the tissue which needs to be studied.
The sample arm also consists of the objective lens which helps in the focusing of the light on the tissue that needs to be studied. The light radiated from the sample arm gets backscattered from the sample tissue and is recombined with the reference light using the reference mirror. It then produces an interference pattern that can be easily detected by the light detector present in the machine. A two-dimensional or three-dimensional image can be formed of the cross-sectional objects by using the beam which is scanned across the sample surface.
There are two types of optical coherence tomography implementations which were introduced. They include the time-domain optical coherence tomography and the Fourier domain optical coherence tomography. The latter one has two versions which are swept-source OCT and spectral-domain OCT.
The spectral-domain OCT is very similar to the time-domain OCT. The only difference is that SD-OCT provides a more detailed structure of the tissue for study than the TD-OCT. SD-OCT is considered to be the best among them for providing better sensitivity, enhanced signal-to-noise ratio, and superior depth penetration.
Working of Optical Coherence Tomography Scan
The optical coherence tomography scan works by emitting a light beam on the retina of the eye. This scan is done without any contact with the eyes. Its working is very similar to the ultrasound machine but instead of using sound waves, it uses light beams. When a scan needs to be done of the patient, they are requested to sit in front of the machine.
The chin of the patient is placed on the support provided by the optical coherence tomography machine. The scan is initiated and is done on one eye at a time. A flash of light appears before the eyes and is quickly taken off. And the scan is completed. The same process is repeated with the other eye too.
Some opticians use pupil dilating drops before the OCT scan so that the scan of layers can be done with more ease. This OCT scan helps the ophthalmologist to study the retina over the years and reduce any possible chances of retinal diseases in the patient.
Applications of Optical Coherence Tomography
Optical coherence tomography is a technology that is a non-invasive imaging technique. It provides a high-resolution image of the layers of the eye including the retina, nerve fiber in the retina, and optic nerve. It has been a revolutionary invention for the clinical field of ophthalmology.
The main application of the OCT has been in diagnosing and early detection of retinal diseases. Optical coherence tomography has been used extensively for the imaging of the macula and optic nerve. It also helps in analyzing the morphological changes of the retina during a diseased state. OCT also can detect the fluid present within the retina. And the alterations in the thickness also help the ophthalmologist to proceed with the most favourable treatment.
Advantages of OCT In Different Diseases
OCT has made it easier to diagnose:
Age-Related Macular Degeneration
AMD is considered the leading cause of eye disease in most adults over 60 years of age. Advancement in optical coherence tomography technology has helped doctors in a better understanding of the disease. The assessment done using the SD-OCT of the choroidal thickness helps in the differentiation of the AMD from CSCR and Polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy.
Central Serous ChorioRetinopathy (CSCR)
It is a disease that can be characterized based on the detachment of the neurosensory retina from the RPE. When an optical coherence tomography scan is done, the presence of empty space can be seen in between the neurosensory retina and RPE. CSCR can be resolved naturally in two to three months in some patients but, in some patients, it might lead to permanent visual dysfunction.
Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic Retinopathy is a disease in which there is damage in the vascular part of the retina. It is mainly caused by the working-age group of people. SD-OCT scan done on such patients revealed a significant thinning of the choroidal part of the eyes when compared to the normal healthy eyes. Using optical coherence tomography choroidal thickness can be measured and the severity of the disease can be determined.
Intraocular Tumors
These tumors can also be determined using OCT technology. The delineation of the tumor borders and analysis of the choriocapillaris and larger vessels inside the tumor can be detected using the SD-OCT.
Retinal Nerve Fibres
OCT can also be used to provide a clear image of the nerve fibers as they provide a high-resolution image of the cross-sectional and volumetric images of the nerve fibers at the real-time imaging speed. The other imaging methods like the CT-scan and MRI also provide good quality results but they lack in providing a spatial resolution. The OCT is now being used on patients having neurological disorders.
Other Disease
Some other diseases which can be diagnosed using optical coherence tomography are the macular hole, macular edema, retinoschisis, and pachychoroid. It has also helped in the detection of diseases like glaucoma and Alzheimer’s disease.
Limitations of Optical Coherence Tomography:
- The advantages of using optical coherence tomography are many but along with these advantages, there are some limitations of the technology which can be improved in the future.
- The opacity of the sample tissue interferes with the proper imaging of the sample as OCT works on the principle of using a light beam to scan the sample tissue. This leads to its limited use in the case of vitreous hemorrhage, dense cataracts, and corneal opacities.
- The stillness of the patient is very necessary for this technology as the movement of a patient leads to poor image quality. Hence, newer technology can help in overcoming this obstacle by making OCT machine scan in a shorter time interval.
- The operator of the machine needs to be highly qualified as the scan depends on the operator of the machine. Optical coherence tomography required the operator to place the image over the desired pathology accurately which sometimes leads to an error in the scan. So, newer technologies like eye-tracking equipment have helped in easing out the problem.