We live in a world where screens are an integral part of our daily lives. From smartphones and tablets to laptops and televisions, screens are ubiquitous, and their influence on our children’s lives is undeniable. In today’s digital landscape, kids as young as toddlers are navigating touchscreens with ease, and teenagers are spending hours on end scrolling through social media, playing games, and watching videos.
Gone are the days of traditional play, where children would spend hours outdoors, exploring nature, and engaging in imaginative play. While these activities are still essential for healthy development, the reality is that screens have become a dominant force in shaping young minds. According to a survey in September 2023, about 46% of urban parents reported that their children spent 3 to 6 hours each day using social media, OTT and online games in India. Comparatively 15% of Indian parents stated that their kids spent more than 6 hours using online media everyday (1).
How digital lifestyle affects brain development?
Excessive screen usage in children can have both positive and negative impact on their development. Talking about cognitive development, screens have the potential to enhance education and learning. However, studies have shown that excessive screen time can negatively affect executive functioning, sensorimotor development associated with lower cognitive abilities (2). When developing brains are exposed to screens such as phones, tablets, televisions and computers for long periods, the chemistry and overall function of the brain can be affected. This can have numerous effects on the young brain, primarily affecting part of the brain called the Frontal lobe (3). It is located behind the forehead. This part of the brain is responsible for many of the function that makes us human, such as memory emotions, impulse control social interaction and critical thinking skills.
Extended screen exposure has been linked to potential negative impact on memory, particularly in children and adolescent. The constant stream of information from screen can lead to over stimulation causing the brain to become fatigue and less effective at consolidating memories. Research suggests that excessive screen exposure during childhood may increase the risk of Alzheimer’s disease and related dementia in adulthood (4). Chronic sensory over stimulation for excessive screen time can result in memory and concentration problem. The constant bombarding of information and stimuli can overwhelm the brain leading to difficulties in processing and retaining information.
Sleep disruption:
Too much screen time can also disrupt a child’s sleep, further affecting their cognitive function and their mood. High level of stimulation and blue light emitted from electronic devices can suppress the release of hormone “Melatonin”, that helps regulate our sleep wake cycle. As bedtime draws closer, the pineal gland releases this hormone to help us fall asleep and stay asleep. If children use their screen closer to bed time, they can experience problem in falling asleep, wake frequently and suffer from disrupted sleep pattern.
Impact on Grey and white matter of the brain:
Studies utilising magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has revealed alarming evidence of impact of prolonged screen time on Brain development. MRI scans have shown significant changes in the structure and volume of both grey and white matter in the brains of children and adolescents who engage in excessive screen use. Specifically, these scans have revealed reduced grey matter volume in areas responsible for attention, emotion regulation, and impulse control, as well as decreased white matter integrity, which can disrupt communication between brain regions (5). These findings suggest that excessive screen time may be damaging the very foundation of our children’s brain development, with potentially long-lasting consequences for their cognitive, emotional, and social well-being.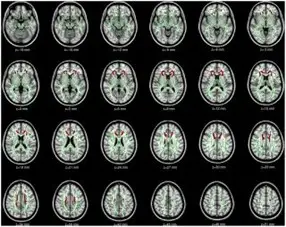
Screen Time impact on kid’s brain:
Between 1½ to 3 years old, children’s language development accelerates rapidly, but excessive screen time can hinder this progress. Research shows that children who engage with adults through talk and play learn language more effectively, whereas those who watch extensive television during early elementary years tend to perform poorly on reading tests and exhibit attention deficits. The ubiquitous nature of mobile devices makes them a significant concern, as they can easily become a child’s norm from infancy. Dr. Jennifer F. Cross notes that excessive screen time may lead to structural brain changes, particularly in areas responsible for critical thinking and reasoning (6). Furthermore, children who spend over two hours daily on screen-time activities score lower on language and thinking tests, while those exceeding seven hours experience cortical thinning. This highlights the importance of balancing screen time with non-electronic activities that foster imagination, social skills, and outdoor exploration.
The verdict:
There’s no denying that screen time and digital technology have become essential tools for life in the 21st century. However, too much screen time can have a highly detrimental effect on a child’s brain development, cognitive skills, physical and mental health and ability to fulfil their potential. By becoming more aware of the amount of time your child or teenager spends online, supervising their use as much as possible and setting clear boundaries and guidelines, you can help mitigate the negative effects of excessive screen time and ensure that your child develops into a happy, healthy, and well-rounded individual. By striking a balance between the benefits of technology and the need for physical and social activity, you can give your child the best possible chance to thrive in today’s digital world.
REFERENCE:
1. Statista. (2023). Average time spent by children on online media in India 2023. Statista. https://www.statista.com/statistics/1415071/india-time-spent-on-online-media-by-children/
2. Muppalla, S. K. (2023). Effects of excessive screen time on child development. PubMed Central. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10353947/
3. Forbrain. (n.d.). How screen time affects mental health and brain development. Forbrain. https://blog.forbrain.com/blog/screen-time-mental-health-brain-development-forbrain
4. NeuroCenter NJ. (n.d.). Digital dementia: How screens and digital devices impact memory. NeuroCenter NJ. https://www.neurocenternj.com/blog/digital-dementia-how-screens-and-digital-devices-impact-memory/
5. Greenberg, J. (2014, February 19). Gray matters: Too much screen time damages the brain. Psychology Today. https://www.psychologytoday.com/intl/blog/mental-wealth/201402/gray-matters-too-much-screen-time-damages-the-brain
6. Cross, J. F. (2023, August 24). What does too much screen time do to children’s brains? Health Matters. New York-Presbyterian. https://healthmatters.nyp.org/what-does-too-much-screen-time-do-to-childrens-brains/
7. Dunckley, V. L. (n.d.). What does screen time do to my brain? SUNY Potsdam. https://www.potsdam.edu/studentlife/wellness/counseling-center/what-does-screen-time-do-my-brain
8. Forbrain. (2022, December 7). Screen time and its impact on mental health and brain development – What can Forbrain do? Forbrain. https://blog.forbrain.com/blog/screen-time-mental-health-brain-development-forbrain