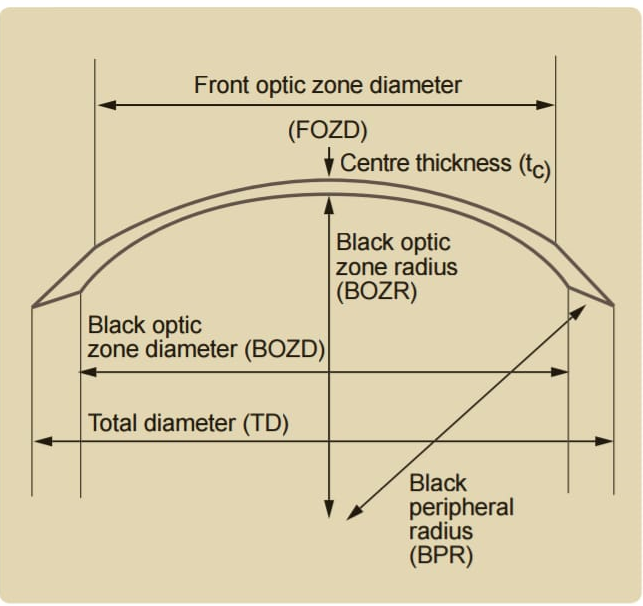
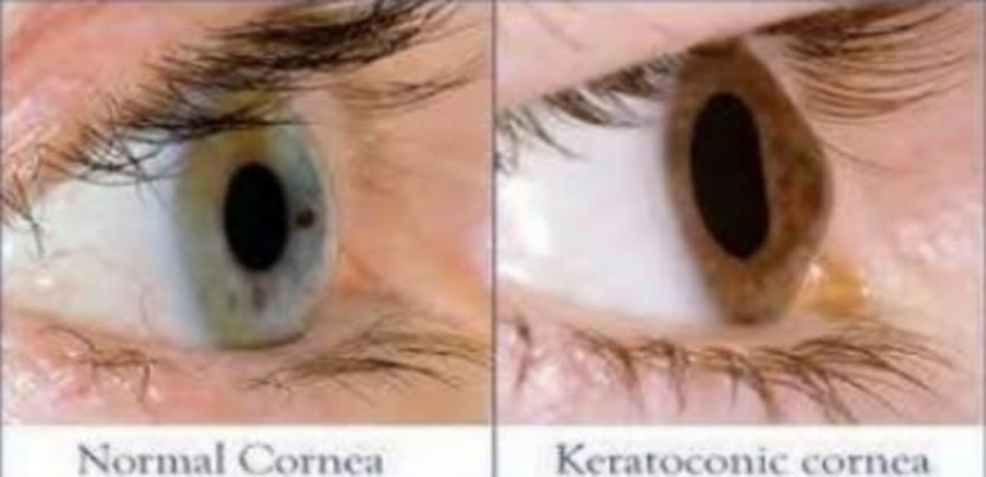
Contact lenses have revolutionized vision correction, offering a convenient and effective alternative to traditional eyeglasses. These tiny, seemingly simple devices are actually complex pieces of technology, composed of several key elements that work together to provide clear vision and comfort. In this blog, we’ll delve into the various components and materials that make up contact lenses, as well as their functions and significancein the realm of vision correction.
1. Material Composition
Contact lenses are primarily made from two types of materials: soft and rigid gas permeable (RGP). Each material offers distinct advantages and is chosen based on the wearer’s specific needs and preferences.
Soft Contact Lenses: Soft lenses are the most commonly prescribed type due to their flexibility and comfort. They are typically made from hydrogels or silicone hydrogels, which are water- absorbing materials that allow oxygen to pass through to the cornea. This helps maintain eye health and ensures that the lenses remain comfortable throughout the day. Silicone hydrogels, in particular, are known for their high oxygen permeability, making them suitable for extended wear.
Rigid Gas Permeable (RGP) Lenses: RGP lenses are made from durable plastics that allow oxygen to pass through the lens material. Unlike soft
lenses, RGPs retain their shape on the eye, which can provide sharper vision, especially for individuals with astigmatism or higher-order aberrations. While they may take some time to adapt to, RGP lenses offer excellent visual acuity and durability.
2. Design and Shape
The design and shape of contact lenses play a crucial role in their functionality and comfort. Lenses are tailored to fit the curvature of the eye and correct specific vision problems such as nearsightedness (myopia), farsightedness (hyperopia), astigmatism, and presbyopia.
Spherical Lenses: These lenses have a uniform curvature across their surface and are used to correct common refractive errors
such as myopia and hyperopia. Spherical lenses are designed to focus light directly on the retina, providing
clear vision.
Toric Lenses: Toric lenses are specially designed for individuals with astigmatism, which occurs when the cornea or lens has an irregular shape. These lenses have different powers in different meridians of the lens to correct the uneven curvature of the eye.
Multifocal Lenses: Multifocal lenses are designed to correct presbyopia, a condition that typically affects individuals over the age of 40 and causes difficulty focusing on close-up objects. These lenses have multiple zones with different powers, allowing wearers to see clearly at varying distances.
3. Surface Coatings and Treatments
To enhance comfort and performance, contact lenses often incorporate various surface coatings and treatments:
Hydrophilic Coatings: These coatings attract and retain moisture, keeping the lenses hydrated and comfortable throughout wear. Hydrophilic coatings are particularly beneficial for soft contact lenses, as they help prevent dryness and irritation.
UV Blocking: Some contact lenses are equipped with UV-blocking capabilities to protect the eyes from harmful ultraviolet radiation. While not a substitute for sunglasses, UV- blocking lenses can help reduce the risk of developing certain eye conditions associated with UV exposure.
Anti-Reflective Coatings: Anti-reflective coatings minimize glare and reflections on the surface of the lenses, improving visual clarity and comfort, especially in challenging lighting conditions.
4. Handling and Care
Proper handling and care are essential for maintaining the effectiveness and longevity of contact lenses. Here are some key tips:
– Cleaning: Clean lenses daily with recommended solutions to remove debris and protein buildup.
– Storage: Store lenses in a clean case filled with fresh disinfecting solution to prevent contamination.
– Replacement Schedule: Follow the prescribed replacement schedule (daily, bi-weekly, monthly) to avoid lens deterioration and reduce the risk of eye infections.
– Avoid Water Contact: Never rinse lenses with water or wear them while swimming to prevent microbial contamination.
5. Innovations in Contact Lens Technology
Advancements in contact lens technology continue to push the boundaries of what is possible in vision correction:
Customized Lenses: Some manufacturers offer custom- made lenses tailored to the unique curvature and prescription needs of individual eyes, providing enhanced comfort and visual acuity.
Extended Wear Lenses: Silicone hydrogel materials have enabled the development of extended wear lenses that can be worn continuously for several days, reducing the need for daily removal and cleaning.
Smart Lenses: Researchers are exploring the integration of sensors into contact lenses to monitor health indicators such as glucose levels in tears, offering potential benefits for individuals with diabetes.
6. Conclusion Contact lenses are remarkable devices that blend advanced materials, precision design, and innovative technologies to provide clear vision and comfort for millions of people worldwide. Whether you prefer the flexibility of soft lenses or the crisp vision of RGP lenses, understanding the elements that make up contact lenses can help you make informed decisions about your eye care needs. As technology continues to evolve, contact
lenses will likely become even more comfortable, durable, and capable of addressing a wider range of vision challenges.