As the world grapples with the growing burden of diabetes, it's essential to acknowledge the devastating impact this disease can have on our eyesight. Diabetes is a leading cause of blindness worldwide, with estimating the prevalence of diabetic retinopathy (DR) at 12.5%, with 4.0% having vision-threatening DR(1), a serious eye condition that can cause vision loss and blindness. In this comprehensive guide, we'll delve into the complex relationship between diabetes and eye health, exploring the ways in which diabetes can affect your vision and providing practical tips and strategies for protecting your eyes.
Understanding the Link Between Diabetes and Eye Disease:
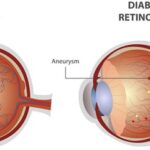
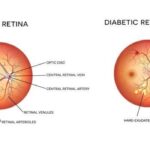
Diabetes can cause damage to the blood vessels in the retina, leading to a range of eye problems(2). The retina is the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye, responsible for converting light into electrical signals that are transmitted to the brain. When diabetes damages the blood vessels in the retina, it can disrupt this process, leading to vision loss and blindness.
There are several eye conditions associated with diabetes, including:
1. Diabetic Retinopathy: This is the most common eye complication of diabetes, causing damage to the blood vessels in the retina. Diabetic retinopathy can cause vision loss and blindness if left untreated.
2. Diabetic Macular Edema: This condition occurs when fluid builds up in the macula, the part of the retina responsible for central vision. Diabetic macular edema can cause blurred vision, double vision, and even blindness.
3. Cataracts: People with diabetes are more likely to develop cataracts (3), a clouding of the lens in the eye. Cataracts can cause blurred vision, double vision, and sensitivity to light.
4. Glaucoma: Diabetes increases the risk of developing glaucoma, a group of eye conditions that can damage the optic nerve (4). Glaucoma can cause vision loss and blindness if left untreated.
Warning Signs of Diabetic Eye Disease
While diabetic eye disease often develops without symptoms in its early stages, there are several warning signs to look out for, including:
– Blurred vision
– Double vision
– Flashes of light
– Floaters
– Pain or pressure in the eyes
If you experience any of these symptoms, it's essential to seek medical attention immediately.
Risk Factors for Diabetic Eye Disease:
While anyone with diabetes can develop diabetic eye disease, there are several risk factors that increase your likelihood of developing this condition. These include:
– Duration of diabetes: The longer you have diabetes, the higher your risk of developing diabetic eye disease.
– Blood sugar control: Poor blood sugar control increases your risk of developing diabetic eye disease.
– High blood pressure: High blood pressure can damage the blood vessels in the retina, increasing your risk of diabetic eye disease.
– High cholesterol: High cholesterol can increase your risk of developing diabetic eye disease.
– Smoking: Smoking can damage the blood vessels in the retina, increasing your risk of diabetic eye disease.
– Family history: If you have a family history of diabetic eye disease, you may be more likely to develop this condition.
Protecting Your Eyes: A Comprehensive Approach
While diabetic eye disease is a serious condition, there are several steps you can take to protect your eyes and reduce your risk of vision loss. Here are some practical tips and strategies for protecting your eyes:
1. Get regular eye exams: Regular eye exams are essential for detecting diabetic eye disease in its early stages. The American Academy of Ophthalmology recommends that people with diabetes have a comprehensive eye exam every 1-2 years.
2. Control your blood sugar: Managing your blood sugar levels is crucial for preventing diabetic eye disease. Work with your healthcare team to develop a personalized treatment plan that includes lifestyle changes and medication.
3. Maintain a healthy blood pressure: High blood pressure can damage the blood vessels in the retina, increasing your risk of diabetic eye disease. Work with your healthcare team to manage your blood pressure through lifestyle changes and medication.
4. Quit smoking: Smoking can damage the blood vessels in the retina (5), increasing your risk of diabetic eye disease. Quitting smoking can significantly reduce your risk of developing this condition.
5. Eat a balanced diet: A healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids can help support eye health. Avoid foods high in sugar, salt, and unhealthy fats.
6. Stay hydrated: Drinking plenty of water can help keep your eyes moist and healthy. Avoid sugary drinks and caffeine, which can dehydrate the eyes.
7. Get regular exercise: Regular exercise can help improve blood flow to the eyes, reducing your risk of diabetic eye disease. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week.
Advanced Treatments for Diabetic Eye Disease:
While prevention and early detection are crucial for managing diabetic eye disease, there are several advanced treatments available for more severe cases. These include:
1. Laser Surgery: Laser surgery can help reduce swelling in the retina and prevent further vision loss. There are several types of laser surgery, including focal laser photocoagulation, grid laser photocoagulation, and pan-retinal photocoagulation.
2. Anti-Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) Injections: Anti-VEGF injections can help reduce swelling in the retina and prevent further vision loss. These injections are typically administered monthly and can be used in combination with laser surgery.
3. Corticosteroid Injections: Corticosteroid injections can help reduce inflammation in the retina and prevent further vision loss. These injections are typically administered monthly and can be used in combination with laser surgery.
4. Vitrectomy: Vitrectomy is a surgical procedure that involves removing the vitreous gel from the eye. This can help improve vision in people with advanced diabetic eye disease.
5. Retinal Detachment Surgery: Retinal detachment surgery is a surgical procedure that involves reattaching the retina to the back of the eye. This can help improve vision in people with advanced diabetic eye disease.
Conclusion:
Diabetes and eye disease are closely linked, but with awareness, proactive care, and regular eye exams, you can significantly reduce your risk of vision loss. By understanding the risks and consequences of diabetic eye disease, you can take the necessary steps to protect your eyes and preserve your vision.
REFERENCE:
1. Vashist, P., Senjam, S. S., Gupta, V., Manna, S., Gupta, N., Shamanna, B. R., Bhardwaj, A., Kumar, A., & Gupta, P. (2021). Prevalence of diabetic retinopathy in India: Results from the National Survey 2015-19. Indian Journal of Ophthalmology, 69(11), 3087–3094.
https://doi.org/10.4103/ijo.IJO_1310_21
2. Mayo Clinic. (n.d.). Diabetic retinopathy. Mayo Clinic. Retrieved March 28, 2025, from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/diabetic-retinopathy/symptoms-causes/syc- 20371611
3. Kiziltoprak, H., Tekin, K., Inanc, M., & Goker, Y. S. (2019). Cataract in diabetes mellitus. World Journal of Diabetes, 10(3), 140–153. https://doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v10.i3.140
4. Glaucoma Research Foundation. (n.d.). The relationship between diabetes and glaucoma. Glaucoma Research Foundation. Retrieved March 28, 2025, from https://glaucoma.org/articles/the-relationship-between-diabetes-and-glaucoma
5. Retinal Medical Group. (2024, September 26). How smoking affects retinal health. Retinal Medical Group. Retrieved March 28, 2025, from https://www.retinalmd.com/blog/how- smoking-affects-retinal-health