Presbyopia affects 1.8 billion people worldwide, according to the World Health Organization (WHO). The American Academy of Ophthalmology (AAO) describes it as a common age-related decline in the eye’s near focusing ability which is usually physiologically-induced. Usually nobody escapes presbyopia, the only difference is its time of onset usually influenced by eye health state which delays or accelerate it. Typical symptoms of presbyopia includes headache, blurred vision, eye strain and far positioning of objects for easier focus.
Near activities that require enough accommodation includes reading, sewing, using gadgets i.e. mobile phone, tablet, computers etc. It tends to mimic but stills differs from hyperopia, since accommodation is reduced in both of them unlike myopia.
With increasingly dependaent near activities and an increased digital near demand. A decline in accommodative ability may end up being detrimental to the extent where it causes an irreversible loss of accommodative ability, in turn affecting the overall quality of life of those that are affected.
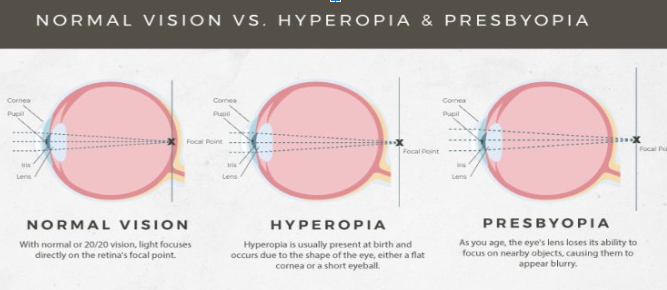
Although Presbyopia is not completely age-dependent. It is usually experienced from 40 years and above, but could occur earlier in hyperopic (far-sighted) patients.
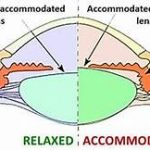
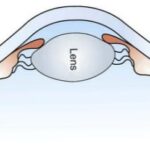
It is hypothesized to be caused by either a weakening of the ciliary muscles or a loss of lens elasticity which in turn affects near focusing ability.
Usually, three things come to mind, when you think of presbyopia management, i.e. either optical and surgical or pharmacological means or all of the above which is either invasive or non-invasive.
Optics is a non-invasive means that involves the use of glasses or contact lenses so as to try to compensation for the additional visual demand caused by this condition while surgical methods simply attempts to modify or repair the structures responsible for vision and/or accommodation, i.e. either the cornea or the crystalline lens that could have, in a way induced it, so as to try and aid accommodation. Both glasses and contact lenses available in bi-, tri- and multifocal (progressive) forms so as to fully satisfy all the extents and limits of vision.
This is the most commonly used remedy for presbyopic treatment. It is important to note that the spectacle lens has also undergone advances to aid presbyopes better. The latest of them being the “free form digital progressive lenses” which allows for tailored individualised presbyopic correction and offers pseudo-dynamic accommodation with eye seeing through wider optical zones.
Surgery is usually an invasive means that involves the use of intraocular implants, use of lasers and ablation therapies e.g. LASIK, corneal reshapening (inlays), monovision, sclera micro-excisions or sclera micro-inserts. All of these methods target structures in the eye that is directly or indirectly influences accommodation. By doing so, it allows for a natural improvement and/or recovery to occur. However, it usually almost always comes with some compromises, such as monovision resulting from intraocular implants or laser therapies. This is why, in most cases, even though success is achieved from surgery, presbyopes may still have to fall back to optical aids for assistance.
In terms of pharmacology, It is a non-invasive means for presbyopia treatment. Over the decades, several drugs has been experimented on, certified and accepted due to their positive outcome and reviews. All approved drugs usually work based on two mechanisms of actions namely; Miosis (thus creating a pinhole effect) and increase in the field of view increase.
Pharmacological advances in the management of presbyopia includes:
- Optimized pilocarpine (AGN-190584/Allergan).
- Microline (Eyenovia).
- Nyxol (Ocuphire Pharma).
- CSF-1 (Orasis Pharmaceuticals).
- BRIMOCHOL (Visus Therapeutics).
- Diclofenac.
Now the latest pharmacological advances in the management of presbyopia includes:
- PresbiDrops.
- PresbyPlus.
- Presbycarrod.
- PRX-100 (Presbyopia Therapies)
- Collagen cross-linking.
- Synthetic inlays.
More clinical trials and reviews are still ongoing with respect to presbyopic treatment.
Clearly, presbyopia poses an importance public health challenge since it can affects one’s productivity and in turn affects economic independence in its entirety.
It is important therefore to establish the cause, onset and severity of presbyopia early enough, so as to maximize good treatment results.