Refractive errors are usually caused by structural irregularities in our eyes. They impact on our visual health. One of the most common refractive error is Hyperopia or Farsightedness.
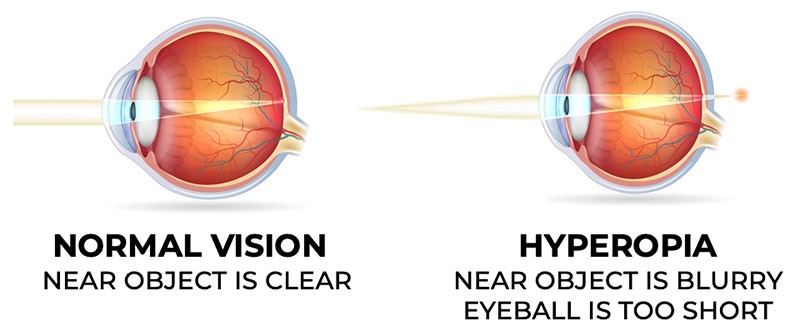
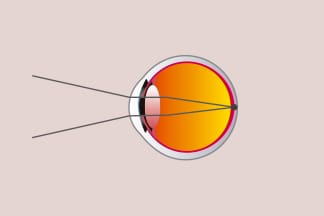
It mainly occurs when the distance between the retina and cornea is to short, that causes, Light rays to focus behind the retina, instead of directly on it. As a result the retina receives a blurred image.
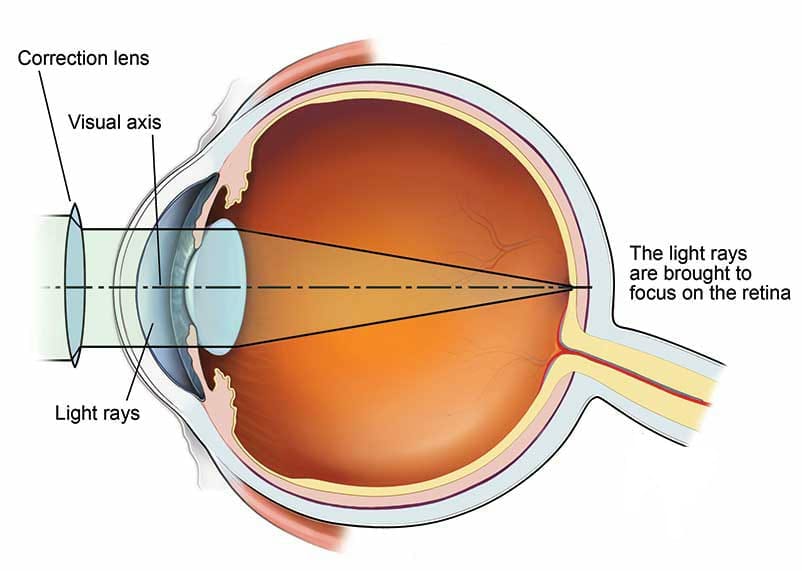
The aim of treating far sightedness is to focus light on the retina through the use of corrective glasses, lens or by refractive surgery.
Let’s discuss about the treatment of hyperopia.
- Corrective glasses
Eye glasses are the simplest and most common therapy for treating hyperopia or far sightedness. Basic principle of the therapy is to converge and focus The light rays on the retina with the help of convex or plus lens.
- Wearing prescription mentioned lens treats far sightedness by opposing the decreased curvature of the cornea. The variety of lenses in wide and includes single vision bifocals trifocals and progressive multifocals and the other hand,
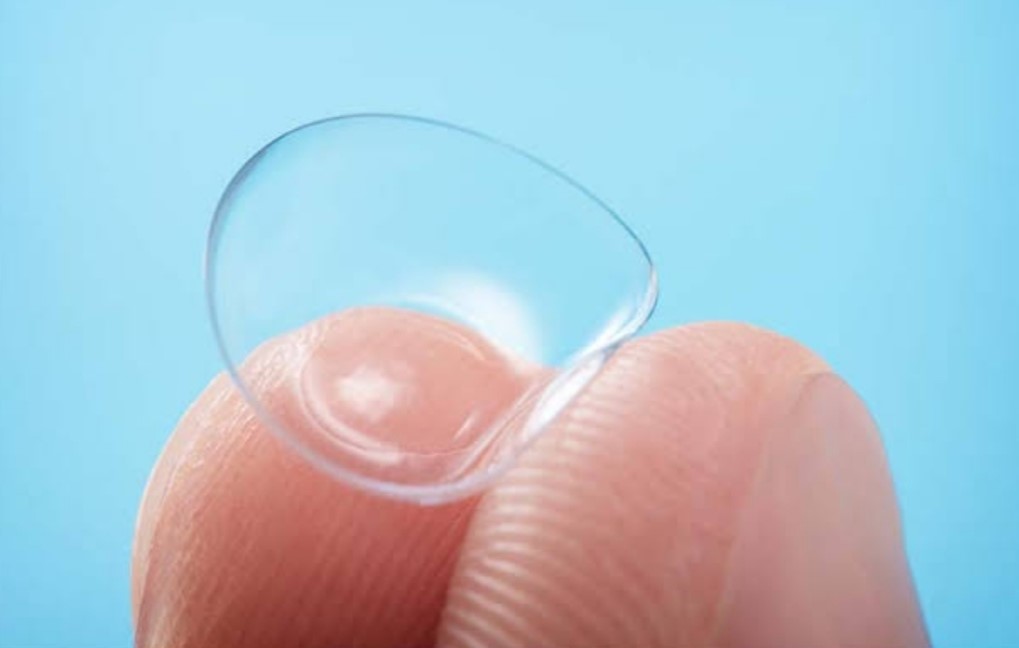
- Contact lens
Contact lenses are varies in materials and designs including soft and rigid gas permeable in combination with spherical, toric, multifocal and monovision designs.
Some basics rules for prescribing glasses for Hyperopia treatment.
- Total hyperopia is determined and convex lenses are prescribed after performing full cycloplegic correction (particularly in children).
- Refraction under atropine is compulsory for small children. Children younger than 4 years of age regarding hyperopic correction may normally except full cycloplegic correction in older children it may be reduced.
- Slowly increased this pedicle correction add six months gap till the patient accept manifest hyperopia.
- If the patient have small total manifest hyperopia that is 1 D or less, correction may be require.
- Astigmatism should fully corrected.
- Hyperopia should be under corrected by about 1 to 2 D when the patient have exophoria.
- In the presence of associated amblyopia or lazy eye in one eye full correction and occlusion therapy should be given.
- In case of accommodative convergent squint full cycloplegic correction should be given.
Prescription of convex lenses
- Glasses are most comfortable safe and easy method for treating hyperopia. In other hand,
- Contact lenses are useful for unilateral hyperopia. For cosmetic reasons contact lens may be prescribed when the refractive power of the eyes were stabilized.
Surgical and laser therapy
- Phakic Intraocular lens (IOL) implant are used to correct high degree of a hypermetropia, about +4 D to +10 D. Phakic IOLs designed as foldable, convex and thin. Lens implanted in the posterior chamber behind the iris and in front of the natural crystalline lens.
- Refractive lens exchange (RLE), in this procedure be natural rains lynch is extracted by implantation of a foldable IOL.
- LASIK or Laser in situ , is Effective in correction of hyperopia up to +4 D. In this procedure a thin, hinged flap is made in the cornea. Elisar is used to adjust the carbs of the cornea that basically corrects the far sightedness. In LASIK surgery cases, there are less discomfort and the recovery rate is much higher than any other corneal surgeries. LASIK provides a long lasting alternative to eye glasses or contact lens.
- Laser assisted sub- epithelial keratectomy or LASEK, In this procedure an ultra thin flap is created in the epithelium layer of the cornea. Then a laser is used for reshape the cornea’s outer layer, and changing its curve, then replaces the epithelium.
- Photo refractive keratectomy or PRK, the principle of the procedure is similar to LASEK surgery, except complete removal of the epithelium. The cornea is reshaped by using a laser. In this surgery the epithelium is not replaced it will grow back naturally.
- Conductive keratoplasty is a non invasive procedure in which radio frequency is used to correct low hypermetropia with or without astigmatism in it. This procedure is effective for correcting hyperopia up to +3 D.
Laser surgery may not be suitable for
- Diabetics patients
- Pregnant or breastfeeding woman.
- Having a weakened immune system.
- Have other I problems like glaucoma or cataracts.