Different Tumors of Eyelids
Eyelid tumors can be concerning, both for their potential impact on vision and thecosmetic implications. Tumors can be benign (non-cancerous) or
malignant (cancerous) and vary widely in their characteristics. Understanding the different types of eyelid tumors, their symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options can help individuals take proactive steps regarding their eye health.
Common Types of Eyelid Tumors
1. Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC)
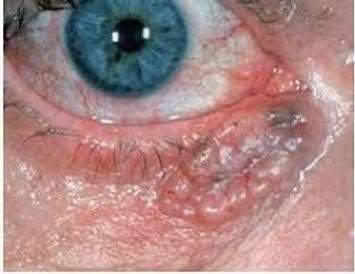
Basal cell carcinoma is the most common type of skin cancer, frequently found on the eyelids. It typically appears as a pearly or waxy bump or a flat, flesh-colored lesion. BCC often grows slowly and rarely metastasizes, but it can invade surrounding tissues if left untreated.
Symptoms:
A small, shiny bump
A sore that doesn’t heal
Red or scaly patches
Treatment: Treatment usually involves surgical excision, Mohs micrographic surgery, or topical chemotherapy for superficial BCC.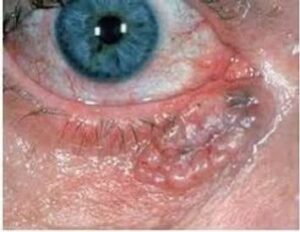
2. Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC)
Squamous cell carcinoma is another common eyelid tumor. It may appear as a firm, red nodule or a flat lesion with a scaly crust. SCC has a higher risk of metastasis compared to BCC, making early detection crucial.
Symptoms:
A firm, red nodule
A scaly patch that bleeds or crusts
Rapid growth of a lesion
Treatment: Surgical removal is the primary treatment, often followed by radiation therapy if the cancer is aggressive or has spread.
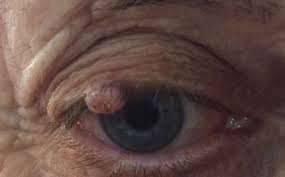
3. Melanoma
Melanoma is less common but more aggressive than BCC and SCC. It can develop in existing moles or appear as a new dark spot on the eyelid. Melanoma has a higher risk of spreading to other body parts.
Symptoms:
A dark, asymmetrical mole
Irregular borders
Color variation within the mole
Treatment: Treatment often involves surgical excision, sometimes with sentinel lymph
node biopsy, followed by immunotherapy or targeted therapy for advanced cases.
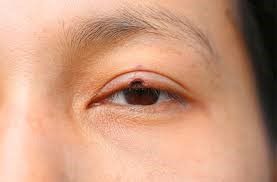
4. Seborrheic Keratosis
Though not a cancer, seborrheic keratosis can resemble a tumor. These benign growths appear as raised, wart-like lesions that can be brown, black, or light tan. They are more common with aging.
Symptoms:
Warty, raised lesions
Varied colors (tan to black)
Usually asymptomatic
Treatment: These lesions do not require treatment unless they cause discomfort or cosmetic concerns. Removal options include cryotherapy, curettage, or laser therapy.
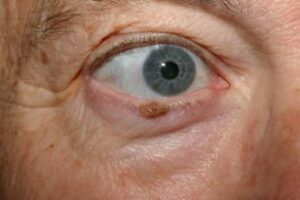
5. Chalazion
A chalazion is a blocked oil gland in the eyelid, leading to a firm lump. While not a tumorin the traditional sense, it can mimic one and cause discomfort or cosmetic issues.
Symptoms:
A painless bump on the eyelid
Swelling or redness
Possible tenderness
Treatment: Most chalazia resolve on their own, but persistent cases may require warm compresses, corticosteroid injections, or surgical drainage.

6. Papilloma
Eyelid papillomas are benign tumors that appear as small, wart-like growths. They can be caused by human papillomavirus (HPV) and are usually painless.
Symptoms:
Small, raised lesions
Can be skin-colored or pigmented
Treatment: Removal is often performed for cosmetic reasons or if the growth is bothersome.
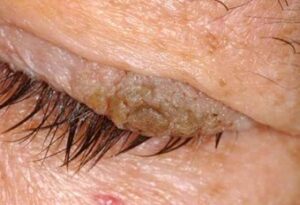
7. Lymphoma
Though rare, lymphoma can occur in the eyelids. It typically presents as a swollen, firm mass that may be mistaken for other lesions.
Symptoms:
Swelling of the eyelid
Possible redness
Vision changes if it affects the eye
Treatment: Treatment may involve chemotherapy, radiation, or targeted therapies
depending on the type and stage of lymphoma.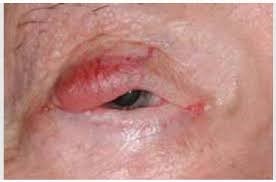
Diagnosis of Eyelid Tumors
Diagnosing eyelid tumors typically involves a thorough eye examination and medical history. An ophthalmologist may use various techniques, including:
Biopsy: Removing a small sample of tissue for laboratory analysis. Imaging Tests: MRI or CT scans may be used to assess deeper structures.
Dermatoscopy: A specialized tool to examine skin lesions closely.
Treatment Options
Treatment varies based on the type and stage of the tumor:
Surgical Excision: The most common treatment for malignant tumors. Mohs Micrographic Surgery: A technique that removes cancerous tissue layer by layer while preserving healthy tissue.
Radiation Therapy: Often used for cancers that are difficult to remove surgically.
Chemotherapy: Typically reserved for more advanced cases. Prevention and Self-Care While not all eyelid tumors can be prevented, several strategies can reduce risk:
Sun Protection: Use sunglasses with UV protection and apply sunscreen around the eyelids.
Regular Check-ups: Annual eye exams can help catch tumors early.
Awareness of Changes: Be vigilant about any changes in eyelid appearance, and consult a healthcare professional if you notice anything unusual.
Conclusion
Eyelid tumors encompass a range of conditions, from benign growths to serious malignancies. Understanding the various types, their symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for maintaining eye health. Regular check-ups and awareness of changes in your eyelids can aid in early detection and improve outcomes. If you notice any unusual growths or changes, seeking medical advice promptly is essential