Introduction:
Follicular Conjunctivitis occurs when follicles — collections of immune cells located on the conjunctiva and under the eyelid — become enlarged and inflamed. It can develop due to adenoviruses, herpes virus, bacterial infection such as chlamydia or a toxic response. Follicular conjunctivitis is the term used when a case of conjunctivitis presents with follicular inflammation. Inflamed follicles typically develop in conjunctivitis or pink eye caused by a virus. About six million cases of pink eye are reported in the U.S. each year, with viral being the most common type. Although follicular conjunctivitis is not typically serious, an underlying cause, such asherpes simplex or chlamydia infection, may lead to vision loss if left untreated.
Signs of follicular conjunctivitis :
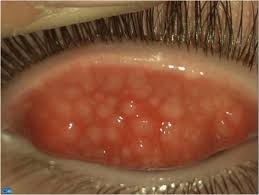
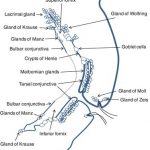
Enlarged follicles can be found on the eye’s conjunctiva. The conjunctiva is a thin, clear tissue that covers the inside of the eyelids and lies above the sclera (the white area) at the front of the eyeball.
Although inflamed follicles are usually seen on the eyelid’s conjunctiva, they can also appear on
the conjunctiva above the sclera.
Symptoms that typically accompany follicular conjunctivitis include:
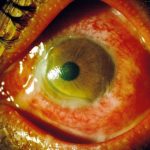
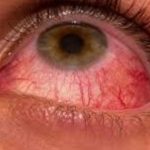
Redness of the eyes
Pain around the eyes
Watery eyes
Overall swelling and irritation of the conjunctiva
Sensitivity to light
Causes follicular conjunctivitis:
Most viral conjunctivitis will have a follicular reaction. However, follicular conjunctivitis can also occur due to other causes, such as bacteria and a toxic response to eye drops.
Virus- Follicular conjunctivitis caused by a virus usually has a rapid onset that affects one eye and then moves to the other eye within a week. Symptoms include watery, red eyes and swollen lymph nodes. These usually go away on their own without treatment. Adenovirus
Viruses account for up to three-fourths of infectious conjunctivitis. The majority are caused by adenoviruses, a common cause of respiratory illnesses that cause cold-like symptoms. As a result, follicular conjunctivitis may be seen alone (as a mild form of viral conjunctivitis caused by an adenovirus) or accompanied by:
Contagious viral pink eye (Epidemic keratoconjunctivitis)
Sore throat and fever (pharyngoconjunctival fever)
Stomach distress (due to adenovirus infection of the gastrointestinal tract)
Herpes virus
Herpes simplex virus that infects the eye, known as ocular HSV, can result in follicular conjunctivitis. Approximately 50,000 cases of ocular HSV are diagnosed yearly in the U.S. These cases include new and recurrent infections, which can be triggered by causes that vary from UV radiation to psychological stress. In addition to a follicular reaction, ocular HSV causes damage to the cornea that causes a classic branching (dendritic) appearance.
Bacteria
Follicular conjunctivitis can result from chlamydia , a common bacterial infection. It can present as inclusion conjunctivitis (an STD and the most common form in developed countries) or trachoma (found in the developing world, commonly due to poor sanitation). Trachoma causes
more cases of blindness in the world than any other infectious disease. In some instances, it infects individuals when they are only children.
Toxic reaction
Not all types of follicular conjunctivitis are due to an infection. A toxic reaction, such as an inflammatory response to an eye drop or other irritants, can cause some follicular conjunctivitis. One such irritant is molluscum contagiosum infection, which causes small white growths on the body. Acute vs. chronic follicular conjunctivitis
Follicular conjunctivitis can have a rapid onset (acute) or a longer-lasting course (chronic).
Acute Viral-
Up to 80% of all cases of acute conjunctivitis are thought to be caused by a virus. The infections that can cause acute or rapid onset of follicular conjunctivitis include:
Adenovirus
Herpes virus
Infectious mononucleosis
Epstein-Barr virus infection
Symptoms include redness, pain, watery eyes and light sensitivity.
Bacterial
Chlamydial bacterial infections can cause a rapid onset of follicular conjunctivitis in the form of a condition called inclusion conjunctivitis. This condition causes pus-like discharge, red eye and irritation, typically in one eye but sometimes in both eyes. Chronic
A long-term follicular response is often seen in cases of:
Trachoma due to chlamydia infection
Toxic conjunctivitis from eye drops
Molluscum contagiosum infection
Trachoma
Chlamydia can also result in chronic follicular conjunctivitis in the form of trachoma, the leading preventable cause of blindness worldwide. It is most often seen in developing countries. In poor countries where trachoma is widespread, children are particularly vulnerable. Trachoma is classified into five progressive stages, the first stage being follicular conjunctivitis, typically found on the upper conjunctiva.
Toxic conjunctivitis
An inflammatory response to eye drops and preservatives can cause chronic follicular conjunctivitis.
Treatment:
In cases of follicular conjunctivitis due to an adenovirus, symptoms such as watery, red eyes and swollen lymph nodes usually go away on their own without treatment. Artificial tears may be used for comfort.
In more serious cases, such as a chlamydial infection, treatment will be determined by a doctor. Chlamydial conjunctivitis treatment typically includes either antibiotic eye drops or oral antibiotics. In cases of ocular HSV, antiviral eye drops and steroid eye drops may be prescribed. For cases of follicular conjunctivitis caused by a toxic inflammatory reaction, an eye doctor will discontinue the offending drops and provide guidance on additional treatment.