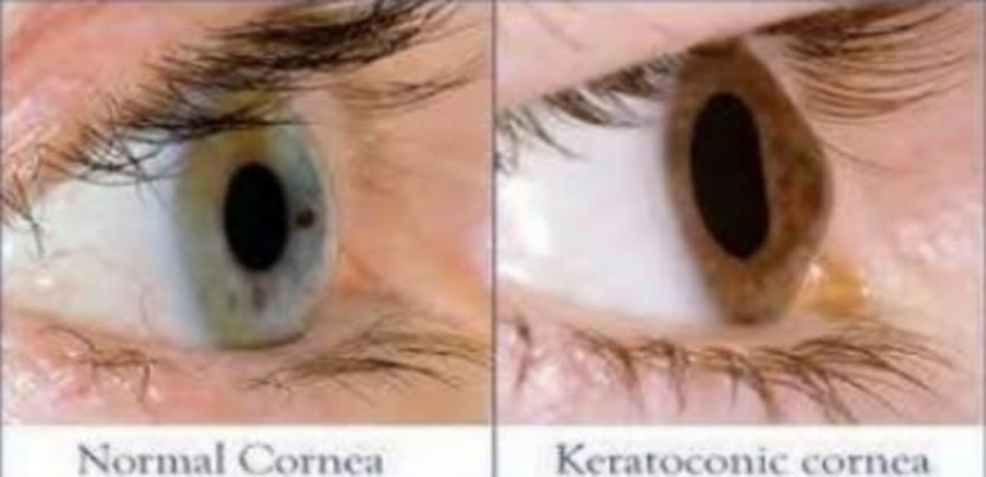
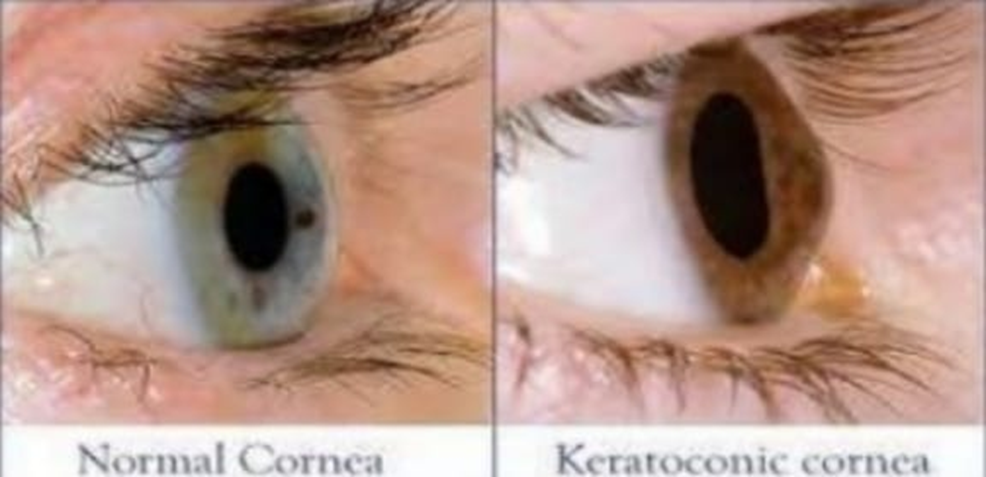
Keratoconus is a non-inflammatory degenerative abnormal condition of the cornea which causes a conic deformity. It is usually bilateral and progressive. The thinning is mostly central and makes the cornea steeper by several diopters. This condition begins at puberty and progresses with varying degrees in individuals usually till 40-45 years of age. The protrusion leads to high astigmatism, myopia, and irregular astigmatism. Due to the irregular refraction through the eye, vision may not improve to pinhole vision with spectacles.
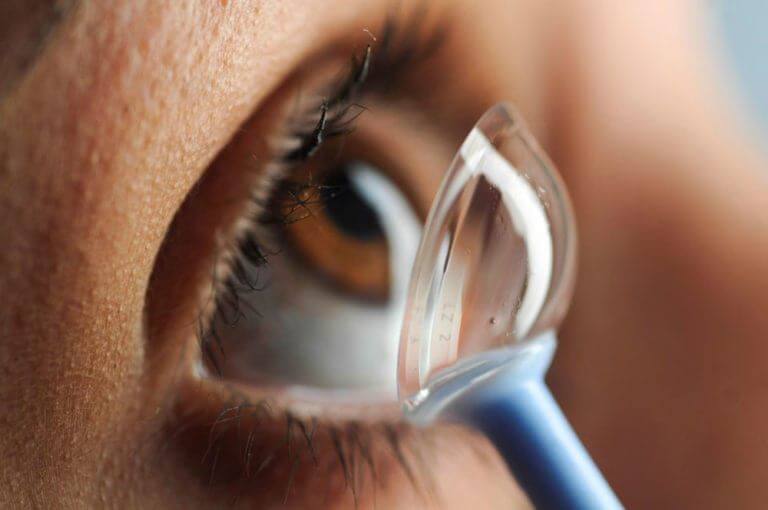
A rigid contact lens is the best method of vision correction.
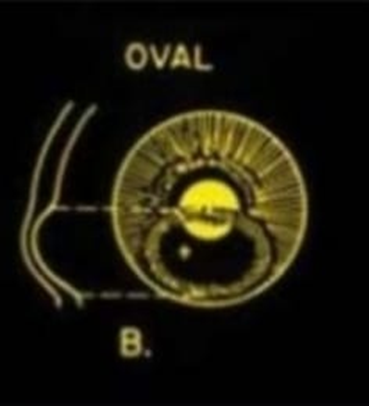
SHAPE AND POSITION OF CONE :
This may be helpful when selecting the design of a contact lens to fit the cornea.
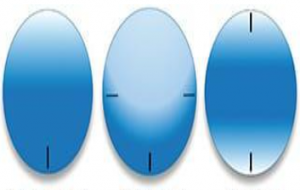
- Nipple cone :
Nipple cones are round and small.
Usually occur near the optical axis or slightly decentred inferonasal.

B. Oval cone:
The area of the cone is larger than nipple cones usually displaced inferno-temporally.
A larger diameter contact lens is required.
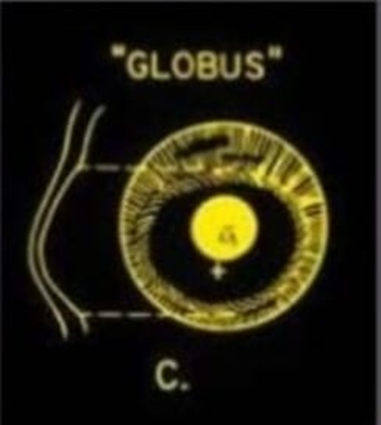
C. Globus cone:
Globus cones are the largest, involving up to 75% of the cornea’s most challenging type to fit.
SPECTACLE MANAGEMENT :
Mild keratoconus in the early stage can be corrected with spectacles.
As the cornea steepens and becomes more irregular, glasses are not capable of providing adequate visual improvement.
Once glasses fail to provide adequate visual function, contact lens fitting is required.
CONTACT LENS MANAGEMENT :
Contact lens wear :
Improves VA by creating a regular anterior refractive surface.
Does not prevent the progression of keratoconus.
May occasionally induce or hasten progression of keratoconus.
Contact lenses give sharper vision than spectacles even in mildest cases of keratoconus.
As keratoconus progresses spectacle’s best-corrected acuity becomes unsatisfactory.
Contact lens fitting in a keratoconic cornea is much more difficult – because of the irregular anterior surface of the keratoconic cornea.
Spectacle magnification:
1.Mild keratoconus in early stage can be corrected with spectacles.
2. As the cornea steepens and becomes more irregular, glasses not capable of providing adequate visual improvement.
3.Once glasses fail to provide adequate visual function, contact lens fitting is required.
CONTACT LENS MANAGEMENT :
Contact lens wear :
Improves VA by creating a regular anterior refractive surface.
Does not prevent the progression of keratoconus.
May occasionally induce or hasten the progression of keratoconus.
Contact lenses give sharper vision than spectacles even in the mildest.
As keratoconus progresses spectacle’s best-corrected acuity becomes unsatisfactory.
Contact lens fitting in a keratoconic cornea is much more difficult because of the irregular anterior surface of the keratoconic cornea.
CONTACT LENS FITTING TECHNIQUE :
The trial method is the best and the only possible method of fitting contact lenses in keratoconus. Once cannot empirically calculate the lens curvatures and power.
- In case of very early keratoconus, soft lenses can be tried, provided the vision improves satisfactorily with them.
- The second choice is the rigid spherical lens. This also works in early keratoconus.
- Soper design is the choice in moderate to advanced cases.
- Piggy back or special designs like Rose K lenses can be tried in cases where the rest fail.
FITTING STEPS :
- Do refraction and record best corrected spectacles visual acuity. Though this will not match with the contact lens power in most of the cases.
- Do keratometry or topography as far as possible.
- Perform a slit lamp anterior segment examination to rule out any contraindication.
- Select the trial lens from the special keratoconus trial set, initial lens is flatter than the K.
- Evaluate the fluorescein pattern to achive the good fit, i.e. the three point touch.
Central touch of 2-3 mm.
Thin band of touch at lens periphery.
Review the centration and the movement with the blink .
- Exchange lenses until the light desirable apical touch is achieved.
- Do over correction and finalize the power.
KERATOCONUS-FITTING PHILOSOPIES :
Three different general fitting philosophies:
1.Apical bearing
2.Apical clearance
3.Three point touch
APICAL BEARING – FLAT FITTING :
- The flat fitting method places almost the entire weight of the lens on the cone.
- Good visual acuity is obtained as a result of apical touch.
- Alingment can be obtained in early keratoconus : between, flat fitting lenses can lead to progression/acceleration of apical changes and corneal abeasions.
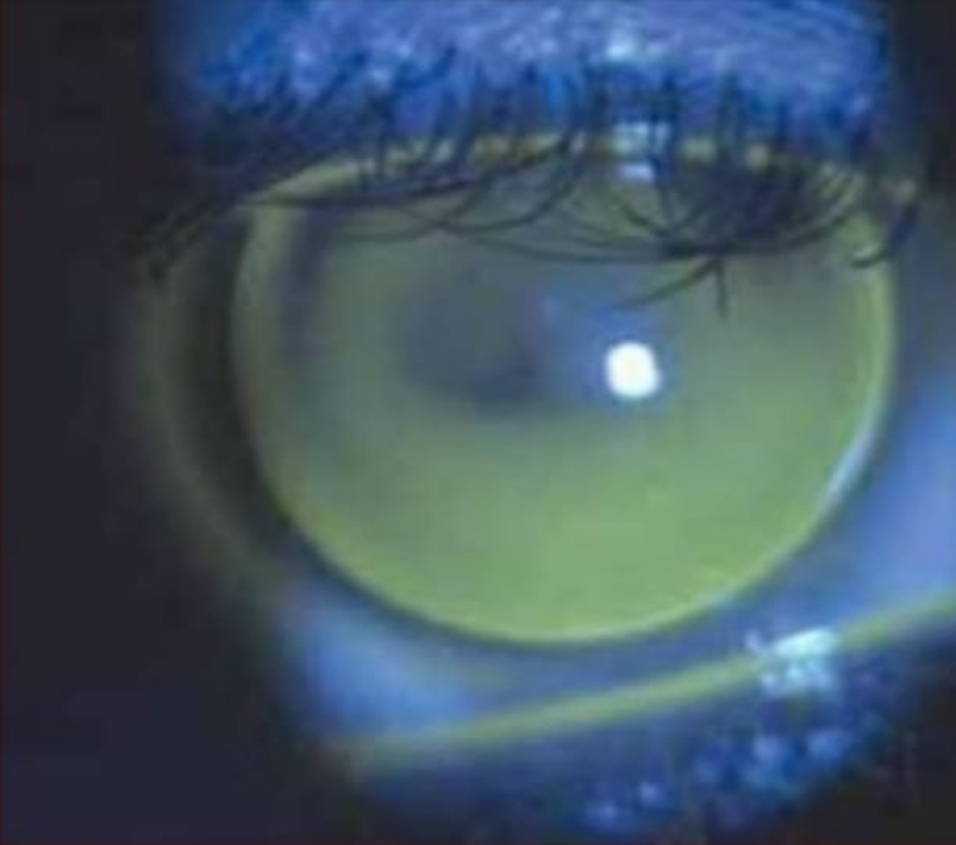
APICAL CLEARANCE :
- The lens vaults the cone and clears the central cornea, resting on the paracentral cornea.
- Apical clearance would minimize trauma to the central cornea.
- The potential advantages of reducing central corneal scarring are out weighted by the disadvantages of poor tear film, corneal edema, and poor visual acuity as a result of bubbles becoming trapped under the lens.
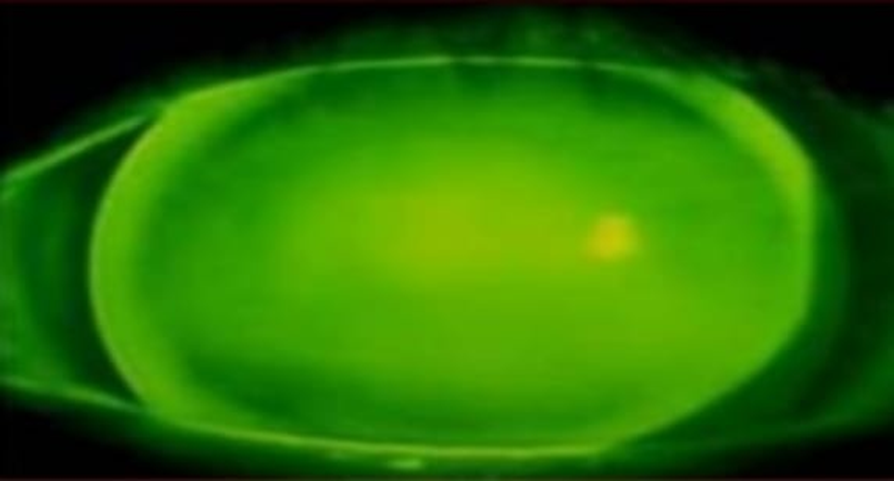
THREE – POINT TOUCH :
- The aim is to distribute the weight of the contact lens as evenly as possible between the cone and peripheral cornea.
- Lens lightly touches the peak of the cone then a very low vault over the edges of the cone, and lastly a thin band of touching near the edge of the lens.
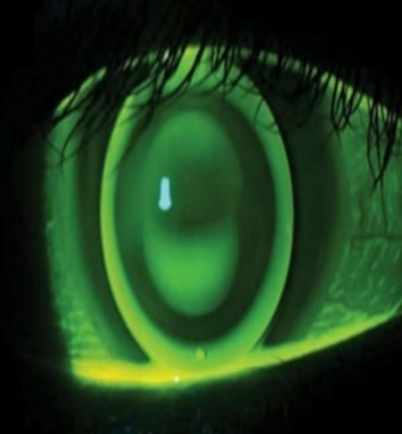


IF ANY PATIENT CANNOT TOLERATE RGP LENSES :
COMBINED LENS SYSTEM :
- PIGGY BLACK SYSTEM : Rigid lens over a hydrogel lens, increases comfort resulting in adequate wearing time with good vision.
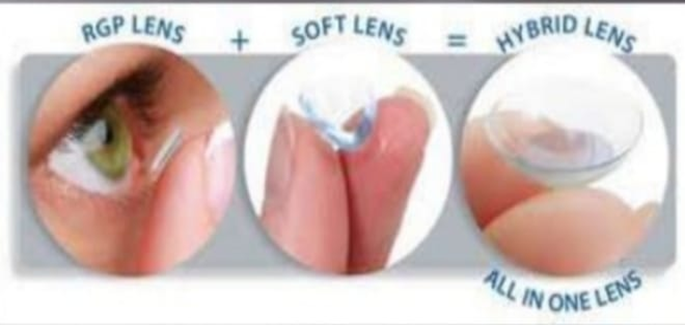
HYBRID LENS SYSTEM :
A hybrid lens has a rigid central portion with the optical neutralizing properties of a normal rigid lens and a soft peripheral portion for improved wearer comfort .
FULLY KERATOCONIC DESIGNED LENSES ?
- Rose K family of lens
- Scleral and Mini sclera lens
Rose K lens :
- Unique keratoconus lens design with complex computer-generated peripheral curves based on data collected by Dr. Paul Rose of Hamilton, New Zealand.
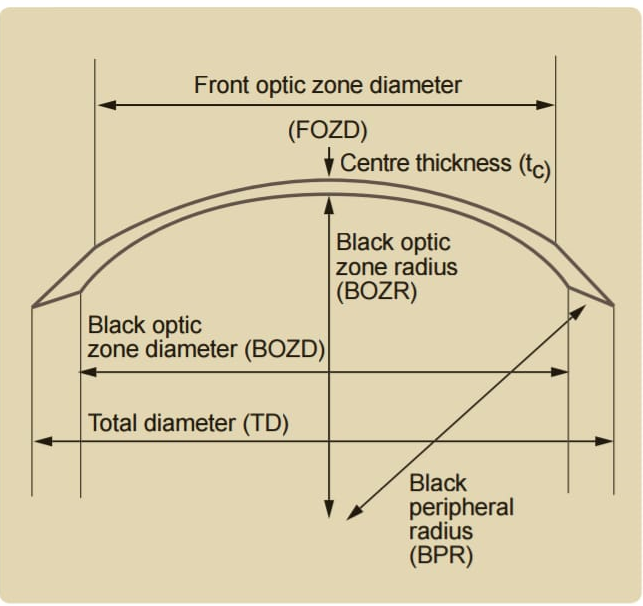
- Standard diameter : 8.7 mm
- BOZD decreases and axial edge lift increases as base curve steepens.
- Every individual rose K2 lens has its own aspheric (ecc).
- Value on the front and back, computer designed to minimize spherical aberration.

Rose K2 family of lenses :
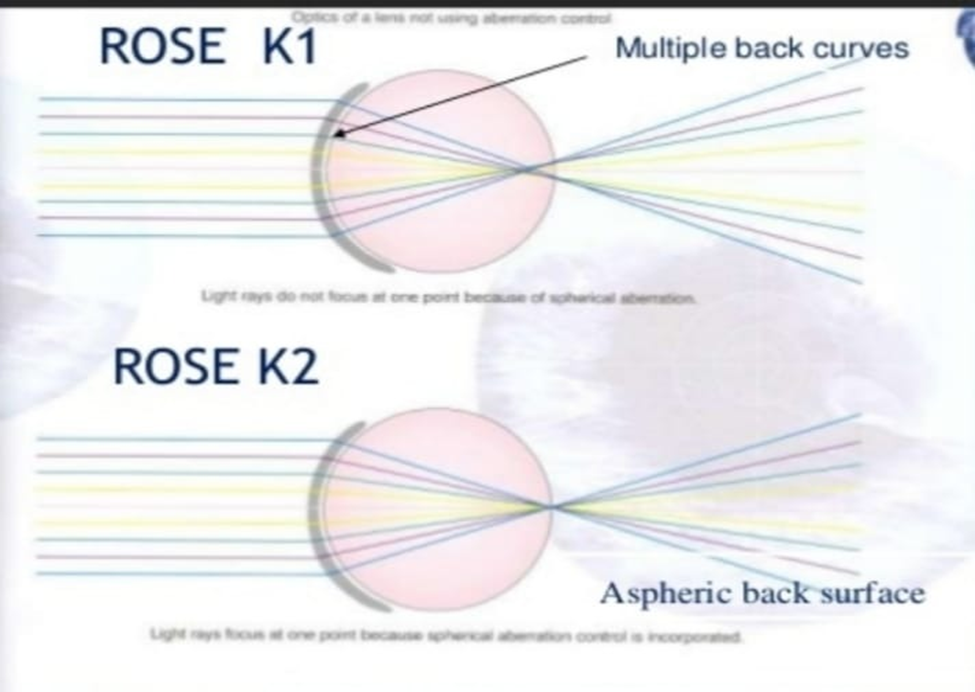
Rose K2 XI :
INDICATIONS : Keratoconus Pellucid Marginal Degeneration , Post Graft , Corneal Rings , Post – Lasik ectasia and dry eye.
Rose K2:
INDICATIONS : Oval Keratoconus, Nipple Keratoconus & early Pellucid Marginal Degeneration.
Rose K2 NC :
INDICATIONS : Moderate & Steep Nipple Cones.
Rose K2 IC :
INDICATIONS : Pellucid Marginal Degeneration, Keratoglobus, Oval Keratoconus, LASIK-induced Ectasia and Post Graft.
Rose K2 PG :
INDICATIONS : For patients who undergone penetrating keratoplasty, Oval Keratoconus, Nipple Keratoconus and LASIK .
SCLERAL AND MINI SCLERAL LENS :

MINI SCLERAL LENSES :
Lens diameter : 15.0 mm and 18.0 mm
- Bear on the sclera &
- Vault the cornea
Design to fit all irregular corneas which don’t tolerate any other RGP or hybrid/soft lens.
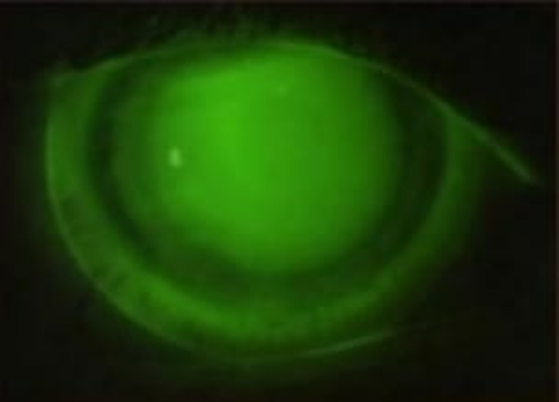
OPTICS OF MINI SCLERAL LENS :
- Cornea is completely vaulted and almost perfect opposite corneal shape is created by tears pooling between the cornea and back surface of keratoconic surface ultimately restoring uniform optical lens and elimination of astigmatism.
- This result in less ghosting and much crisper vision.
ADVANTAGES :
- Better comfort
- Less mechanical trauma to the cornea
- Better vision
Boston (PROSE) scleral lens :
PROSE is an acronym for “ Prosthetic Replacement of the Ocular Surface Ecosystem “.
Customized prosthetic corneo – scleral devices for each patient’s condition and unique eye shape.
Prosthetic devices used in prose are transparent domes, about the size of a nickel, made of gas permeable plastic ( Boston XO2 and Menicon Z ) that allows oxygen to reach the ocular surface.
PROSE creates :
A new transparent , smooth optical surface over the irregular, damaged or diseased cornea.
An expanded artificial tear reservoir that provides constant lubrication while maintaining necessary oxygen supply.
KERATOCONUS FITTING CONSIDERATION :
- Cone position , cone sized and shape , degree of myopia and corneal astigmatism.
- Corneal radius ( central and steepest ) , corneal toricity.
- Corneal topography.
- Disease progression
– Degree
-Rate
- Visual acuity
- Contact lens tolerance.