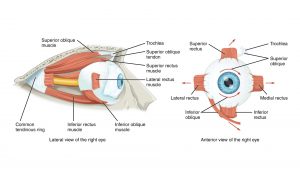
Eye exercise or visual training is simply brain training for the eyes. While muscles, speed, and stamina are important, the eyes are an athlete’s most critical sensory tool. Visual training uses specific exercises to make an athlete’s eyes and brain work faster and better together.
The goal is to improve how quickly and accurately an athlete can see, process, and react to the game. It’s about turning a good performer into an exceptional one by upgrading their ability to perceive and interact with the competitive environment.
Sports vision training encompasses specialized programs designed to improve the visual skills athletes need to excel in their respective sports. Unlike traditional eye exams that focus primarily on visual acuity, sports vision training addresses the complex interplay between the eyes and brain, targeting specific abilities such as reaction time, hand-eye coordination, depth perception, and tracking accuracy. This targeted approach
recognizes that athletic performance depends heavily on how efficiently the visual system processes information and translates it into physical action.
The science behind eye exercises centers on training eye muscles and enhancing communication between the eyes and brain. When athletes engage in targeted visual exercises, they strengthen the neural pathways responsible for visual processing, leading to improved reaction times and enhanced peripheral awareness. This
neuroplasticity allows the visual system to adapt and optimize performance, much like how physical training strengthens muscles and improves coordination. Core benefits for eye exercise
Enhanced focus and concentration: The biggest benefit of eye exercises for athletes is giving them super-sharp focus. These workouts train the eyes to lock onto what’s important, like tracking a speeding ball without losing it, spotting a small opening in the defense. When the game drags on, athletes with this training can keep their focus and not get visually tired. This means they’re less likely to miss a crucial detail late in the game, which is often when games are won or lost
Improved reaction time: Visual perception enhancement through structured eye exercises significantly reduces reaction time, providing athletes with a competitive edge in fast-paced sports environments. When the visual system processes information more efficiently, athletes can respond to stimuli more quickly, whether reacting to a sudden pass in basketball or responding to an opponent’s movement in tennis. This improved reaction time often represents the difference between successful defensive plays and missed opportunities
Better eye-hand coordination: Stronger eye muscles contribute directly to improved hand-eye coordination, a critical skill across numerous sports disciplines. Eye exercises that focus on tracking moving objects help athletes develop the precise coordination necessary for catching, throwing, hitting, and manipulating sports equipment. This enhanced coordination translates into more accurate passes, better ball control, and improved precision in technical movements
Enhanced depth perception: Depth perception training helps athletes judge distances quickly and accurately, which proves essential in sports requiring precise spatial awareness. Whether judging the distance to a basketball hoop, timing a jump in volleyball, or positioning for a soccer header, improved depth perception enables athletes to make more accurate spatial calculations during dynamic play situations
Expanded peripheral vision: Peripheral awareness allows athletes to notice movement and objects outside their direct line of sight, providing crucial environmental awareness during competition. Sports that require constant awareness of multiple players, such as soccer, basketball, and hockey, benefit tremendously from enhanced peripheral vision. Athletes with well-developed peripheral awareness can anticipate plays, avoid collisions, and identify scoring opportunities that others might miss.
Types of exercises and their benefits for athletes
Saccadic Eye Movement Training: Saccadic exercises target the rapid eye movements essential for tracking fast-moving objects and shifting visual attention between multiple targets. Athletes who completed structured saccadic training programs showed decreased saccade duration and improved accuracy in target acquisition. These exercises are particularly beneficial for sports requiring rapid visual scanning, such as basketball, tennis, and soccer, where athletes must quickly locate and track multiple moving objects simultaneously.
Smooth Pursuit Training: Smooth pursuit exercises focus on developing the eye’s ability to track moving objects continuously and accurately. These movements are crucial for sports involving projectiles, such as baseball, cricket, and tennis, where athletes must maintain visual contact with rapidly moving balls. Pursuit training enhances the coordination between the visual and vestibular
systems, improving overall balance and spatial orientation during dynamic
movements.
Accommodation Exercises: Accommodation training targets the eye's focusing mechanism, enabling rapid adjustments between near and far objects. These exercises involve repetitive stimulation and relaxation of the eye’s accommodation processes, leading to improved flexibility and responsiveness of the ciliary muscles. For athletes, strong accommodation helps maintain sharp vision at varying distances, enhances reaction times, and supports accurate performance during dynamic activities.
Vergence Training: Vergence exercises target the coordinated movement of both eyes to maintain single, clear vision at different distances. These exercises are particularly important for depth perception and binocular vision stability. The relationships between the accommodative system, vergence, and binocular vision, with improvements in one system often enhancing the others. Vergence training has been shown to improve binocular vision, which in turn enhances accommodation facility and overall visual performance in sports requiring precise depth judgment.
Peripheral Vision Enhancement: Peripheral vision training focuses on improving the detection and processing of visual information outside the central field of view. Peripheral vision training reduces reaction time gaps between central and peripheral stimuli. Training programs involving maintaining central focus while detecting peripheral stimuli demonstrate significant improvements in reaction times for team sports athletes.
Eye exercises offer significant advantages for athletes by enhancing their visual abilities and performance. These specialized training programs strengthen the connection between eyes and brain, improving focus, reaction time, hand-eye coordination, depth perception, and peripheral vision. By practicing specific exercises like saccadic movement training, smooth pursuit, and accommodation exercises, athletes can transform their visual skills from good to exceptional, gaining crucial competitive advantages in their sports.